
Define matter.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Matter is the “substance” that makes up the universe. Everything that occupies the space and mass is called the matter.
The matter is the "stuff" that makes up the universe — everything that takes up space and has mass is matter. Atoms combine together to form molecules this acts as the building blocks for all types of matter. Atoms and molecules are held together by means of the intermolecular force of attraction. There are three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gases.
Complete step by step answer:
Any substance that has mass and occupies space is called the matter.
The matter is composed of atoms or molecules. The arrangement of building blocks which are atoms and molecules gives a matter of various states, Physical and chemical properties. The force of interaction between these particles of matter gives a matter of its physical properties. The properties based on which matter can be classified as solid, liquid, or gases. The force of interaction between atoms or molecules is found to be highest in solids and least in liquid which is still less in gases.
The states of matter are as follows:
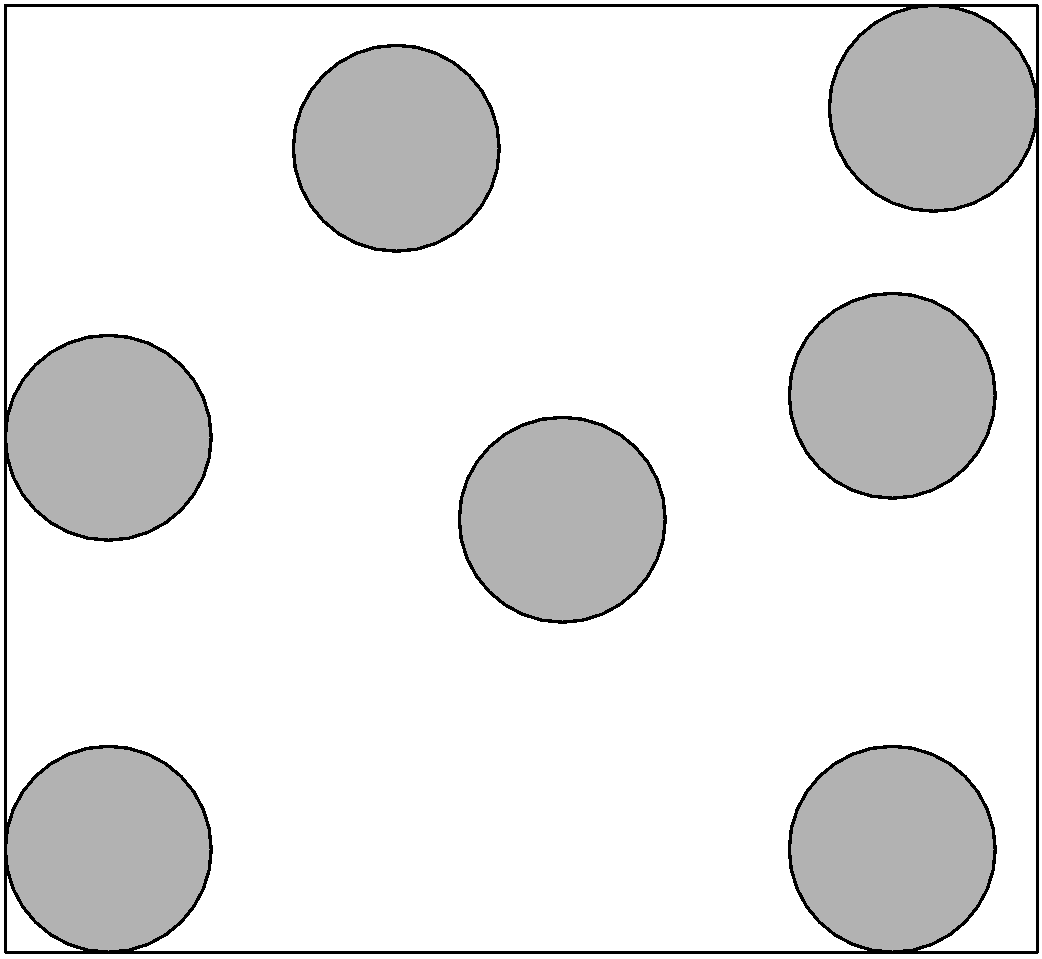
1) Solid:
Solid-state is a state of matter in which the particles are packed tightly. The constituent particles can be atoms or solid.
