
Define bicollateral vascular bundle
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: Vascular bundles are called conducting vessels. They consist of xylem and phloem. Xylem helps in transport of water and minerals whereas phloem helps in transport of food material [glucose or starch].
Complete step-by-step answer:
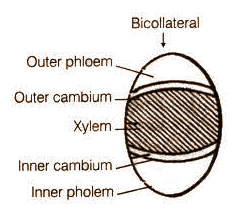
-Bicollateral vascular bundle: It is a special type of vascular bundle where two phloem poles separated from the central xylem or a type of conjoint vascular bundle where the xylem is situated in the middle of two phloem strands. Example: stem of Cucurbita, Solanaceae (the potato family).
-It is an open type of vascular bundle where a strip of vascular cambium is present between the peripheral phloem and xylem and another strip of cambium present between inner phloem and xylem.
-The peripheral phloem is termed as outer phloem whereas the inner or internal phloem is called inner phloem.
-Cambium is a layer of actively dividing cells which help during secondary growth.
-Cambial activity help in development of secondary xylem which make soft stem into hard or woody stem but in cucurbita secondary thickening occurs only by the outer cambium I,e cambium present between the outer phloem and xylem
-The xylem consists of tracheids, vessels elements, xylem parenchyma, xylem fiber, xylem sclerenchyma. -The first formed xylem is called protoxylem and later formed is called metaxylem.
-The phloem consists of Sieve elements, Companion cells, Phloem parenchyma, Phloem fibres and Sclereids. The first formed phloem is called protophloem and later formed is called secondary phloem.
Note: The closed type of vascular bundle where cambium is absent between xylem and phloem commonly found in Monocots plants. Such plants will not show secondary growth.
Complete step-by-step answer:
-Bicollateral vascular bundle: It is a special type of vascular bundle where two phloem poles separated from the central xylem or a type of conjoint vascular bundle where the xylem is situated in the middle of two phloem strands. Example: stem of Cucurbita, Solanaceae (the potato family).
-It is an open type of vascular bundle where a strip of vascular cambium is present between the peripheral phloem and xylem and another strip of cambium present between inner phloem and xylem.
-The peripheral phloem is termed as outer phloem whereas the inner or internal phloem is called inner phloem.
-Cambium is a layer of actively dividing cells which help during secondary growth.
-Cambial activity help in development of secondary xylem which make soft stem into hard or woody stem but in cucurbita secondary thickening occurs only by the outer cambium I,e cambium present between the outer phloem and xylem
-The xylem consists of tracheids, vessels elements, xylem parenchyma, xylem fiber, xylem sclerenchyma. -The first formed xylem is called protoxylem and later formed is called metaxylem.
-The phloem consists of Sieve elements, Companion cells, Phloem parenchyma, Phloem fibres and Sclereids. The first formed phloem is called protophloem and later formed is called secondary phloem.

Note: The closed type of vascular bundle where cambium is absent between xylem and phloem commonly found in Monocots plants. Such plants will not show secondary growth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




