
Define hydrogen bond. Is it weaker or stronger than the van der Waals forces?
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: A chemical bond refers to the lasting attraction between atoms or molecules to enable formation of chemical compounds. There are mainly four types of bonds based on their mode of formation: chemical bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrogen bond is a special class of attractive forces forming due to the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom and highly electronegative atom. For example In \[{{H}_{2}}O\](water) molecule hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to oxygen atom. Here hydrogen bonding forms in the water due to the dipole-dipole interaction of hydrogen atom of one molecule and oxygen atom of another water molecule.
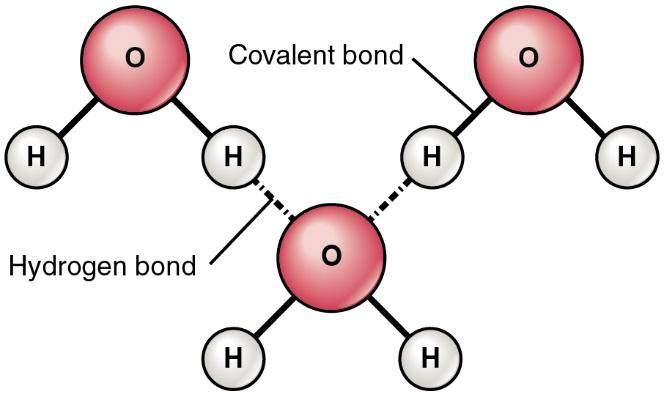
From the above picture we can see that covalent bond is within the molecules of water molecules between hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Hydrogen bonding is formed between the molecules of the water atom.
There are mainly two types of hydrogen bonding:
1.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding: Hydrogen bonding forms between different molecules of the same or different compounds. For example hydrogen bonding ammonia, alcohol
2.Intramolecular hydrogen bonding: Hydrogen bonding takes place within a molecule itself is called intra molecular hydrogen bonding.
The hydrogen bond is stronger than van der Waals force. Van der Waals force is a weak short-range attraction between molecules which arises from permanent electric dipole moments.
Note: Other than hydrogen bond and van der waals force, there are two types of bonds. I.e. Ionic bond and Covalent bond. Ionic bond is formed between two oppositely charged ions by forming complete transfer of valence electrons. Covalent bond is formed by sharing their electrons between them from outermost orbit to obtain octet.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrogen bond is a special class of attractive forces forming due to the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom and highly electronegative atom. For example In \[{{H}_{2}}O\](water) molecule hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to oxygen atom. Here hydrogen bonding forms in the water due to the dipole-dipole interaction of hydrogen atom of one molecule and oxygen atom of another water molecule.

From the above picture we can see that covalent bond is within the molecules of water molecules between hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Hydrogen bonding is formed between the molecules of the water atom.
There are mainly two types of hydrogen bonding:
1.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding: Hydrogen bonding forms between different molecules of the same or different compounds. For example hydrogen bonding ammonia, alcohol
2.Intramolecular hydrogen bonding: Hydrogen bonding takes place within a molecule itself is called intra molecular hydrogen bonding.
The hydrogen bond is stronger than van der Waals force. Van der Waals force is a weak short-range attraction between molecules which arises from permanent electric dipole moments.
Note: Other than hydrogen bond and van der waals force, there are two types of bonds. I.e. Ionic bond and Covalent bond. Ionic bond is formed between two oppositely charged ions by forming complete transfer of valence electrons. Covalent bond is formed by sharing their electrons between them from outermost orbit to obtain octet.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