Properties of solid:
i) Solid have definite mass, volume, and shape
ii) Intermolecular distances between the solid particles are short and hence the forces of attraction are strong. As the intermolecular forces are inversely related to the distance between the particles.
iii) The atoms or molecules of the solid have a fixed position. They can oscillate about their mean positions.
iv) Solids change their shape on applying the force on it.
v) Based on the properties solid are classified as crystalline and amorphous solids. In crystalline solids, atoms are arranged in regular order. for example, ice.
vi) The solids in which the atoms are not packed in regular order or randomly ordered are called the non-crystalline or amorphous solids. For example, glass.
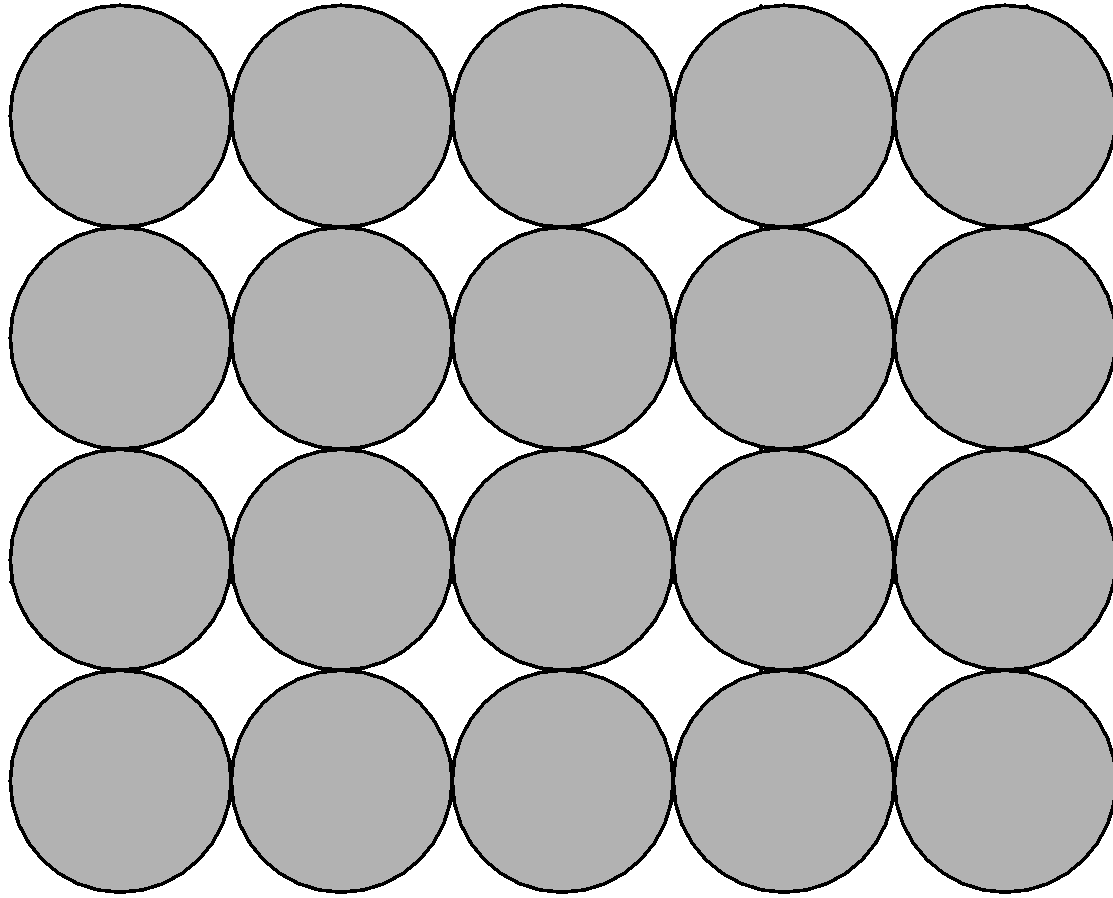
2) Liquid state:
The liquid state is a state of matter where the intermolecular forces of attraction are weaker than the solid-state but stronger than the gaseous state.
