
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD in which \[AB=4cm\], \[AC=5cm\], \[AD=5.5cm\] and \[\angle ABC=\angle ACD={{90}^{\circ }}\]
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: We solve this problem by constructing the quadrilateral using steps from angle to side length. First, we take a reference axes then we construct angle \[\angle ABC\] which is easy by using the protractor then we use the compass or ruler to construct the sides of the quadrilateral which gives the required quadrilateral.
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given that for a quadrilateral ABCD such that \[AB=4cm\], \[AC=5cm\], \[AD=5.5cm\] and \[\angle ABC=\angle ACD={{90}^{\circ }}\]
Let us construct the angle \[\angle ABC={{90}^{\circ }}\] of some unknown length as

Now let us point the vertex A on the ray BY such that \[AB=4cm\] then we get

Now, let us point the vertex C on the ray BX such that \[AC=5cm\] then we get
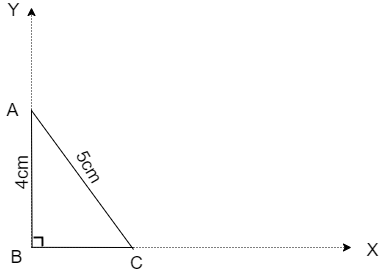
We are given with another angle that is \[\angle ACD={{90}^{\circ }}\]
Now, let us construct a ray CZ such that \[\angle ACD={{90}^{\circ }}\] using the protractor then we get
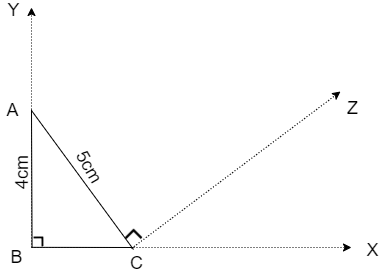
Now, let us point the vertex D on the ray CZ such that \[AD=5.5cm\] then we get
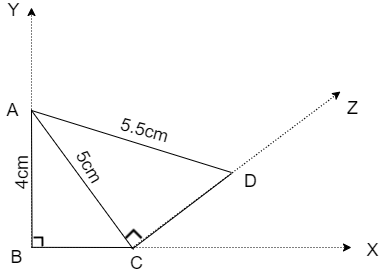
Now by removing the rays and drawing the quadrilateral ABCD we get
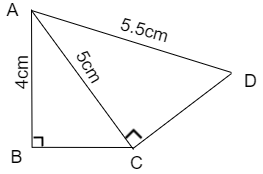
Therefore, we can say that the quadrilateral ABCD such that \[AB=4cm\], \[AC=5cm\], \[AD=5.5cm\] and \[\angle ABC=\angle ACD={{90}^{\circ }}\] has been constructed.
Note: The question can be extended furthermore that is to find the length of BC and CD.
We use the Pythagoras theorem for finding the length of BC and CD
We know that the Pythagoras Theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides that is for the triangle shown below
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given that for a quadrilateral ABCD such that \[AB=4cm\], \[AC=5cm\], \[AD=5.5cm\] and \[\angle ABC=\angle ACD={{90}^{\circ }}\]
Let us construct the angle \[\angle ABC={{90}^{\circ }}\] of some unknown length as

Now let us point the vertex A on the ray BY such that \[AB=4cm\] then we get

Now, let us point the vertex C on the ray BX such that \[AC=5cm\] then we get

We are given with another angle that is \[\angle ACD={{90}^{\circ }}\]
Now, let us construct a ray CZ such that \[\angle ACD={{90}^{\circ }}\] using the protractor then we get

Now, let us point the vertex D on the ray CZ such that \[AD=5.5cm\] then we get

Now by removing the rays and drawing the quadrilateral ABCD we get

Therefore, we can say that the quadrilateral ABCD such that \[AB=4cm\], \[AC=5cm\], \[AD=5.5cm\] and \[\angle ABC=\angle ACD={{90}^{\circ }}\] has been constructed.
Note: The question can be extended furthermore that is to find the length of BC and CD.
We use the Pythagoras theorem for finding the length of BC and CD
We know that the Pythagoras Theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides that is for the triangle shown below
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





