
Define non-benzenoid aromatic compound with example.
Answer
566.1k+ views
Hint: As the name suggests, non-benzenoid aromatic compounds are those ‘aromatic’ hydrocarbons which do not contain a benzene. Any aromatic compound containing multiple rings, with none of them being benzene is a non-benzenoid aromatic compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Benzene is a compound which is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon. It is very stable in nature.
- In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a unique property of cyclic unsaturated compounds that are very stable thermodynamically. All aromatic compounds follow Huckle’s rule. Any compound can be checked for aromaticity by checking for these parameters –
i. Cyclic
ii. Conjugation
iii. Planar
iv. (4n+2)$\pi$ electrons
- Benzene is an aromatic compound. Almost all benzene containing aromatic compounds are stable in nature. The compounds that do not contain a benzene ring are known as non-benzenoid aromatic compounds.
For example –
- Azulene – It is a compound containing two fused rings – 7 carbon rings and 5 carbon rings. It follows all four rules of aromaticity. As we can see, the compound is cyclic, exhibits conjugation, is planar and has 10$\pi$ electrons.
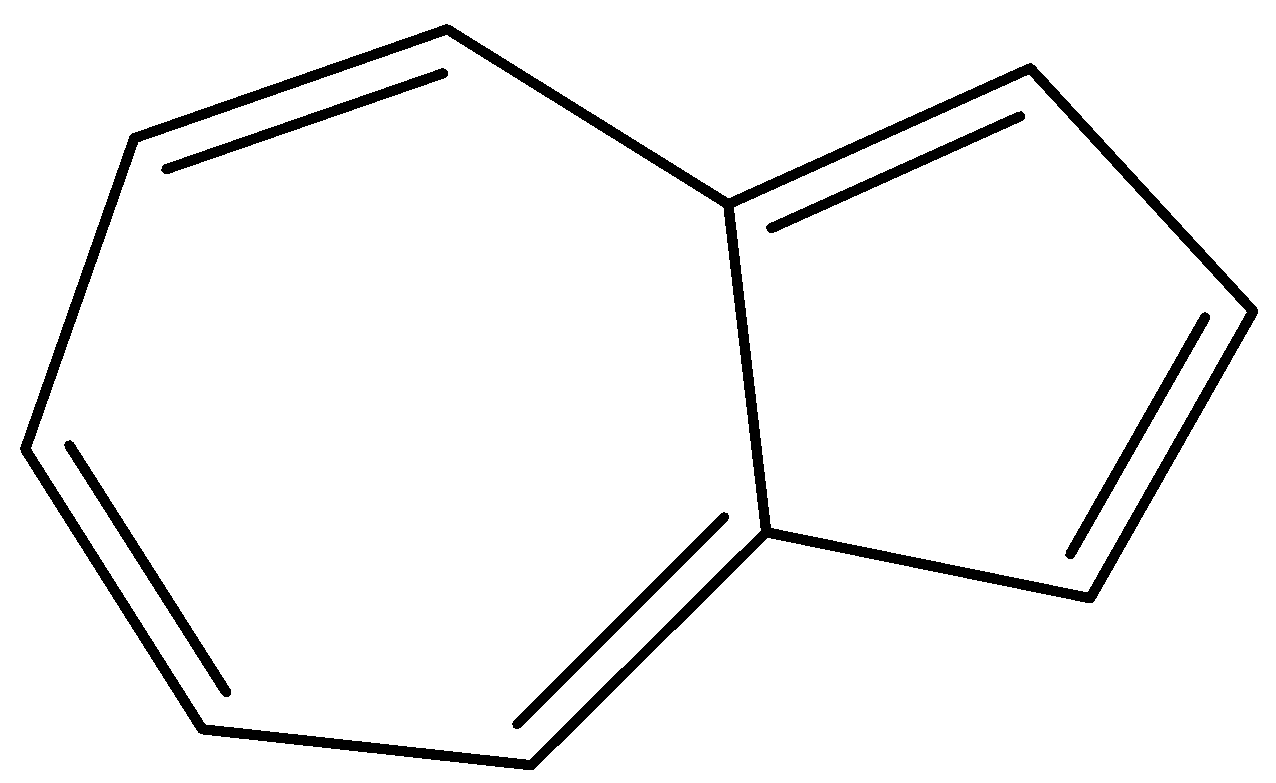
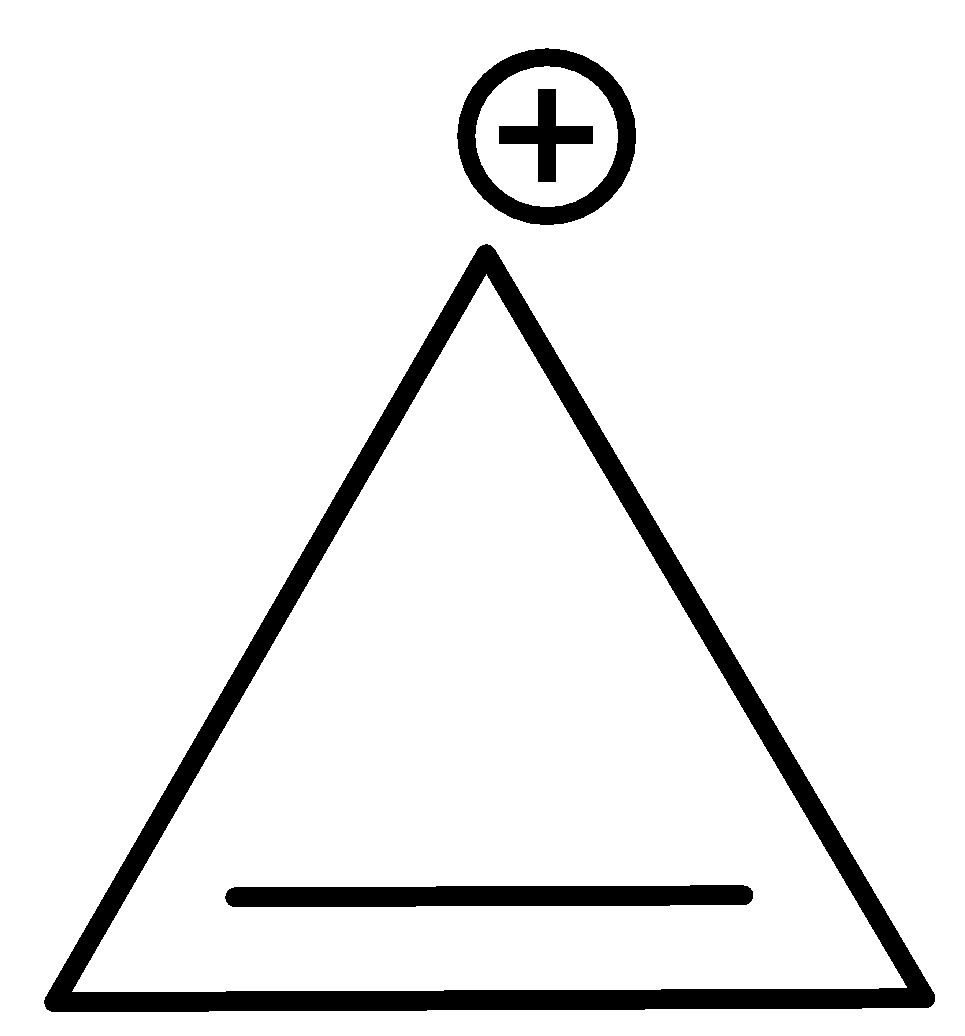
- Cyclopropenium ion – It is a three-carbon ring, with a positive charge and a double bond. It is the smallest aromatic cation, and is very stable in nature. As we can see, the compound is cyclic, exhibits conjugation, is planar and has 2$\pi$ electrons.
Additional Information: People often confuse biphenyl as an anti-aromatic compound (it has 12$\pi$ electrons), but it is aromatic in nature.
