
Contains carbon that are $s{p^2}$ hybridized:
A. ${C_2}{H_6}$
B. ${C_2}{H_4}$
C. ${C_2}{H_2}$
D. ${C_2}{H_5}OH$
E. ${C_3}{H_8}$
Answer
535.5k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this question, you must recall the concepts of Hybridization and Chemical Bonding. Use the formula or the concepts for finding the $s{p^2}$ Hybridization among the given option and choose the correct option.
Complete step by step solution:
Hybridization is defined as the concept of mixing two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a degenerated new type of orbitals. This intermixing is based on quantum mechanics. The atomic orbitals of the same energy level can only take part in hybridization and both full-filled and half-filled orbitals can also take part in this process, provided they have equal energy.
$\text{Hybridization = No. of sigma bonds + No. of lone pairs}$
On substituting the values for given compound we get
${C_2}{H_6}$ the carbon is $s{p^3}$ having hybridization number 4.
${C_2}{H_4}$ the carbon is $s{p^2}$ having hybridization number 3.
${C_2}{H_2}$ the carbon is $s{p^2}$ having hybridization number 2.
${C_2}{H_5}OH$ the carbon is $s{p^2}$ having hybridization number 4.
${C_3}{H_8}$ the carbon is $s{p^2}$ having hybridization number 4.
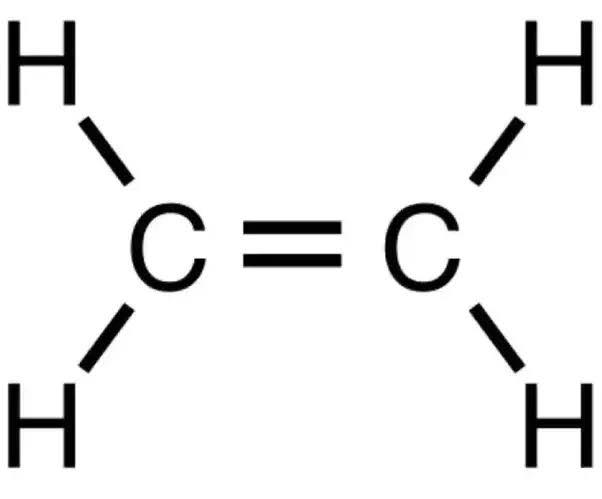
In ethene there are three sigma bonds and zero lone pair therefore the hybridization number is 3 hence the carbon atom is. $s{p^2}$ hybridization is observed when one s and two p orbitals of the same shell of an atom mix to form 3 equivalent orbital.
The new orbitals formed are called $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals. Ethene or ${C_2}{H_4}$ is $s{p^2}$ hybridized. Here, each carbon atom has three $s{p^2}$ hybridized orbitals. Two of them form sigma bonds with two Hydrogen atoms. While, the other forms another sigma bond with the second carbon atom.
Hence, we got the required answer i.e. ${C_2}{H_4}$
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Ethene ${C_2}{H_4}$ has a double bond between the carbons. In this case, carbon will $s{p^2}$ hybridize; in $s{p^2}$ hybridization, the 2s orbital mixes with only two of the three available 2p orbitals, forming a total of three sp hybrid orbitals with one p-orbital remaining. The three hybridized orbitals explain the three sigma bonds that each carbon forms.
Complete step by step solution:
Hybridization is defined as the concept of mixing two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a degenerated new type of orbitals. This intermixing is based on quantum mechanics. The atomic orbitals of the same energy level can only take part in hybridization and both full-filled and half-filled orbitals can also take part in this process, provided they have equal energy.
$\text{Hybridization = No. of sigma bonds + No. of lone pairs}$
On substituting the values for given compound we get
${C_2}{H_6}$ the carbon is $s{p^3}$ having hybridization number 4.
${C_2}{H_4}$ the carbon is $s{p^2}$ having hybridization number 3.
${C_2}{H_2}$ the carbon is $s{p^2}$ having hybridization number 2.
${C_2}{H_5}OH$ the carbon is $s{p^2}$ having hybridization number 4.
${C_3}{H_8}$ the carbon is $s{p^2}$ having hybridization number 4.

In ethene there are three sigma bonds and zero lone pair therefore the hybridization number is 3 hence the carbon atom is. $s{p^2}$ hybridization is observed when one s and two p orbitals of the same shell of an atom mix to form 3 equivalent orbital.
The new orbitals formed are called $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals. Ethene or ${C_2}{H_4}$ is $s{p^2}$ hybridized. Here, each carbon atom has three $s{p^2}$ hybridized orbitals. Two of them form sigma bonds with two Hydrogen atoms. While, the other forms another sigma bond with the second carbon atom.
Hence, we got the required answer i.e. ${C_2}{H_4}$
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Ethene ${C_2}{H_4}$ has a double bond between the carbons. In this case, carbon will $s{p^2}$ hybridize; in $s{p^2}$ hybridization, the 2s orbital mixes with only two of the three available 2p orbitals, forming a total of three sp hybrid orbitals with one p-orbital remaining. The three hybridized orbitals explain the three sigma bonds that each carbon forms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




