
Construct a rhombus of side $6cm$ and one diagonal $10cm$ of length. The length of the other diagonal is:
$A)4.2cm$
$B)6.6cm$
$C)5.5cm$
$D)7.4cm$
Answer
542.4k+ views
Hint: To construct a rhombus the given diagonal is taken as the horizontal line so as to make the construction a bit easier. To find the length of the other diagonal, it is important for us to know that the diagonal in the rhombus meets ay right angle which is at ${{90}^{\circ }}$. We need to find the square root of the sum of the half of the square root of the two diagonals, which is mathematically shown as
$A{{B}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{AC}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{BD}{2} \right)}^{2}}$.
Complete step by step solution:
To construct the rhombus $ABCD$ where $AB$ is the side and $AC$ is the diagonal, use the following steps:
1. Draw $AC=1Ocm$ . We know that the four sides of the rhombus are equal. In this question the one side is given as $AB=6cm$ , Hence all the sides are $6cm$.
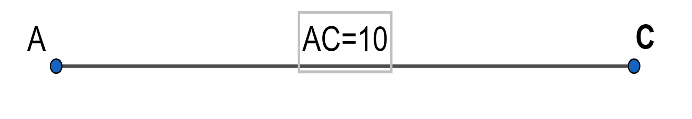
2. Now, taking $A$ as the center, draw arcs of radius $6cm$ above and below the segment$AC$.
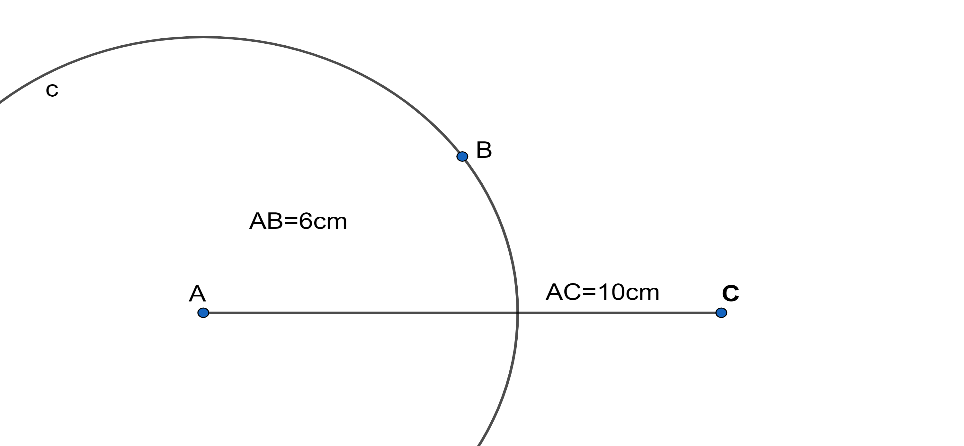
3. Similarly, taking $C$ as the center, draws arcs of radius $6cm$ above and below the segment$AC$.
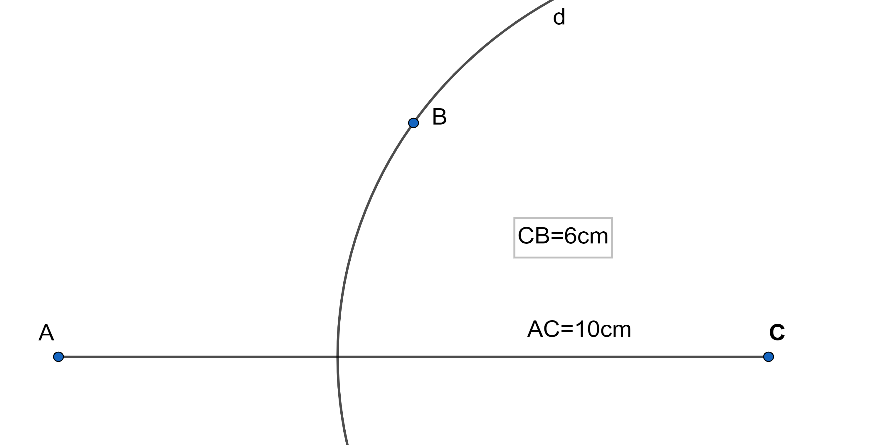
4. The point of intersection of the arc below the segment $AC$ is the vertex $D$ and the point of intersection of the arcs below the segment $AC$ is the vertex $B$ .
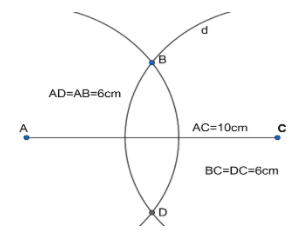
5. Hence, rhombus $ABCD$ has been constructed with the given measurements.
Below is the rhombus after construction
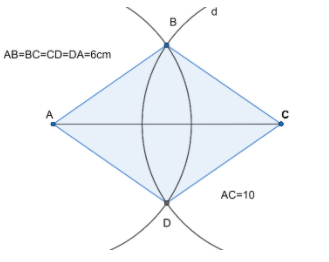
We know that the diagonals in the rhombus meet at ${{90}^{\circ }}$. So on using Pythagoras Theorem $A{{B}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{AC}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{BD}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
Further calculating, we get:
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{A{{B}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{AC}{2} \right)}^{2}}}=\left( \dfrac{BD}{2} \right)$
On putting the value we get,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{BD}{2}=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{10}{2} \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow BD=2\times \sqrt{36-25}$
$\Rightarrow BD=2\times \sqrt{11}$
On finding the square-root of the number $\sqrt{11}$ , we get $3.3$ , so substituting $3.3$in the place of $\sqrt{11}$ we get:
$\Rightarrow 2\times 3.3$
$\Rightarrow 6.6$
$\therefore $ The length of the diagonal is $B)=6.6cm$when one side is $4cm$and the other diagonal given is $10cm$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We can calculate the length of the other diagonal after the construction just by measuring the length $BD$. We can check the length of the diagonal by back calculation. We can square add the half of the diagonals and the find the square root of the it. If the side of the rhombus comes to be same as $6cm$, then the length of the diagonal is correct.
$A{{B}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{AC}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{BD}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
On putting the value we get:
$\Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{10}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{6.6}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}={{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3.3 \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}=35.89$
To find the side of the length we will find the square root of the above number, on calculating we get:
$\Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{35.89}$
$\Rightarrow AB=5.99$
On taking the round off of the number we get
$\Rightarrow AB=6cm$
Since the value of $AB$, which is on the side of the rhombus is the same , so the answer is correct.
$A{{B}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{AC}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{BD}{2} \right)}^{2}}$.
Complete step by step solution:
To construct the rhombus $ABCD$ where $AB$ is the side and $AC$ is the diagonal, use the following steps:
1. Draw $AC=1Ocm$ . We know that the four sides of the rhombus are equal. In this question the one side is given as $AB=6cm$ , Hence all the sides are $6cm$.

