
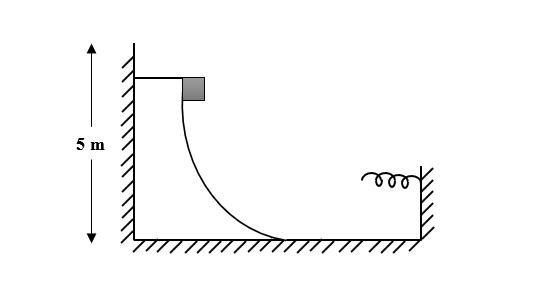
Consider the situation shown in figure. A spring of spring constant 400N/m is attached at one end to a wedge fixed rigidly with the horizontal part. A 40 g mass is released from rest while situated at a height 5 m the curved track. The maximum deformation in the spring is nearly equal to?
A. 9.8 m
B. 9.8 cm
C. 0.98 cm
D. 0.009 km

Answer
576k+ views
Hint: Loss in gravitational potential energy is equal to the gain in the elastic potential. So, at maximum deformation, all the gravitational potential energy would get converted to elastic energy. Use the formula for gravitational potential energy, substitute the values and find the gravitational potential energy. Then, use the formula for elastic potential energy, substitute the values and find its value. Then equate the value of gravitational potential energy to elastic potential energy. Solve it and calculate the value of x. This value will be the maximum deformation in the spring.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: height (h)= 5 m
Mass (m)= 40 g= 0.04 kg
g= 9.8 m/s
Spring constant (k)= 400 N/m
The loss in gravitational potential energy is equal to the gain in elastic potential energy. This implies that at the maximum deformation, all the gravitational potential energy gets converted to elastic potential energy.
$\Rightarrow {E}_{gravitational}= {E}_{elastic}$ …(1)
Gravitational potential energy is given by,
${E}_{gravitational}= mgh$ …(2)
Where, m is the mass in kg
g is the gravitational field strength in ${N}/{kg}$
h is the height in meters
Substituting values in the equation. (2) we get,
${E}_{gravitational}= 0.04 \times 9.8 \times 5$
$\Rightarrow {E}_{gravitational}= 1.96 J$
Elastic potential energy is given by,
${E}_{elastic}= \dfrac {1}{2}k{x}^{2}$ …(3)
Where, k is the spring constant in ${N}/{m}$
x is the displacement in meters
Substituting values in the equation. (3) we get,
${E}_{elastic}= \dfrac {1}{2} \times 400{x}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow {E}_{elastic}= 200{x}^{2}$
Now, substituting values in the equation. (1) we get,
$1.96= 200{x}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow {x}^{2}= \dfrac {1.96}{200}$
$\Rightarrow {x}^{2}= 0.0098$
Taking out the square root on both the sides we get,
$x= 0.099 m$
$\therefore x= 9.9cm$
Thus, the maximum deformation in the spring is nearly equal to 9.8 cm.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Students must make sure that they convert all the units to their S.I. units. Not converting the units to their S.I. units will give them a wrong output altogether. Gravitational potential energy is directly proportional to the height of the object. Doubling the height will result in doubling of the gravitational potential energy and tripling the height of the object will result in tripling of the gravitational potential energy.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: height (h)= 5 m
Mass (m)= 40 g= 0.04 kg
g= 9.8 m/s
Spring constant (k)= 400 N/m
The loss in gravitational potential energy is equal to the gain in elastic potential energy. This implies that at the maximum deformation, all the gravitational potential energy gets converted to elastic potential energy.
$\Rightarrow {E}_{gravitational}= {E}_{elastic}$ …(1)
Gravitational potential energy is given by,
${E}_{gravitational}= mgh$ …(2)
Where, m is the mass in kg
g is the gravitational field strength in ${N}/{kg}$
h is the height in meters
Substituting values in the equation. (2) we get,
${E}_{gravitational}= 0.04 \times 9.8 \times 5$
$\Rightarrow {E}_{gravitational}= 1.96 J$
Elastic potential energy is given by,
${E}_{elastic}= \dfrac {1}{2}k{x}^{2}$ …(3)
Where, k is the spring constant in ${N}/{m}$
x is the displacement in meters
Substituting values in the equation. (3) we get,
${E}_{elastic}= \dfrac {1}{2} \times 400{x}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow {E}_{elastic}= 200{x}^{2}$
Now, substituting values in the equation. (1) we get,
$1.96= 200{x}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow {x}^{2}= \dfrac {1.96}{200}$
$\Rightarrow {x}^{2}= 0.0098$
Taking out the square root on both the sides we get,
$x= 0.099 m$
$\therefore x= 9.9cm$
Thus, the maximum deformation in the spring is nearly equal to 9.8 cm.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Students must make sure that they convert all the units to their S.I. units. Not converting the units to their S.I. units will give them a wrong output altogether. Gravitational potential energy is directly proportional to the height of the object. Doubling the height will result in doubling of the gravitational potential energy and tripling the height of the object will result in tripling of the gravitational potential energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




