
Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: A graphical representation which shows the relationship between different living organisms at different trophic levels. G. Evelyn Hutchinson and Raymond Lindeman discovered ecological pyramids.
Complete answer: A graphical representation designed to show the bio productivity or biomass at every trophic level in a given ecosystem is known as ecological pyramids. There are three different types of pyramids which are as follows:
a) Pyramid of numbers
b) Pyramid of biomass
c) Pyramid of energy
Biomass is the living and dead tissues in an ecosystem. The total biomass at each trophic level is represented by a graphical representation known as the pyramid of biomass. In an ecosystem, the biomass always decreases at a particular trophic level of the food chain. In the pyramid of biomass, the base represents the producers or the first trophic level and the apex represents the tertiary or top consumer. The pyramid of biomass in a grassland ecosystem is always upright. This pyramid of biomass is upright in a grassland ecosystem because the number of secondary consumers or carnivores are less in number as compared to primary consumers or herbivores at the base of the pyramid. The biomass of secondary consumers is less as compared to others in this ecosystem. Whereas the pyramid of biomass is inverted in the case of a pond ecosystem because the number of secondary consumers (large fishes) are more as compared to the number of primary consumers.
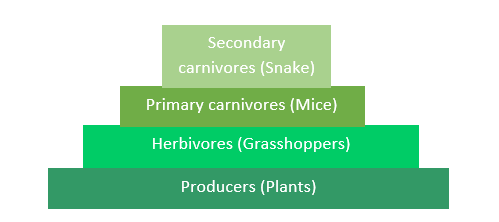
In the pyramid of numbers, each trophic level has a particular number of organisms. It is usually upright but sometimes it can be inverted also. An inverted pyramid of numbers exists in the detritus food chain where many organisms feed on a dead plant or animal. For example, grass grasshoppers, rats, etc.
Note: The ecological pyramid shows the feeding habits of different organisms in different ecosystems. The condition of the ecosystem can be observed and damage can be prevented. A pyramid of biomass shows a more accurate representation of energy flow through a food chain than the pyramid of numbers.
Complete answer: A graphical representation designed to show the bio productivity or biomass at every trophic level in a given ecosystem is known as ecological pyramids. There are three different types of pyramids which are as follows:
a) Pyramid of numbers
b) Pyramid of biomass
c) Pyramid of energy
Biomass is the living and dead tissues in an ecosystem. The total biomass at each trophic level is represented by a graphical representation known as the pyramid of biomass. In an ecosystem, the biomass always decreases at a particular trophic level of the food chain. In the pyramid of biomass, the base represents the producers or the first trophic level and the apex represents the tertiary or top consumer. The pyramid of biomass in a grassland ecosystem is always upright. This pyramid of biomass is upright in a grassland ecosystem because the number of secondary consumers or carnivores are less in number as compared to primary consumers or herbivores at the base of the pyramid. The biomass of secondary consumers is less as compared to others in this ecosystem. Whereas the pyramid of biomass is inverted in the case of a pond ecosystem because the number of secondary consumers (large fishes) are more as compared to the number of primary consumers.

In the pyramid of numbers, each trophic level has a particular number of organisms. It is usually upright but sometimes it can be inverted also. An inverted pyramid of numbers exists in the detritus food chain where many organisms feed on a dead plant or animal. For example, grass grasshoppers, rats, etc.
Note: The ecological pyramid shows the feeding habits of different organisms in different ecosystems. The condition of the ecosystem can be observed and damage can be prevented. A pyramid of biomass shows a more accurate representation of energy flow through a food chain than the pyramid of numbers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