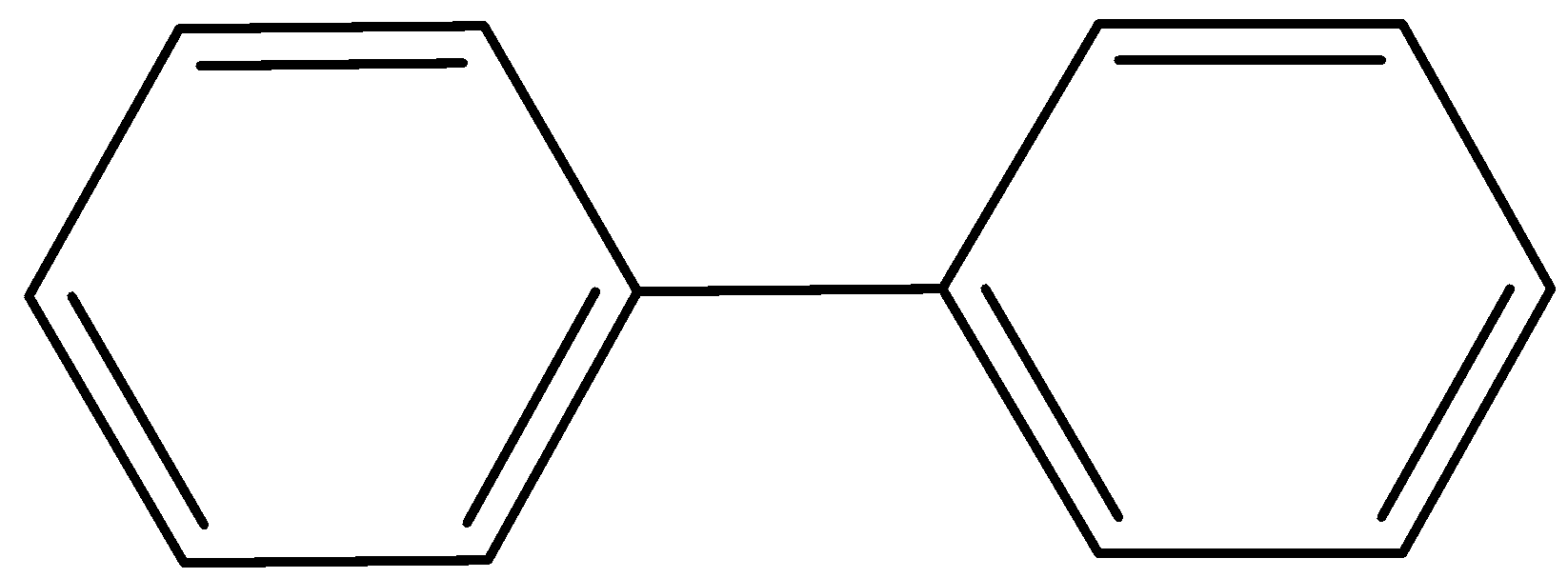
It is because we consider both the rings separately, which has 6$\pi$ electrons each.
Note: Do not be confused between the benzenoid and non benzenoid aromatics as benzenoid in which the name itself suggests that it has at least one benzene ring attached to it that are aromatic in nature whereas non benzenoid are those where there are no benzene rings but are the fused ring system which is aromatic.
Complete step by step answer:
Benzene is a compound which is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon. It is very stable in nature.
- In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a unique property of cyclic unsaturated compounds that are very stable thermodynamically. All aromatic compounds follow Huckle’s rule. Any compound can be checked for aromaticity by checking for these parameters –
i. Cyclic
ii. Conjugation
iii. Planar
iv. (4n+2)$\pi$ electrons
- Benzene is an aromatic compound. Almost all benzene containing aromatic compounds are stable in nature. The compounds that do not contain a benzene ring are known as non-benzenoid aromatic compounds.
For example –
- Azulene – It is a compound containing two fused rings – 7 carbon rings and 5 carbon rings. It follows all four rules of aromaticity. As we can see, the compound is cyclic, exhibits conjugation, is planar and has 10$\pi$ electrons.

- Cyclopropenium ion – It is a three-carbon ring, with a positive charge and a double bond. It is the smallest aromatic cation, and is very stable in nature. As we can see, the compound is cyclic, exhibits conjugation, is planar and has 2$\pi$ electrons.

Additional Information: People often confuse biphenyl as an anti-aromatic compound (it has 12$\pi$ electrons), but it is aromatic in nature.

It is because we consider both the rings separately, which has 6$\pi$ electrons each.
Note: Do not be confused between the benzenoid and non benzenoid aromatics as benzenoid in which the name itself suggests that it has at least one benzene ring attached to it that are aromatic in nature whereas non benzenoid are those where there are no benzene rings but are the fused ring system which is aromatic.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




