
Define angle of declination at a place:
A. Angle between the vertical plane and the geographical meridian
B. Angle between the vertical plane and magnetic meridian
C. Angle between the geometrical meridian and magnetic meridian
D. Angle between the geometrical meridian and horizontal plane
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Magnetic declination at a particular place is the angle which gives the relation between geographical meridian with magnetic meridian. The geographical meridian is the plane containing the geographic north and South Pole and the magnetic meridian is the plane containing the magnetic north and south pole.
Complete step-by-step solution:
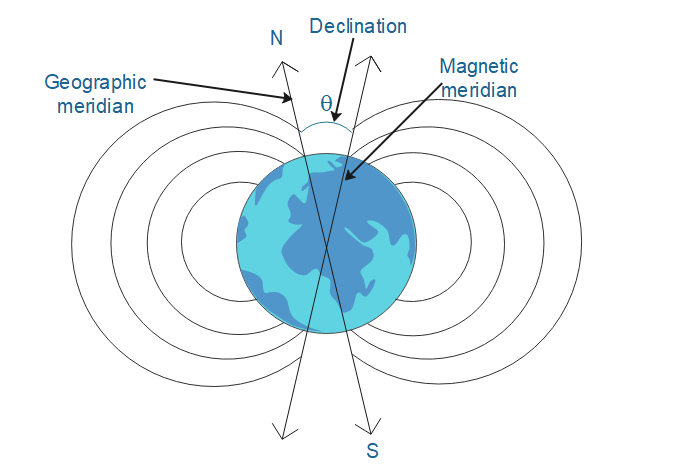
The magnetic meridian is equal to the imaginary line which connects the magnetic south and north poles. It can be taken as the magnetic force lines along the surface of the earth. Therefore a compass needle shows that the needle is parallel to the magnetic meridian.
Since the magnetic field of the earth constantly changes, magnetic declination is calculated in relation to the geographic north and geographic surface. Magnetic declination is the angle between the local measurement of the magnetic north (whose direction the north end of a compass needle points) and true north (geodetic or geographic north). When the magnetic north is east of true north then the declination is positive.
Hence, the angle of declination at a place is the angle between the geographical meridian and magnetic meridian, therefore option (C) is the correct option.
Note: Angle of declination is relevant for navigating with a compass. Opposite to Magnetic declination, there exists Magnetic inclination. The magnetic inclination is the angle made by a compass needle when the compass is held in a vertical orientation or direction. Positive values of inclination indicate that the field is pointing in a downward direction, into the Earth, particularly at the point of measurement. These values are local and change over the years.
Complete step-by-step solution:

The magnetic meridian is equal to the imaginary line which connects the magnetic south and north poles. It can be taken as the magnetic force lines along the surface of the earth. Therefore a compass needle shows that the needle is parallel to the magnetic meridian.
Since the magnetic field of the earth constantly changes, magnetic declination is calculated in relation to the geographic north and geographic surface. Magnetic declination is the angle between the local measurement of the magnetic north (whose direction the north end of a compass needle points) and true north (geodetic or geographic north). When the magnetic north is east of true north then the declination is positive.
Hence, the angle of declination at a place is the angle between the geographical meridian and magnetic meridian, therefore option (C) is the correct option.
Note: Angle of declination is relevant for navigating with a compass. Opposite to Magnetic declination, there exists Magnetic inclination. The magnetic inclination is the angle made by a compass needle when the compass is held in a vertical orientation or direction. Positive values of inclination indicate that the field is pointing in a downward direction, into the Earth, particularly at the point of measurement. These values are local and change over the years.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




