
Decolourization of alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ is used as a test for
A. Aromatic hydrocarbons
B. Olefinic hydrocarbons
C. Acetylenic hydrocarbons
D. Cycloalkanes
Answer
357.3k+ views
Hint: Potassium permanganate,$KMn{{O}_{4}}$ decolourised unsaturated compounds (hydrocarbons) and consists of double or triple bonds between carbon and hydrogen atom ($C-H$). In this process, the unsaturated compound oxidises and potassium permanganate is reduced.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$reacts with unsaturated hydrocarbons to produce a vicinal alcohol or $1,2-$diol compound(For alkene) and with an alkyne, it produces carboxylic acid. This test is known as Baeyer's test and cold, alkaline potassium permanganate is called Bayer’s reagent.
When unsaturated compounds react with potassium permanganate, they are oxidised to alcohols, and one hydroxyl group ($-OH$ ) is attached to each carbon on either side of the carbon-carbon double or triple bond, thereby producing $1,2-$glycols or vicinal. Potassium permanganate is further reduced $Mn{{O}_{2}}$.
Alkenes are the olefinic hydrocarbons that reacts with alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$, thereby producing vicinal alcohol.
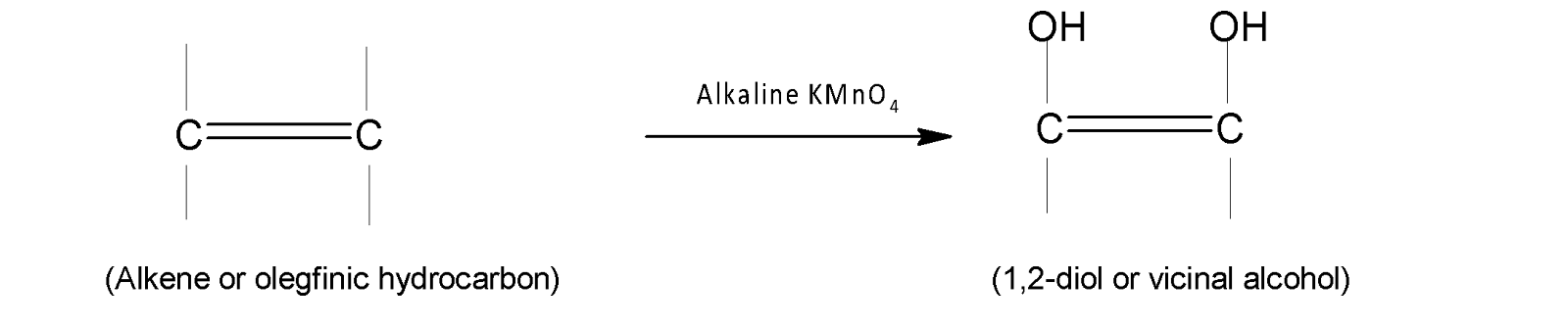
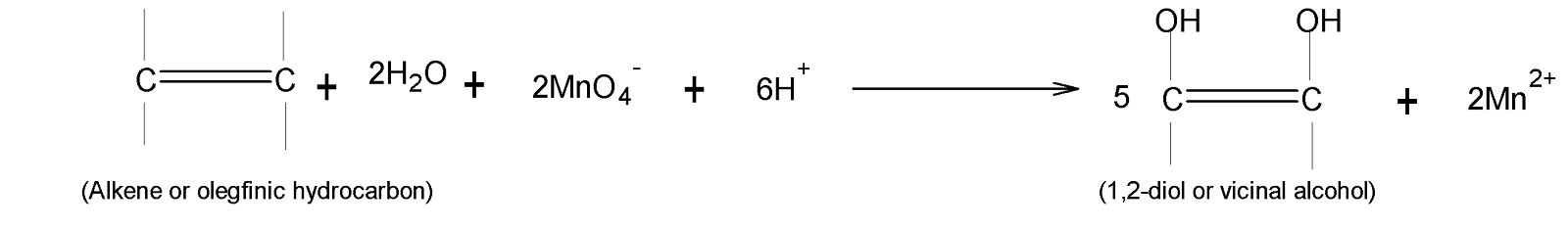
In Potassium permanganate, potassium is in $(+7)$an oxidation state and it is a strong oxidising agent. After oxidising the olefinic hydrocarbons it is reduced to manganese ions which are in $(+2)$ the state. Therefore the overall reaction is written as follows:
Acetylenic hydrocarbons can also decolorize alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$and form a carboxylic acid.
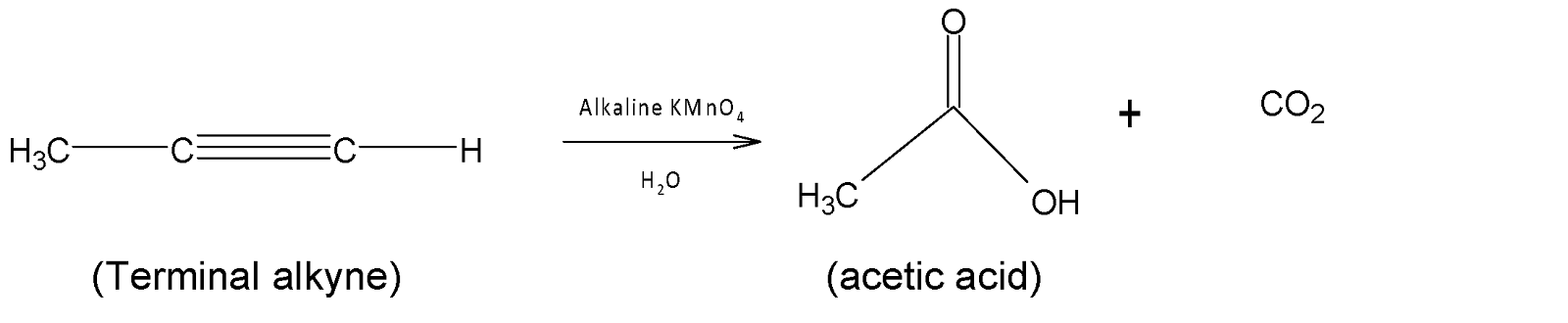
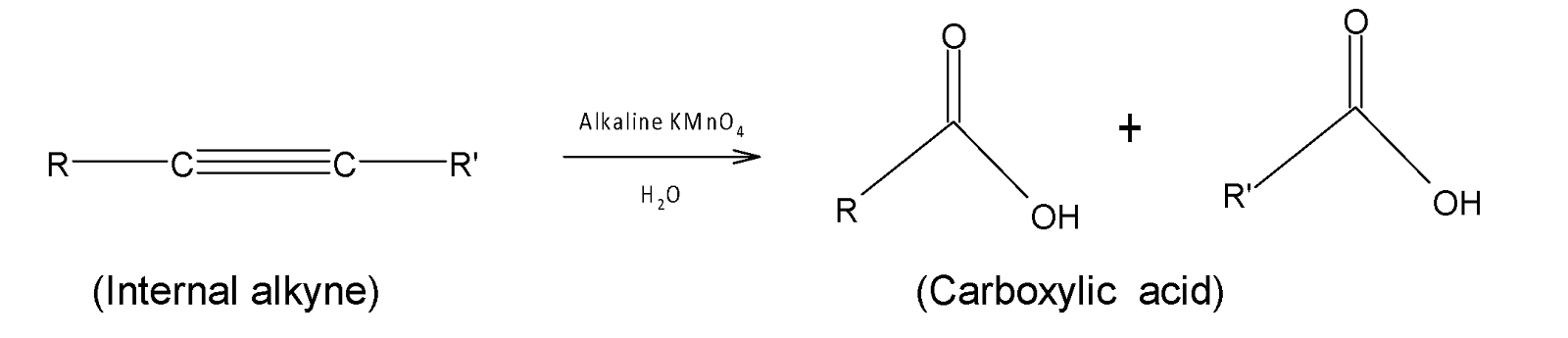
The rate of decolorization of alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ is very rapid. Other aromatic hydrocarbons like aromatic hydrocarbon and alkane compounds do not decolorize alkaline potassium permanganate.
Therefore decolorization of alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$is used as a test for olefinic hydrocarbons.
Thus, option (B) and (C) is correct.