Properties of liquid:
i) Molecules in the liquid state are so close to each other that there are small intermolecular spaces between them.
ii) Molecules of liquid are held together by attractive forces.
iii) The liquid does have a definite volume this is because the molecule does not separate from each other unless the energy is applied to it. It takes the shape of the container.
iv) Molecules of liquid are free to move therefore liquids can flow, can be poured, and assume to take the shape of the container in which it is stored
v) When the solid is heated above its melting point, it converts into liquid.
vi) The best known example of liquid is water.
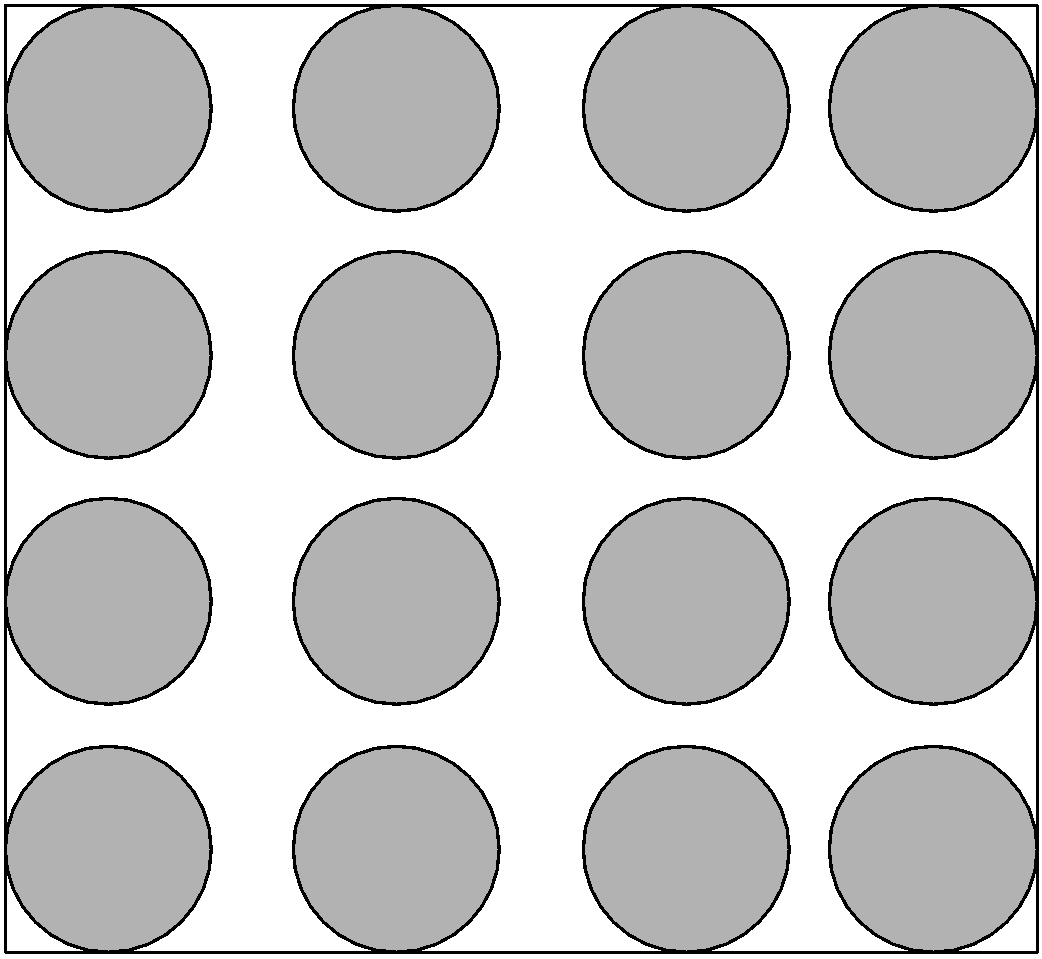
3) Gaseous state:
The gas state is a state of matter where the intermolecular forces of attraction are even low than liquid. The gas particles have a larger distance between the particles. The molecule possesses the kinetic energy and hence has the small intermolecular forces.
