
How will you convert benzene into m-nitro chlorobenzene?
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: We know that m-nitro chlorobenzene is $1 - $chloro$ - 3 - $nitro benzene can be synthesised by the substitution reaction on a benzene ring. We can convert benzene in m-nitro chlorobenzene by nitration of benzene followed by chlorination of the compound formed by nitration.
Step-By-Step answer:
Nitration of benzene happens when one or more than one hydrogen atom from the benzene ring is replaced by a nitro group. To accomplish this reaction benzene is treated with concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid at a temperature not more than ${50^0}$ C. The nitration mechanism involves the formation of nitronium ions. An electrophilic substitution reaction occurs between benzene and nitric acid.
Chlorination of nitrobenzene is also an electrophilic substitution reaction where chloronium ion acts as an electrophile. Chloronium ion attacks on the nitrobenzene on the nitrobenzene ring. The attack is possible at three positions, ortho, meta and para position of nitrobenzene ring. But meta attack is more stable in comparison to ortho and para attack. Thus the chlorination gives meta nitrobenzene as a major product. Ferric chloride or aluminium chloride is used as a catalyst to give chloronium ion. The reaction of converting benzene to m-nitro chlorobenzene is given below;
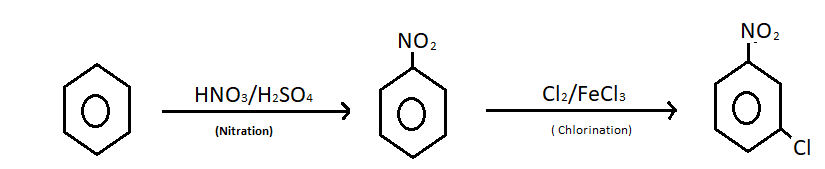
Note: This is a compound which is used in synthesis of various compounds. m-nitrochlorobenzene is an important intermediate of pharmaceuticals and dyes. It is used in the production of chloroaniline, azo dyes, pesticides, drugs, pigments etc. It is a precursor to other compounds due to the presence of the two relative sites on the molecules. Purification of m-nitro chlorobenzene is difficult since other isomers are formed during chlorination of nitrobenzene.
Step-By-Step answer:
Nitration of benzene happens when one or more than one hydrogen atom from the benzene ring is replaced by a nitro group. To accomplish this reaction benzene is treated with concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid at a temperature not more than ${50^0}$ C. The nitration mechanism involves the formation of nitronium ions. An electrophilic substitution reaction occurs between benzene and nitric acid.
Chlorination of nitrobenzene is also an electrophilic substitution reaction where chloronium ion acts as an electrophile. Chloronium ion attacks on the nitrobenzene on the nitrobenzene ring. The attack is possible at three positions, ortho, meta and para position of nitrobenzene ring. But meta attack is more stable in comparison to ortho and para attack. Thus the chlorination gives meta nitrobenzene as a major product. Ferric chloride or aluminium chloride is used as a catalyst to give chloronium ion. The reaction of converting benzene to m-nitro chlorobenzene is given below;

Note: This is a compound which is used in synthesis of various compounds. m-nitrochlorobenzene is an important intermediate of pharmaceuticals and dyes. It is used in the production of chloroaniline, azo dyes, pesticides, drugs, pigments etc. It is a precursor to other compounds due to the presence of the two relative sites on the molecules. Purification of m-nitro chlorobenzene is difficult since other isomers are formed during chlorination of nitrobenzene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