Note: Alkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons do not decolorize the alkaline potassium permanganate solution. As it contains only sigma bonds and we know sigma bonds are more strong than pi bonds. Hence they are stable and do not decolorize the alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ solution. The reason for not participating in the decolorization of aromatic hydrocarbons is resonance stability.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$reacts with unsaturated hydrocarbons to produce a vicinal alcohol or $1,2-$diol compound(For alkene) and with an alkyne, it produces carboxylic acid. This test is known as Baeyer's test and cold, alkaline potassium permanganate is called Bayer’s reagent.
When unsaturated compounds react with potassium permanganate, they are oxidised to alcohols, and one hydroxyl group ($-OH$ ) is attached to each carbon on either side of the carbon-carbon double or triple bond, thereby producing $1,2-$glycols or vicinal. Potassium permanganate is further reduced $Mn{{O}_{2}}$.
Alkenes are the olefinic hydrocarbons that reacts with alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$, thereby producing vicinal alcohol.

In Potassium permanganate, potassium is in $(+7)$an oxidation state and it is a strong oxidising agent. After oxidising the olefinic hydrocarbons it is reduced to manganese ions which are in $(+2)$ the state. Therefore the overall reaction is written as follows:

Acetylenic hydrocarbons can also decolorize alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$and form a carboxylic acid.


The rate of decolorization of alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ is very rapid. Other aromatic hydrocarbons like aromatic hydrocarbon and alkane compounds do not decolorize alkaline potassium permanganate.
Therefore decolorization of alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$is used as a test for olefinic hydrocarbons.
Thus, option (B) and (C) is correct.
Note: Alkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons do not decolorize the alkaline potassium permanganate solution. As it contains only sigma bonds and we know sigma bonds are more strong than pi bonds. Hence they are stable and do not decolorize the alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ solution. The reason for not participating in the decolorization of aromatic hydrocarbons is resonance stability.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




