
Define optical activity. How many optical isomers are possible for glucose?
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Optical activity is related to the ability of chiral compounds and the plane of polarized light. If a compound has n chiral carbon atoms, then it can have a maximum of \[{{\text{2}}^n}\] optical isomers.
Complete Step by step answer: You can call a carbon atom a chiral carbon atom if the carbon atom is having four different atoms/groups. If a compound contains a chiral carbon atom, then you can call the compound a chiral compound. Chiral compounds are optically active.
Chiral compounds have the ability to rotate the plane of plane polarized light either in clockwise direction or in counter clockwise (anticlockwise) direction. You can call this ability of chiral compounds as optical activity. Achiral compounds do not have this ability and are optically inactive.
You can use the polarimeter to measure the optical activity.
If a compound has n chiral carbon atoms, then it can have a maximum of \[{{\text{2}}^n}\] optical isomers.
Write the structure of glucose as shown below. In the structure, mark the chiral carbon atoms with an asterisk.
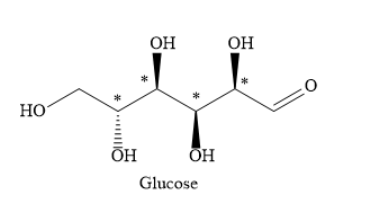
As you can see, there are four chiral carbon atoms in glucose molecules.
So the value of n is 4.
Calculate the number of optical isomers possible for glucose molecule:
\[{{\text{2}}^n} = {2^4} = 16\]
Thus, glucose can have 16 optical isomers.
Note: Achiral compounds are optically inactive. An achiral compound is the one in which no chiral carbon atom is present. In other words, when two or more same atoms/groups are attached to a carbon atom, then this carbon atom is achiral and compounds containing achiral carbon atoms are achiral.
Complete Step by step answer: You can call a carbon atom a chiral carbon atom if the carbon atom is having four different atoms/groups. If a compound contains a chiral carbon atom, then you can call the compound a chiral compound. Chiral compounds are optically active.
Chiral compounds have the ability to rotate the plane of plane polarized light either in clockwise direction or in counter clockwise (anticlockwise) direction. You can call this ability of chiral compounds as optical activity. Achiral compounds do not have this ability and are optically inactive.
You can use the polarimeter to measure the optical activity.
If a compound has n chiral carbon atoms, then it can have a maximum of \[{{\text{2}}^n}\] optical isomers.
Write the structure of glucose as shown below. In the structure, mark the chiral carbon atoms with an asterisk.

As you can see, there are four chiral carbon atoms in glucose molecules.
So the value of n is 4.
Calculate the number of optical isomers possible for glucose molecule:
\[{{\text{2}}^n} = {2^4} = 16\]
Thus, glucose can have 16 optical isomers.
Note: Achiral compounds are optically inactive. An achiral compound is the one in which no chiral carbon atom is present. In other words, when two or more same atoms/groups are attached to a carbon atom, then this carbon atom is achiral and compounds containing achiral carbon atoms are achiral.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




