
Define crystal lattice.
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: A solid particle is said to be crystalline if its various constituent particles (i.e, atoms, ions, molecules) are arranged in a definite geometric pattern in three dimensional space so that there is short range as well as long range order of the constituent particles, On the other hand, a solid is said to be amorphous if there is no regular arrangement of its constituent particles.
Complete step by step answer:
Crystal lattice can be defined as the type of regular arrangement of the constituent particles which are either atoms or molecules even it could be ions, in a three dimensional space, is termed as the crystal lattice. Given below is the structure of a crystal lattice, see how it has eight corners just like a cube has, and these corners will be occupied by some particles, about which we will discuss now.
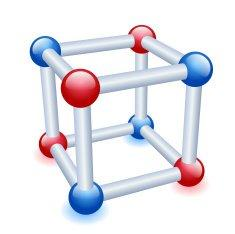
Now we will look at the definition of a unit cell as it is an important part of the crystal lattice. From a complete space lattice, it is possible for us to select a smallest three dimensional portion which repeats itself in all the direction, we can say that it is kind of like the monomer present in a polymer which is its constituent particle and it repeats itself in all direction to finally form a polymer. These repeating units are individually termed as the unit cell.
There are different types of lattices which are known to us, they are divided into the following categories,
1.Primitive unit cells: we can define them as, these are the unit cells in which the constituent particles or the particles from which it is made up of, are present at the corner of the cell, so we call them simple unit cells or primitive unit cells.
2.Non-primitive or centred unit cells: Now these are a type of unit cell which are different from the primitive ones as we discussed above, as the name suggest ‘centred’ so we can figure out from the name, that the particles are not only present at the corners but also at the centre of the unit cell.
Note: A crystal lattice is formed by a number of repeating units of atoms or molecules or ions, called unit cells. These unit cells could be primitive, where the particles would be present only at the corners, or they could be non-primitive where the particles would be present at the corners as well as the centre of the unit cell.
Complete step by step answer:
Crystal lattice can be defined as the type of regular arrangement of the constituent particles which are either atoms or molecules even it could be ions, in a three dimensional space, is termed as the crystal lattice. Given below is the structure of a crystal lattice, see how it has eight corners just like a cube has, and these corners will be occupied by some particles, about which we will discuss now.

Now we will look at the definition of a unit cell as it is an important part of the crystal lattice. From a complete space lattice, it is possible for us to select a smallest three dimensional portion which repeats itself in all the direction, we can say that it is kind of like the monomer present in a polymer which is its constituent particle and it repeats itself in all direction to finally form a polymer. These repeating units are individually termed as the unit cell.
There are different types of lattices which are known to us, they are divided into the following categories,
1.Primitive unit cells: we can define them as, these are the unit cells in which the constituent particles or the particles from which it is made up of, are present at the corner of the cell, so we call them simple unit cells or primitive unit cells.
2.Non-primitive or centred unit cells: Now these are a type of unit cell which are different from the primitive ones as we discussed above, as the name suggest ‘centred’ so we can figure out from the name, that the particles are not only present at the corners but also at the centre of the unit cell.
Note: A crystal lattice is formed by a number of repeating units of atoms or molecules or ions, called unit cells. These unit cells could be primitive, where the particles would be present only at the corners, or they could be non-primitive where the particles would be present at the corners as well as the centre of the unit cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