2. Now, taking $A$ as the center, draw arcs of radius $6cm$ above and below the segment$AC$.

3. Similarly, taking $C$ as the center, draws arcs of radius $6cm$ above and below the segment$AC$.

4. The point of intersection of the arc below the segment $AC$ is the vertex $D$ and the point of intersection of the arcs below the segment $AC$ is the vertex $B$ .

5. Hence, rhombus $ABCD$ has been constructed with the given measurements.
Below is the rhombus after construction

We know that the diagonals in the rhombus meet at ${{90}^{\circ }}$. So on using Pythagoras Theorem $A{{B}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{AC}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{BD}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
Further calculating, we get:
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{A{{B}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{AC}{2} \right)}^{2}}}=\left( \dfrac{BD}{2} \right)$
On putting the value we get,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{BD}{2}=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{10}{2} \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow BD=2\times \sqrt{36-25}$
$\Rightarrow BD=2\times \sqrt{11}$
On finding the square-root of the number $\sqrt{11}$ , we get $3.3$ , so substituting $3.3$in the place of $\sqrt{11}$ we get:
$\Rightarrow 2\times 3.3$
$\Rightarrow 6.6$
$\therefore $ The length of the diagonal is $B)=6.6cm$when one side is $4cm$and the other diagonal given is $10cm$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We can calculate the length of the other diagonal after the construction just by measuring the length $BD$. We can check the length of the diagonal by back calculation. We can square add the half of the diagonals and the find the square root of the it. If the side of the rhombus comes to be same as $6cm$, then the length of the diagonal is correct.
$A{{B}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{AC}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{BD}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
On putting the value we get:
$\Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{10}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{6.6}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}={{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3.3 \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}=35.89$
To find the side of the length we will find the square root of the above number, on calculating we get:
$\Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{35.89}$
$\Rightarrow AB=5.99$
On taking the round off of the number we get
$\Rightarrow AB=6cm$
Since the value of $AB$, which is on the side of the rhombus is the same , so the answer is correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




