
Define functional group. Write any four functional groups with their formula.
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: Specific substituents or moieties within molecules that are responsible for characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules are functional groups. Regardless of the size of molecule, the same functional group will undergo similar chemical reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
-Before we move forward with the solution for the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
-Organic chemistry is basically the chemistry of carbon compounds. The most commonly used elements in organic chemistry are carbon and hydrogen. These elements form chain and ring - based structures to form compounds. The electronic configurations of these elements aid them in their flexible bonding capabilities. Along with being bonded as atoms, there are situations wherein there are either positive or negative sites available on these molecules in the form of a carbocation or a carbanion.
-When these sites are formed on these molecules, there is a chance for other chemical substituents to get linked with the given organic compound via the bonding site. These chemical substituents bring new properties to the organic compound and aid in the forming of various other substituent organic compounds. These chemical substituents are known as functional groups. Functional groups are basically groups of one or more atoms of distinctive chemical properties irrespective of the molecule they are attached to.
-Some of the common functional groups are as follows:
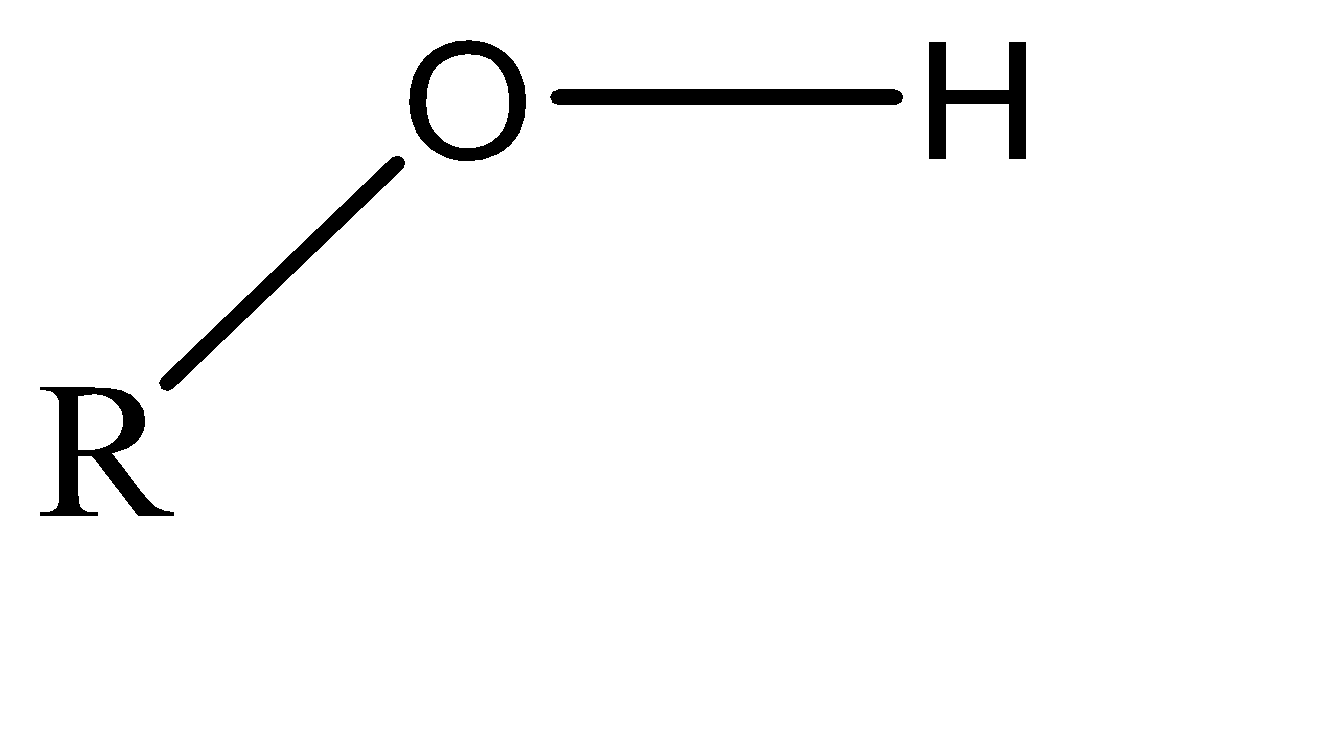
Alcohol: The molecular formula of the alcoholic functional group is \[\left( { - OH} \right)\] and the general representation of this functional group is \[R - OH\] . The alcoholic functional groups are also known as the hydroxyl group. The molecular structure for the same can be shown as:
