
How do you count single covalent bonds?
Answer
547.8k+ views
Hint:In chemistry, covalent bonds are the bonds that are formed by sharing of electrons. They are also known as molecular bonds. When sharing of electrons takes place, then an electrostatic force of attraction and repulsion between the atoms takes place that is known as chemical bonding.
Complete step-by-step answer: There are three types of covalent bonds-
1.Single covalent bond
2.Double covalent bond
3.Triple covalent bond
In this question, we will only discuss the single covalent bonds.
Single covalent bonds are defined as the bonds that are formed when one pair of electrons is shared between the two participating atoms. These bonds are weaker than the double and triple bond but these bonds are the most stable bond.
Let us take an example-
\[HCl\] contain one hydrogen atom having one valence electron and one chlorine atom having seven valence electrons. Hence a single bond is formed when sharing of electrons takes place and therefore completes its octet.
One atom combines with another atom and forms a single bond that is covalent in nature. This bond is formed due to sharing of electrons and completes its octet.
To count the single covalent bond, we need to draw the structure of a molecule and then have to count every single bond in the molecule. It includes $C-C$ covalent bonds, $C-H$ covalent bonds, $C-X$ ($X$ is a halogen) covalent bond and so on.
For example- ethane
Let us draw the structure of ethane
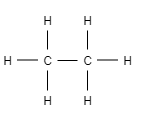
Here you can see, one $C-C$single covalent bond and six $C-H$single covalent bond. If we add all these single covalent bonds together then it results into seven covalent bonds.
Note:Properties of covalent bond-
-These bonds are formed between the non metallic elements. For example- hydrogen, oxygen.
-The compounds that have covalent bonds have low melting point and low boiling point.
-Compounds that have covalent bonds are not soluble in water.
-Compounds that have covalent bonds do not conduct electricity because of lack of free electrons.
Complete step-by-step answer: There are three types of covalent bonds-
1.Single covalent bond
2.Double covalent bond
3.Triple covalent bond
In this question, we will only discuss the single covalent bonds.
Single covalent bonds are defined as the bonds that are formed when one pair of electrons is shared between the two participating atoms. These bonds are weaker than the double and triple bond but these bonds are the most stable bond.
Let us take an example-
\[HCl\] contain one hydrogen atom having one valence electron and one chlorine atom having seven valence electrons. Hence a single bond is formed when sharing of electrons takes place and therefore completes its octet.
One atom combines with another atom and forms a single bond that is covalent in nature. This bond is formed due to sharing of electrons and completes its octet.
To count the single covalent bond, we need to draw the structure of a molecule and then have to count every single bond in the molecule. It includes $C-C$ covalent bonds, $C-H$ covalent bonds, $C-X$ ($X$ is a halogen) covalent bond and so on.
For example- ethane
Let us draw the structure of ethane

Here you can see, one $C-C$single covalent bond and six $C-H$single covalent bond. If we add all these single covalent bonds together then it results into seven covalent bonds.
Note:Properties of covalent bond-
-These bonds are formed between the non metallic elements. For example- hydrogen, oxygen.
-The compounds that have covalent bonds have low melting point and low boiling point.
-Compounds that have covalent bonds are not soluble in water.
-Compounds that have covalent bonds do not conduct electricity because of lack of free electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




