
Define coefficient of self-inductance and write its unit.
Answer
589.8k+ views
- Hint: When current flows through a coil, a magnetic field is created in the coil. This magnetic field opposes alternating current to pass through it. Coefficient of self-inductance is related to the induced magnetic field in a coil. Self-inductance is an important property of a coil, utilised in many filtering processes.
Complete step-by-step solution
Self-inductance is the property of a coil by virtue of which, the coil opposes any change in the current flowing through it, by inducing an electromotive force in itself. When current in a coil is changed with the help of a resistor as shown in the diagram, an emf is induced in the coil. This self-induced emf opposes further alternating current to flow through the coil.
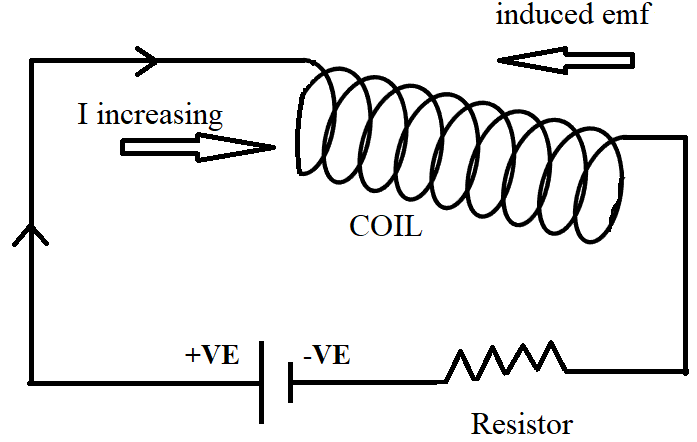
Let a current of strength $I$ flow through a coil and $\phi $ be the magnetic flux induced in the coil. It is found that
$\phi \propto I\Rightarrow \phi =LI$
where
$L$ is the coefficient of self-inductance
The value of $L$depends upon the number of turns, area of cross-section and nature of the material used in the core of the coil, on which the coil is wound.
If unit current flows through a coil, self-inductance is equal to the magnetic flux induced in the coil.
For $I=1$, $\phi =LI=L(1)=L$
Numerically, the coefficient of self-inductance of a coil is equal to the amount of magnetic flux linked with the coil when unit current flows through the coil.
Self-inductance can also be defined in terms of emf induced in a coil. We know that emf induced in a coil is given by a negative rate of change of magnetic flux.
$emf=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
Let this be equation 1.
Equation 1 can be rewritten as
$emf=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}=-\dfrac{d(LI)}{dt}=-L\times \dfrac{dI}{dt}$
If rate of change of current with respect to time is unity, then,
$emf=-L\times \dfrac{dI}{dt}=-L\times 1\Rightarrow L=-emf$
Hence, coefficient of self-inductance can also be defined as the emf induced in a coil, when the rate of change of current is unity.
Inductance is a scalar quantity and the unit of coefficient of self-inductance is $henry(H)$
Coefficient of self-inductance of a coil is said to be $1H$, when a current-change, at the rate of $1A{{s}^{-1}}$, induces an $emf$ of $1V$ in the coil.
Note: Induced $emf$ is dependent on its direction. When current in a coil is increasing in a particular direction, the induced $emf$ has a direction opposite to the direction of current flow. When current in a coil is decreasing in a particular direction, the induced $emf$ has a direction opposing the decrease of current flow. This means that induced $emf$ has the same direction as that of current flow.
Complete step-by-step solution
Self-inductance is the property of a coil by virtue of which, the coil opposes any change in the current flowing through it, by inducing an electromotive force in itself. When current in a coil is changed with the help of a resistor as shown in the diagram, an emf is induced in the coil. This self-induced emf opposes further alternating current to flow through the coil.

Let a current of strength $I$ flow through a coil and $\phi $ be the magnetic flux induced in the coil. It is found that
$\phi \propto I\Rightarrow \phi =LI$
where
$L$ is the coefficient of self-inductance
The value of $L$depends upon the number of turns, area of cross-section and nature of the material used in the core of the coil, on which the coil is wound.
If unit current flows through a coil, self-inductance is equal to the magnetic flux induced in the coil.
For $I=1$, $\phi =LI=L(1)=L$
Numerically, the coefficient of self-inductance of a coil is equal to the amount of magnetic flux linked with the coil when unit current flows through the coil.
Self-inductance can also be defined in terms of emf induced in a coil. We know that emf induced in a coil is given by a negative rate of change of magnetic flux.
$emf=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
Let this be equation 1.
Equation 1 can be rewritten as
$emf=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}=-\dfrac{d(LI)}{dt}=-L\times \dfrac{dI}{dt}$
If rate of change of current with respect to time is unity, then,
$emf=-L\times \dfrac{dI}{dt}=-L\times 1\Rightarrow L=-emf$
Hence, coefficient of self-inductance can also be defined as the emf induced in a coil, when the rate of change of current is unity.
Inductance is a scalar quantity and the unit of coefficient of self-inductance is $henry(H)$
Coefficient of self-inductance of a coil is said to be $1H$, when a current-change, at the rate of $1A{{s}^{-1}}$, induces an $emf$ of $1V$ in the coil.
Note: Induced $emf$ is dependent on its direction. When current in a coil is increasing in a particular direction, the induced $emf$ has a direction opposite to the direction of current flow. When current in a coil is decreasing in a particular direction, the induced $emf$ has a direction opposing the decrease of current flow. This means that induced $emf$ has the same direction as that of current flow.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




