
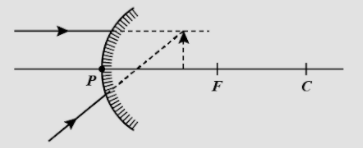
Converging rays strike a spherical convex mirror such that they can form the image in the absence of a mirror between pole and focus. Which of the following is a characteristic of the final image formed by the mirror?
A. Real
B. Virtual
C. Erect
D. Inverted

Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint:In this solution, observing the object as virtual, then using mirror formula and find the magnification out of it.
Complete step by step solution:
Here, we observed that object is virtual. So the object distance is positive.
From mirror formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
$\dfrac{1}{v} = - \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{f}$
$v < 0$
On the left of the mirror, the image is created and thus it’s virtual.
A spherical mirror magnification is given by:
$m = \dfrac{{ - v}}{u} > 0$
Hence, it is erect, Options B and C are correct.
Additional information:
Converging rays: If reflected rays converge after reflecting to a single point, it is called a converging mirror behavior. This is seen by the creation of a real picture. This can be used in applications in which all light intensity is concentrated at a time.
Spherical convex mirror (Curved mirror): A curved mirror is a reflection surface mirror. It may be convex (externally bolting) or concave (inwardly recessed). The surfaces of most curved mirrors are shaped like a part of a sphere, but in optical instruments, another form is often used. Parabolic reflectors, used in optical devices such as telescopes to view distant objects, are the most common non-spherical type since spherical mirror structures, including spherical lenses, suffer from spherical aberrations. For fun, distorting mirrors are used.
Mirror formula: It's an equation that applies to object distance and the focal length of the image are called a mirror equation. It is also called the composition of a mirror. In a spherical mirror: a focus length (f) is the distance from the main focus and the pole of the mirror.
Concave mirror: $\dfrac{1}{F} = \dfrac{1}{U} + \dfrac{1}{V}$
Convex mirror: $\dfrac{1}{U} - \dfrac{1}{V} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{F}$
Note: The image distance should be taken less than zero. By taking more than zero it may affect the result. Use proper mirror formula which is $\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$.
Complete step by step solution:
Here, we observed that object is virtual. So the object distance is positive.
From mirror formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
$\dfrac{1}{v} = - \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{f}$
$v < 0$
On the left of the mirror, the image is created and thus it’s virtual.
A spherical mirror magnification is given by:
$m = \dfrac{{ - v}}{u} > 0$
Hence, it is erect, Options B and C are correct.
Additional information:
Converging rays: If reflected rays converge after reflecting to a single point, it is called a converging mirror behavior. This is seen by the creation of a real picture. This can be used in applications in which all light intensity is concentrated at a time.
Spherical convex mirror (Curved mirror): A curved mirror is a reflection surface mirror. It may be convex (externally bolting) or concave (inwardly recessed). The surfaces of most curved mirrors are shaped like a part of a sphere, but in optical instruments, another form is often used. Parabolic reflectors, used in optical devices such as telescopes to view distant objects, are the most common non-spherical type since spherical mirror structures, including spherical lenses, suffer from spherical aberrations. For fun, distorting mirrors are used.
Mirror formula: It's an equation that applies to object distance and the focal length of the image are called a mirror equation. It is also called the composition of a mirror. In a spherical mirror: a focus length (f) is the distance from the main focus and the pole of the mirror.
Concave mirror: $\dfrac{1}{F} = \dfrac{1}{U} + \dfrac{1}{V}$
Convex mirror: $\dfrac{1}{U} - \dfrac{1}{V} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{F}$
Note: The image distance should be taken less than zero. By taking more than zero it may affect the result. Use proper mirror formula which is $\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




