
Define karyokinesis.
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: The word Karyokinesis consists of two words- ‘karyo’ i.e. nucleus and ‘kinesis’ i.e. movement. Karyokinesis is followed by cytokinesis during cell division.
Complete answer:
Karyokinesis is the process of the division of a cell nucleus during mitosis or meiosis. It is followed by the division of the cytoplasm which is known as cytokinesis. During cell division, the process of partition of a cell's nucleus into the daughter cells is called Karyokinesis. It takes place in a series of phases called prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Prophase- At the start of prophase, chromatin begins condensing into chromosomes. Mitotic spindles begin to form and the centrosomes begin to move in opposite directions.
Prometaphase- During this stage the nuclear envelope begins to break down, allowing spindle fibers to attach to the chromosomes. The mitotic spindles attach at a site called the kinetochore.
Metaphase- During this phase, the chromosomes align at the equator in an imaginary plane known as the metaphase plate.
Anaphase- During this stage, the spindle fibers attached to the kinetochore of the chromosomes pull the sister chromatids apart.
Telophase- This phase marks the end of nuclear division and the cell is generally elongated. It is also associated with the reappearance of organelles and the formation of two nuclei (one for each cell).
The eukaryotic cell cycle consists of four distinct phases: G1 phase, S phase (DNA synthesis phase), G2 phase (collectively known as interphase), and M phase (karyokinesis and cytokinesis).
Note: -The centrosomes is a membranous structure consisting of small tubular structures called centrioles, placed at right angles to each other. The center of the organelle is filled with PCM (Pericentriolar Material).
-Centrioles are absent in plant cells and most of the fungi.
-Meiosis involves two phases of karyokinesis.
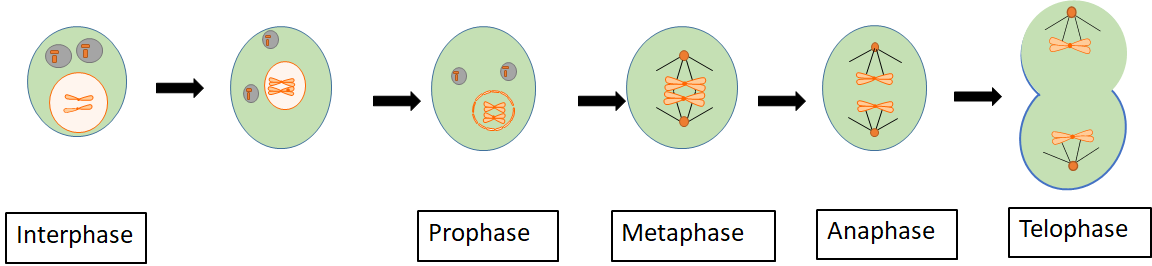
Complete answer:
Karyokinesis is the process of the division of a cell nucleus during mitosis or meiosis. It is followed by the division of the cytoplasm which is known as cytokinesis. During cell division, the process of partition of a cell's nucleus into the daughter cells is called Karyokinesis. It takes place in a series of phases called prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Prophase- At the start of prophase, chromatin begins condensing into chromosomes. Mitotic spindles begin to form and the centrosomes begin to move in opposite directions.
Prometaphase- During this stage the nuclear envelope begins to break down, allowing spindle fibers to attach to the chromosomes. The mitotic spindles attach at a site called the kinetochore.
Metaphase- During this phase, the chromosomes align at the equator in an imaginary plane known as the metaphase plate.
Anaphase- During this stage, the spindle fibers attached to the kinetochore of the chromosomes pull the sister chromatids apart.
Telophase- This phase marks the end of nuclear division and the cell is generally elongated. It is also associated with the reappearance of organelles and the formation of two nuclei (one for each cell).
The eukaryotic cell cycle consists of four distinct phases: G1 phase, S phase (DNA synthesis phase), G2 phase (collectively known as interphase), and M phase (karyokinesis and cytokinesis).
Note: -The centrosomes is a membranous structure consisting of small tubular structures called centrioles, placed at right angles to each other. The center of the organelle is filled with PCM (Pericentriolar Material).
-Centrioles are absent in plant cells and most of the fungi.
-Meiosis involves two phases of karyokinesis.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




