
Could anybody explain why the alpha hydrogen of the carbon of acetophenone takes part in the aldol condensation reaction and not that of the one conjoined to the phenyl ring?
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: One of the most important compounds in organic chemistry is Benzene. It is one of the aromatic compounds. The molecular formula of benzene is \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\]. Phenol is one of the derivatives of benzene. I simply said that phenol is one of the aromatic alcohols. In chemistry, one of the important bonds is the Hydrogen bond. Without hydrogen bonds nothing in the world. There are two types of hydrogen bonds. They are intermolecular hydrogen bonds and intramolecular hydrogen bonds. The hydrogen bond depends on the most electronegativity atom in the molecule.
Complete answer:
The given data is
The alpha hydrogen of the carbon of acetophenone takes part in the aldol condensation reaction and not that of the one conjoined to the phenyl ring.
The molecular formula of acetophenone is \[{C_6}{H_5} - CO - C{H_3}\].
The structural formula of acetophenone is
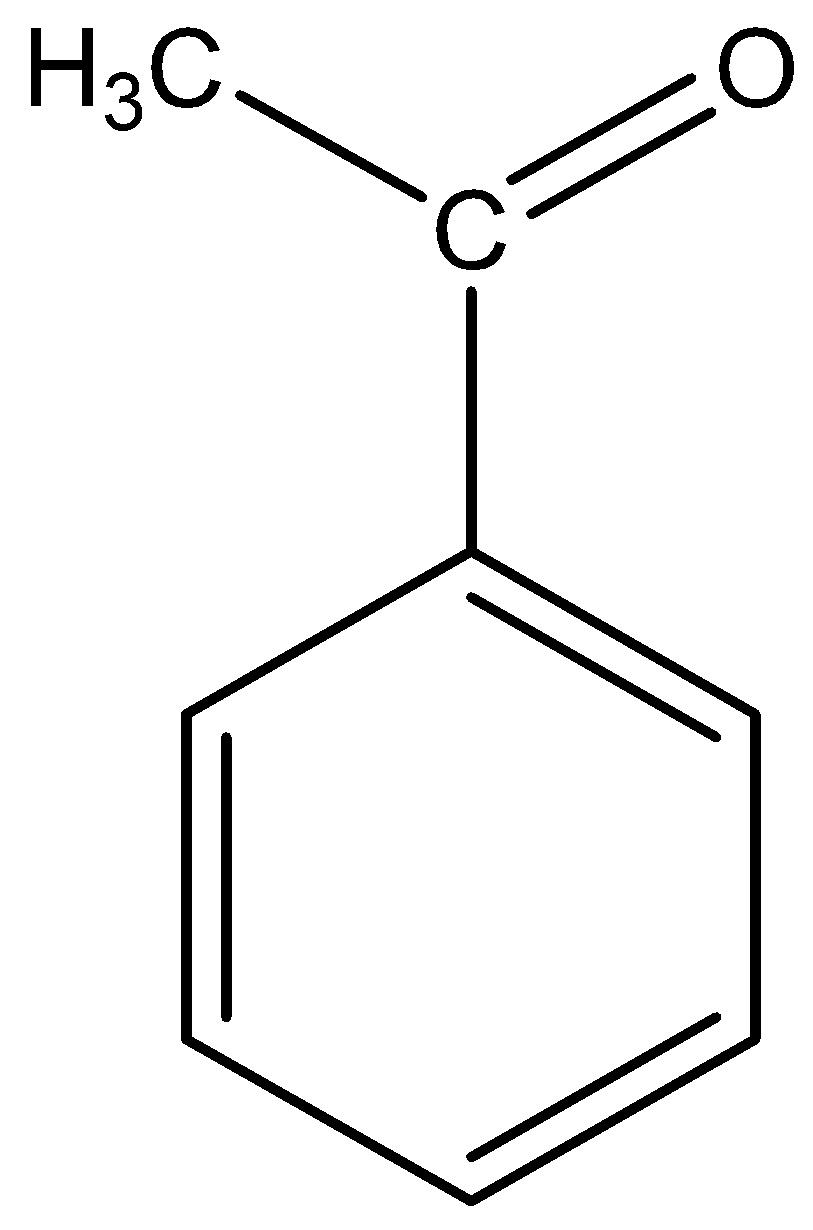
The base abstracts the proton of acetophenone in methyl group in the molecule and it from the carbanion in two ways.
One is proton abstract from the methyl and another is phenyl range.
The carbanion in the methyl range is more stable compare to the phenyl ring.
\[{C_6}{H_5} - CO - C{H_2}^ - \rightleftarrows {C_6}{H_5} - C{O^ - } - C{H_3}\]
Because the phenyl ring is more electron-rich. So, in the aldol condensation reaction, the alpha hydrogen of the carbon of acetophenone takes part and not that of the one conjoined to the phenyl ring.
According to the above discussion, we conclude the alpha hydrogen of the carbon of acetophenone takes part in the aldol condensation reaction and not that of the one conjoined to the phenyl ring.
Note:
One of the mono substituent benzene compounds is Phenol. Each mono substituent moiety having three named positions in the ring. In the ring nearby mono substituent group is called as ortho position, that means two ortho position are in the ring because left and right side of the substituent group. The alternative position of the substituent group in the ring is called a meta-position, there are also two meta-positions possible in the left and right sides of the substituent group. Para position nothing but directly opposite to the substituent group in the ring. Electrophilic substitution attacks in ortho and para positions in the ring.
Complete answer:
The given data is
The alpha hydrogen of the carbon of acetophenone takes part in the aldol condensation reaction and not that of the one conjoined to the phenyl ring.
The molecular formula of acetophenone is \[{C_6}{H_5} - CO - C{H_3}\].
The structural formula of acetophenone is

The base abstracts the proton of acetophenone in methyl group in the molecule and it from the carbanion in two ways.
One is proton abstract from the methyl and another is phenyl range.
The carbanion in the methyl range is more stable compare to the phenyl ring.
\[{C_6}{H_5} - CO - C{H_2}^ - \rightleftarrows {C_6}{H_5} - C{O^ - } - C{H_3}\]
Because the phenyl ring is more electron-rich. So, in the aldol condensation reaction, the alpha hydrogen of the carbon of acetophenone takes part and not that of the one conjoined to the phenyl ring.
According to the above discussion, we conclude the alpha hydrogen of the carbon of acetophenone takes part in the aldol condensation reaction and not that of the one conjoined to the phenyl ring.
Note:
One of the mono substituent benzene compounds is Phenol. Each mono substituent moiety having three named positions in the ring. In the ring nearby mono substituent group is called as ortho position, that means two ortho position are in the ring because left and right side of the substituent group. The alternative position of the substituent group in the ring is called a meta-position, there are also two meta-positions possible in the left and right sides of the substituent group. Para position nothing but directly opposite to the substituent group in the ring. Electrophilic substitution attacks in ortho and para positions in the ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




