
What is decreasing order of boiling point-
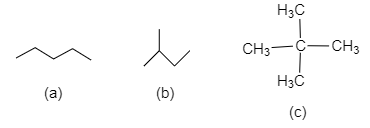
$A)$ $a > b > c$
$B)$ $b > c > a$
$C)$ $a > c > b$
$D)$ $c > b > a$

Answer
514.2k+ views
Hint: Boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapour pressure of liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure. Boiling point of an organic compound can give information about the other physical properties and structural characteristics.
Complete answer:
Boiling point of a compound tells about its volatility. The higher the boiling point, the less volatile is the compound and lower the boiling point, the more volatile is the compound.
The length of the carbon-carbon chain affects the boiling point of the compound. As the length of the carbon chain increases, the boiling point also increases. This is because the intermolecular forces between the molecules increases as the molecule gets longer. As a result, more energy will be required to overcome this force of attraction and hence the boiling point increases.
Branching in the compound decreases the boiling point. This is because the Vander Waals dispersion force is directly proportional to the surface area. Branching in the molecule will decrease the surface area as a result of which attractive forces between individual molecules decrease and hence the boiling point decreases.
Now coming to our question-
It can be seen that in (c) 2,2-dimethylpropane there are two branched methyl groups and in (b)2-methylbutane there is one branched methyl group while in (a) n-pentane there is a straight chain of five carbons. As we have seen, more branching leads to lower intermolecular forces between the molecules and hence lower boiling point.
Thus, the decreasing order of boiling point is;
$a > b > c$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
We have seen that boiling point depends upon the length of the carbon chain and branching. It also depends upon the polarity of the molecule. It was found that greater the polarity, higher is the boiling point.
Complete answer:
Boiling point of a compound tells about its volatility. The higher the boiling point, the less volatile is the compound and lower the boiling point, the more volatile is the compound.
The length of the carbon-carbon chain affects the boiling point of the compound. As the length of the carbon chain increases, the boiling point also increases. This is because the intermolecular forces between the molecules increases as the molecule gets longer. As a result, more energy will be required to overcome this force of attraction and hence the boiling point increases.
Branching in the compound decreases the boiling point. This is because the Vander Waals dispersion force is directly proportional to the surface area. Branching in the molecule will decrease the surface area as a result of which attractive forces between individual molecules decrease and hence the boiling point decreases.
Now coming to our question-
It can be seen that in (c) 2,2-dimethylpropane there are two branched methyl groups and in (b)2-methylbutane there is one branched methyl group while in (a) n-pentane there is a straight chain of five carbons. As we have seen, more branching leads to lower intermolecular forces between the molecules and hence lower boiling point.
Thus, the decreasing order of boiling point is;
$a > b > c$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
We have seen that boiling point depends upon the length of the carbon chain and branching. It also depends upon the polarity of the molecule. It was found that greater the polarity, higher is the boiling point.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life

In Dows process haloarene is converted to phenol with class 11 chemistry CBSE

During the charging of lead storage battery the reaction class 11 chemistry CBSE




