
Define a function. What do you mean by Domain and Range of a function? Give examples.
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: According to Set theory a function is defined as a relation between two sets A and B such that every element of the first set has exactly one image in the second set.
Complete step by step solution: If any element of the first set does not have an image in the second set, or if an element in the first set has more than one image in the second set, then the relation Is not a function from A to B.
The first set which contains the elements $'x'$ is called the Domain of the function $f$ while the second set which contains the images defined as per the function $f$, that is,$f(x)$is called the range of the function $f$.
For example:
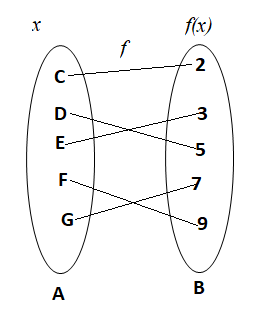
Now, let us take two sets A and B respectively containing the elements A =$\left\{ {C,D,E,F,G} \right\}$and B = $\left\{ {2,3,5,7,9} \right\}$such that for all elements $'x'$ of the domain A there exists the image elements $f(x)$ in B under the function $f$, respectively. Such that:
$ f\left( C \right) = 2 \\
f\left( D \right) = 5 \\
f\left( E \right) = 3 \\
f\left( F \right) = 9 \\
f\left( G \right) = 7 \\ $
However the function $f$, will not be a function if any element of the Domain is associated with more than one element in the range. For example,
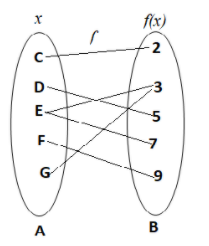
Now, the function $f$ is not a function because the element E $ \in $Domain set A, has two images at 3 and 7 in the Range B.
Hence $f$ is not a function.
Therefore, we conclude by defining a function $f$as a rule from one set A to another set B, such that the first set A containing the elements $'x'$, is called the Domain , while the set B containing the corresponding images $f(x)$is called the Range of the function $f$.
Note: Functions are of many types. Let us consider two sets A and B. A one-to-one function is one where every element belonging to a set A, that has exactly one unique image in set B. An onto function is one where every element belonging to set B has at least one preimage in the set A. A function which is both one-to-one and onto, is called an injective function. If either of the characteristics is missing, the function will not be an injective function.
Complete step by step solution: If any element of the first set does not have an image in the second set, or if an element in the first set has more than one image in the second set, then the relation Is not a function from A to B.
The first set which contains the elements $'x'$ is called the Domain of the function $f$ while the second set which contains the images defined as per the function $f$, that is,$f(x)$is called the range of the function $f$.
For example:

Now, let us take two sets A and B respectively containing the elements A =$\left\{ {C,D,E,F,G} \right\}$and B = $\left\{ {2,3,5,7,9} \right\}$such that for all elements $'x'$ of the domain A there exists the image elements $f(x)$ in B under the function $f$, respectively. Such that:
$ f\left( C \right) = 2 \\
f\left( D \right) = 5 \\
f\left( E \right) = 3 \\
f\left( F \right) = 9 \\
f\left( G \right) = 7 \\ $
However the function $f$, will not be a function if any element of the Domain is associated with more than one element in the range. For example,

Now, the function $f$ is not a function because the element E $ \in $Domain set A, has two images at 3 and 7 in the Range B.
Hence $f$ is not a function.
Therefore, we conclude by defining a function $f$as a rule from one set A to another set B, such that the first set A containing the elements $'x'$, is called the Domain , while the set B containing the corresponding images $f(x)$is called the Range of the function $f$.
Note: Functions are of many types. Let us consider two sets A and B. A one-to-one function is one where every element belonging to a set A, that has exactly one unique image in set B. An onto function is one where every element belonging to set B has at least one preimage in the set A. A function which is both one-to-one and onto, is called an injective function. If either of the characteristics is missing, the function will not be an injective function.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




