
Correct ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond length follows the sequence:
A) ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2} < {\text{BF}}_4^ - $
B) \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3} < {\text{BF}}_4^ - \]
C) \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3} < {\text{BF}}_4^ - < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\]
D) \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}} < {\text{BF}}_4^ - \]
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint:We know that ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$ undergoes back bonding. This leads to double bond character in ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$. \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}\] and \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\] have oxygen and nitrogen atoms which are electronegative atoms and oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen.
Complete answer :
We are given four species: ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$, ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $, ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}$ and \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\]. The structures of ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$, ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $, ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}$ and \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\] are as follows:
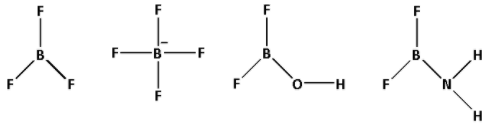
Consider ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$: From the structure of ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$, we can see that it is a $s{p^2}$ hybridised and a trigonal planar structure. Boron atom has a vacant $2p$ orbital and the fluorine atom has completely filled $2p$ orbital. Both the orbitals have the same energy and thus, back bonding occurs between boron and fluorine atoms. The lone pair of electrons from the completely filled $2p$ orbitals of fluorine atom are transferred to the vacant $2p$ orbitals of boron atom. This develops a double bond character between boron and fluorine and thus, the ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond length becomes shorter. Thus, ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$ has the shortest bond length.
Consider ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $:- From the structure of ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $, we can see that it is a $s{p^3}$ hybridised and a tetrahedral structure. The boron atom does not have any vacant $2p$ orbital left. Thus, no back bonding occurs between boron and fluorine atoms. Thus, ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond in ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $ are purely single bonds. Thus, the ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond length in ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $ is higher than that in ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$.
Consider ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}$ and \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\]: \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}\] and \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\] have oxygen and nitrogen atoms which are electronegative atoms and oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen. A more electronegative atom has a greater tendency to pull the bond forming electron pair towards itself. Thus, the ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond length in \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\] is higher than that in ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}$. But the ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond length in ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}$ and \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\] is more than the double bond length and less than the single bond length.
Thus, the order of ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond length is ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2} < {\text{BF}}_4^ - $.
Thus, the correct option is (A) ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2} < {\text{BF}}_4^ - $.
Note:The back bonding occurs when one atom has a vacant orbital and the other atom has a lone pair of electrons. Both the atoms involved in back bonding must have the orbitals of the same energy. Also, a more electronegative atom has a greater tendency to attract the electron pair involved in bonding towards itself and thus, reducing the bond length.
Complete answer :
We are given four species: ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$, ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $, ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}$ and \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\]. The structures of ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$, ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $, ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}$ and \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\] are as follows:

Consider ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$: From the structure of ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$, we can see that it is a $s{p^2}$ hybridised and a trigonal planar structure. Boron atom has a vacant $2p$ orbital and the fluorine atom has completely filled $2p$ orbital. Both the orbitals have the same energy and thus, back bonding occurs between boron and fluorine atoms. The lone pair of electrons from the completely filled $2p$ orbitals of fluorine atom are transferred to the vacant $2p$ orbitals of boron atom. This develops a double bond character between boron and fluorine and thus, the ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond length becomes shorter. Thus, ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$ has the shortest bond length.
Consider ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $:- From the structure of ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $, we can see that it is a $s{p^3}$ hybridised and a tetrahedral structure. The boron atom does not have any vacant $2p$ orbital left. Thus, no back bonding occurs between boron and fluorine atoms. Thus, ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond in ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $ are purely single bonds. Thus, the ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond length in ${\text{BF}}_4^ - $ is higher than that in ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3}$.
Consider ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}$ and \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\]: \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}\] and \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\] have oxygen and nitrogen atoms which are electronegative atoms and oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen. A more electronegative atom has a greater tendency to pull the bond forming electron pair towards itself. Thus, the ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond length in \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\] is higher than that in ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}$. But the ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond length in ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}}$ and \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2}\] is more than the double bond length and less than the single bond length.
Thus, the order of ${\text{B}} - {\text{F}}$ bond length is ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2} < {\text{BF}}_4^ - $.
Thus, the correct option is (A) ${\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_3} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{OH}} < {\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_2} < {\text{BF}}_4^ - $.
Note:The back bonding occurs when one atom has a vacant orbital and the other atom has a lone pair of electrons. Both the atoms involved in back bonding must have the orbitals of the same energy. Also, a more electronegative atom has a greater tendency to attract the electron pair involved in bonding towards itself and thus, reducing the bond length.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