Ether: Ether functional group basically contains 2 alkyl groups held together by an oxygen atom in the centre. The molecular for the same can be given as:
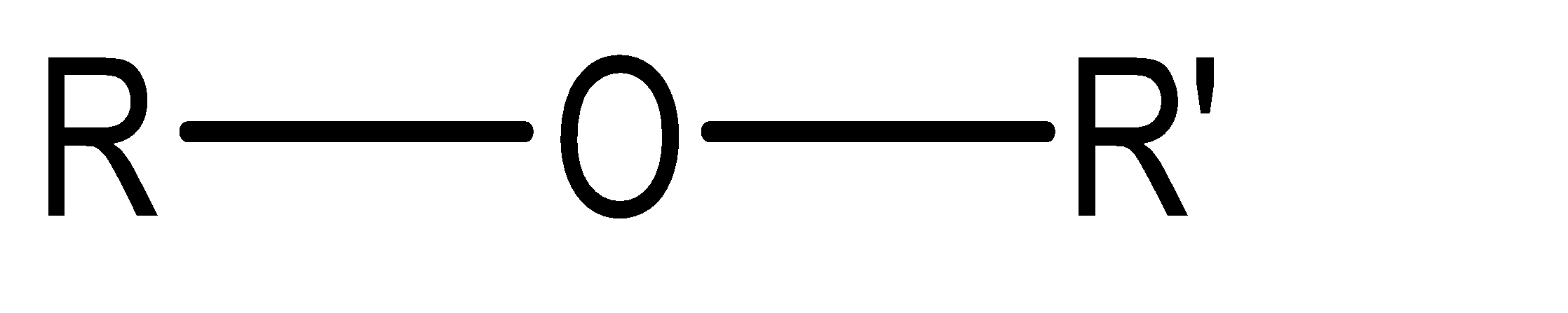
Where R and R’ are the two alkyl groups.
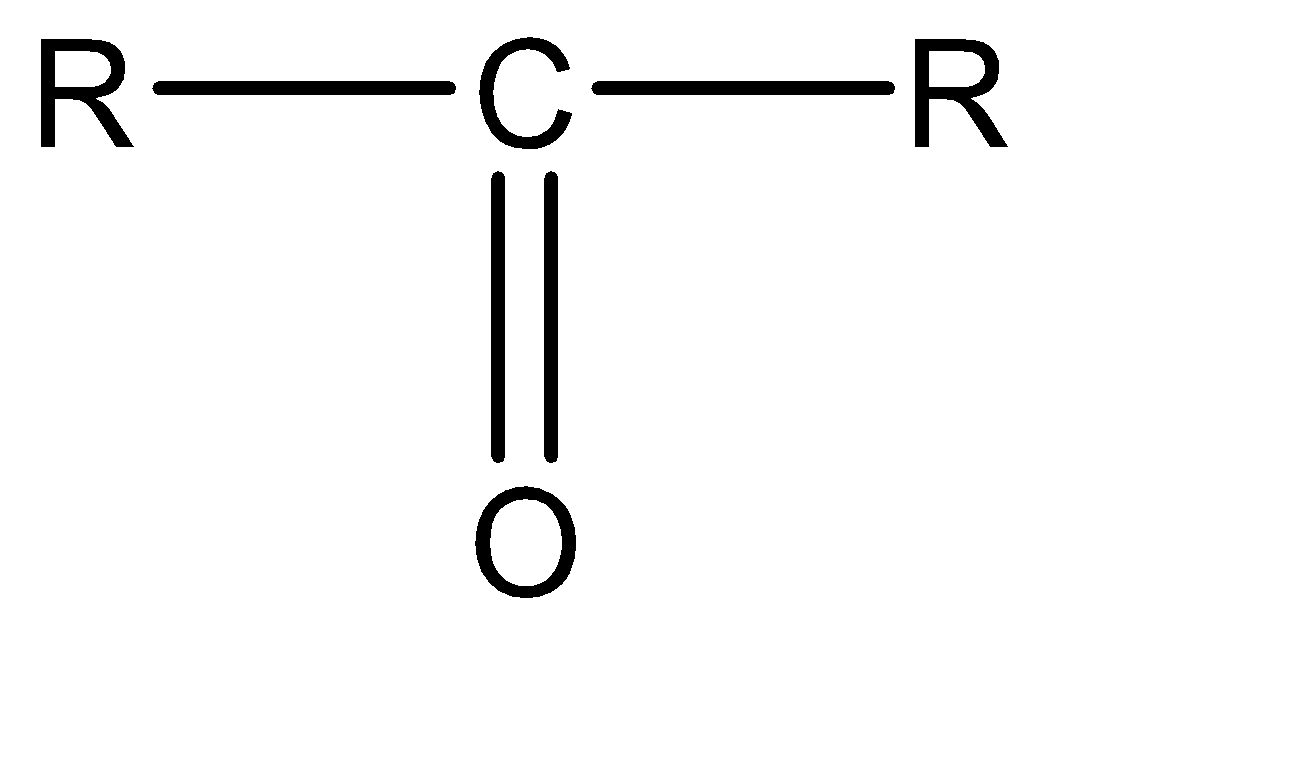
Ketone: Ketone functional group can be explained as a double bonded oxygen atom attached to a single carbon atom. This combination of carbon and double bonded oxygen is also known as carbonyl group. The molecular structure for the same can be given as:
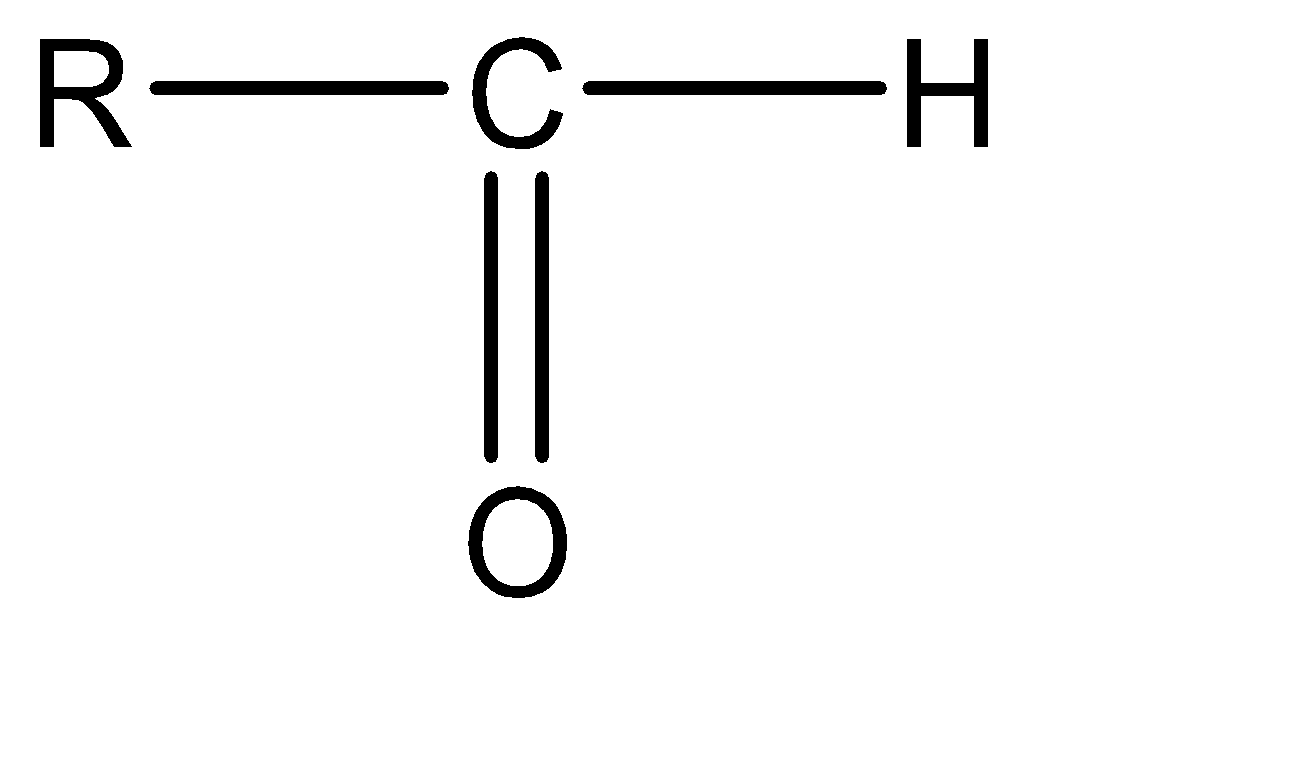
Aldehyde: Aldehydes are formed when the carbonyl group is formed at the terminal carbon. The molecular structure for aldehyde can be given as:
Note:
Functional groups can also be charged, e.g. in carboxylate salts, which turns the molecule into a polyatomic ion or a complex ion. Functional groups binding to a central atom in a coordination complex are called ligands.