Properties of gas state:
i) The intermolecular forces of attraction in gases are the weakest.
ii) Due to larger empty spaces in between the gas particles, gas particles are highly compressible.
iii) They have lower density than the solids and liquids.
iv) Gases have volume and expand in the container they are placed.
v) Gases have the property of diffusion. They mix with others in all proportions without any mechanical aid.
vi) For example, $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{,}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$gases.
Note: Apart from these three states there two more known states of matter: plasma and Bose-Einstein condensate. Plasma is the electrically conductive gas. In plasma state of matter, the positively charged nuclei swim in a sea of negatively charged freely moving electrons.
The matter is the "stuff" that makes up the universe — everything that takes up space and has mass is matter. Atoms combine together to form molecules this acts as the building blocks for all types of matter. Atoms and molecules are held together by means of the intermolecular force of attraction. There are three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gases.
Complete step by step answer:
Any substance that has mass and occupies space is called the matter.
The matter is composed of atoms or molecules. The arrangement of building blocks which are atoms and molecules gives a matter of various states, Physical and chemical properties. The force of interaction between these particles of matter gives a matter of its physical properties. The properties based on which matter can be classified as solid, liquid, or gases. The force of interaction between atoms or molecules is found to be highest in solids and least in liquid which is still less in gases.
The states of matter are as follows:
1) Solid:
Solid-state is a state of matter in which the particles are packed tightly. The constituent particles can be atoms or solid.
Properties of solid:
i) Solid have definite mass, volume, and shape
ii) Intermolecular distances between the solid particles are short and hence the forces of attraction are strong. As the intermolecular forces are inversely related to the distance between the particles.
iii) The atoms or molecules of the solid have a fixed position. They can oscillate about their mean positions.
iv) Solids change their shape on applying the force on it.
v) Based on the properties solid are classified as crystalline and amorphous solids. In crystalline solids, atoms are arranged in regular order. for example, ice.
vi) The solids in which the atoms are not packed in regular order or randomly ordered are called the non-crystalline or amorphous solids. For example, glass.

2) Liquid state:
The liquid state is a state of matter where the intermolecular forces of attraction are weaker than the solid-state but stronger than the gaseous state.
Properties of liquid:
i) Molecules in the liquid state are so close to each other that there are small intermolecular spaces between them.
ii) Molecules of liquid are held together by attractive forces.
iii) The liquid does have a definite volume this is because the molecule does not separate from each other unless the energy is applied to it. It takes the shape of the container.
iv) Molecules of liquid are free to move therefore liquids can flow, can be poured, and assume to take the shape of the container in which it is stored
v) When the solid is heated above its melting point, it converts into liquid.
vi) The best known example of liquid is water.

3) Gaseous state:
The gas state is a state of matter where the intermolecular forces of attraction are even low than liquid. The gas particles have a larger distance between the particles. The molecule possesses the kinetic energy and hence has the small intermolecular forces.
Properties of gas state:
i) The intermolecular forces of attraction in gases are the weakest.
ii) Due to larger empty spaces in between the gas particles, gas particles are highly compressible.
iii) They have lower density than the solids and liquids.
iv) Gases have volume and expand in the container they are placed.
v) Gases have the property of diffusion. They mix with others in all proportions without any mechanical aid.
vi) For example, $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{,}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$gases.

Note: Apart from these three states there two more known states of matter: plasma and Bose-Einstein condensate. Plasma is the electrically conductive gas. In plasma state of matter, the positively charged nuclei swim in a sea of negatively charged freely moving electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