Complete step by step answer:
-Before we move forward with the solution for the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
-Organic chemistry is basically the chemistry of carbon compounds. The most commonly used elements in organic chemistry are carbon and hydrogen. These elements form chain and ring - based structures to form compounds. The electronic configurations of these elements aid them in their flexible bonding capabilities. Along with being bonded as atoms, there are situations wherein there are either positive or negative sites available on these molecules in the form of a carbocation or a carbanion.
-When these sites are formed on these molecules, there is a chance for other chemical substituents to get linked with the given organic compound via the bonding site. These chemical substituents bring new properties to the organic compound and aid in the forming of various other substituent organic compounds. These chemical substituents are known as functional groups. Functional groups are basically groups of one or more atoms of distinctive chemical properties irrespective of the molecule they are attached to.
-Some of the common functional groups are as follows:
Alcohol: The molecular formula of the alcoholic functional group is \[\left( { - OH} \right)\] and the general representation of this functional group is \[R - OH\] . The alcoholic functional groups are also known as the hydroxyl group. The molecular structure for the same can be shown as:

Ether: Ether functional group basically contains 2 alkyl groups held together by an oxygen atom in the centre. The molecular for the same can be given as:
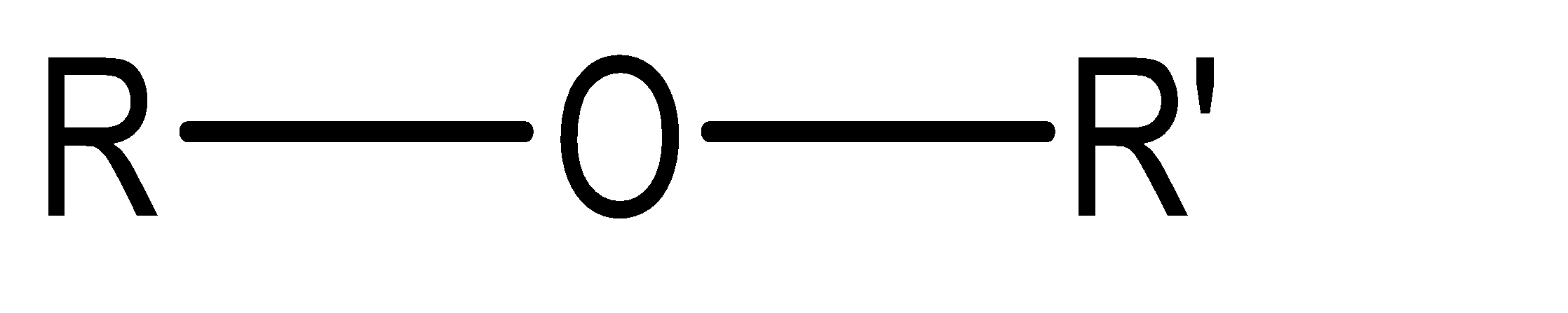
Where R and R’ are the two alkyl groups.
Ketone: Ketone functional group can be explained as a double bonded oxygen atom attached to a single carbon atom. This combination of carbon and double bonded oxygen is also known as carbonyl group. The molecular structure for the same can be given as:

Aldehyde: Aldehydes are formed when the carbonyl group is formed at the terminal carbon. The molecular structure for aldehyde can be given as:

Note:
Functional groups can also be charged, e.g. in carboxylate salts, which turns the molecule into a polyatomic ion or a complex ion. Functional groups binding to a central atom in a coordination complex are called ligands.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




