
Consider the following two complex ions: \[{\left[ {Co{F_6}} \right]^{3 - }}\] and \[{\left[ {Co{{\left( {{C_2}{O_4}} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 - }}\]. Which of the following statement(s) is/are false?
I. Both are octahedral.
II. \[{\left[ {Co{{\left( {{C_2}{O_4}} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 - }}\] is diamagnetic while \[{\left[ {Co{F_6}} \right]^{3 - }}\] is paramagnetic.
III. Both are outer orbital complexes.
IV. In both the complexes, the central metal is in the same oxidation state.
A. Both (II) and (III)
B. I), (III) and (IV)
C. Only (III) [Comment: the option is wrong, it should be only (II)]
D. Both (III) and (IV)
E. (I), (II) and (IV)
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: These are coordination compounds of cobalt (\[Co\]). The first complex is called hexafluoro cobalt and the second is the tris oxalato cobalt complex. Both of them are anionic complexes.
Complete step by step answer: In both the complexes cobalt is the central metal ion. In order to understand the characteristics of the given complexes we have to identify the type of coordination between the ligand and the central metal ion. In \[{\left[ {Co{F_6}} \right]^{3 - }}\] the ligand is the fluoride ion and in \[{\left[ {Co{{\left( {{C_2}{O_4}} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 - }}\] the ligand is the oxalate ion. Let us evaluate the statements one by one.
-Both are octahedral.
In \[{\left[ {Co{F_6}} \right]^{3 - }}\] the ligand fluoride is a monodentate ligand and can form only one coordinate bond. Thus the coordination number of the complex is , C.No = $6 \times 1 = 6.$
In \[{\left[ {Co{{\left( {{C_2}{O_4}} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 - }}\] the ligand oxalate is a bidentate ligand and can form two coordinate bonds. Thus the coordination number of the complex is, C.No. =$3 \times 2 = 6.$
Hence both the complexes are octahedral.
- \[{\left[ {Co{{\left( {{C_2}{O_4}} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 - }}\] is diamagnetic while \[{\left[ {Co{F_6}} \right]^{3 - }}\] is paramagnetic.
In both the complexes the central metal ion is in \[ + 3\] oxidation state. The electronic configuration of cobalt and \[C{o^{3 + }}\] are:
$Co = [Ar]3{d^7}4{s^2}$
$C{o^{3 + }} = [Ar]3{d^6}$
In \[C{o^{3 + }}\] the two electrons are lost from \[4s\] orbital and one electron from \[3d\] orbital.
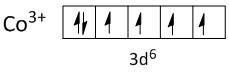
Both ligands, fluoride and oxalate are weak field ligands and cannot pair up the electrons of the central metal ion. Thus the electrons in the shell of \[3d\] orbitals remain unpaired. So both complexes are paramagnetic.
-Both are outer orbital complexes.
As no pairing of electrons takes in the inner \[3d\] orbital of \[C{o^{3 + }}\], the electrons from ligands will fill up the outer orbitals of\[4s\], \[4p\] and\[4d\]. This makes the orbitals of \[C{o^{3 + }}\] \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] hybridized.
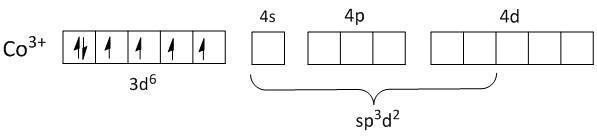
Thus both the complexes are outer orbital complexes.
IV. In both the complexes, the central metal is in the same oxidation state.
In \[{\left[ {Co{F_6}} \right]^{3 - }}\] the oxidation state of \[Co\] is:
$x + 6( - 1) = - 3$ , (fluoride caries \[ - 1\] charge)
$x = + 3$ , the oxidation state is \[ + 3\].
In \[{\left[ {Co{{\left( {{C_2}{O_4}} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 - }}\]the oxidation state of \[Co\] is:
$x + 3( - 2) = - 3$
$x = + 3$ , the oxidation state is\[ + 3\]. Thus in both complexes the central metal has \[ + 3\] oxidation state.
Hence, the option C is the correct answer, the false statement is only (II) as both complexes are paramagnetic.
Note: The number of ligands which combine with the central metal ion is referred as the coordination number of the complex. From every ligand the metal ion accepts electrons and forms coordinate covalent bonds. The ligands are Lewis bases and are electron donors.
Complete step by step answer: In both the complexes cobalt is the central metal ion. In order to understand the characteristics of the given complexes we have to identify the type of coordination between the ligand and the central metal ion. In \[{\left[ {Co{F_6}} \right]^{3 - }}\] the ligand is the fluoride ion and in \[{\left[ {Co{{\left( {{C_2}{O_4}} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 - }}\] the ligand is the oxalate ion. Let us evaluate the statements one by one.
-Both are octahedral.
In \[{\left[ {Co{F_6}} \right]^{3 - }}\] the ligand fluoride is a monodentate ligand and can form only one coordinate bond. Thus the coordination number of the complex is , C.No = $6 \times 1 = 6.$
In \[{\left[ {Co{{\left( {{C_2}{O_4}} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 - }}\] the ligand oxalate is a bidentate ligand and can form two coordinate bonds. Thus the coordination number of the complex is, C.No. =$3 \times 2 = 6.$
Hence both the complexes are octahedral.
- \[{\left[ {Co{{\left( {{C_2}{O_4}} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 - }}\] is diamagnetic while \[{\left[ {Co{F_6}} \right]^{3 - }}\] is paramagnetic.
In both the complexes the central metal ion is in \[ + 3\] oxidation state. The electronic configuration of cobalt and \[C{o^{3 + }}\] are:
$Co = [Ar]3{d^7}4{s^2}$
$C{o^{3 + }} = [Ar]3{d^6}$
In \[C{o^{3 + }}\] the two electrons are lost from \[4s\] orbital and one electron from \[3d\] orbital.

Both ligands, fluoride and oxalate are weak field ligands and cannot pair up the electrons of the central metal ion. Thus the electrons in the shell of \[3d\] orbitals remain unpaired. So both complexes are paramagnetic.
-Both are outer orbital complexes.
As no pairing of electrons takes in the inner \[3d\] orbital of \[C{o^{3 + }}\], the electrons from ligands will fill up the outer orbitals of\[4s\], \[4p\] and\[4d\]. This makes the orbitals of \[C{o^{3 + }}\] \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] hybridized.

Thus both the complexes are outer orbital complexes.
IV. In both the complexes, the central metal is in the same oxidation state.
In \[{\left[ {Co{F_6}} \right]^{3 - }}\] the oxidation state of \[Co\] is:
$x + 6( - 1) = - 3$ , (fluoride caries \[ - 1\] charge)
$x = + 3$ , the oxidation state is \[ + 3\].
In \[{\left[ {Co{{\left( {{C_2}{O_4}} \right)}_3}} \right]^{3 - }}\]the oxidation state of \[Co\] is:
$x + 3( - 2) = - 3$
$x = + 3$ , the oxidation state is\[ + 3\]. Thus in both complexes the central metal has \[ + 3\] oxidation state.
Hence, the option C is the correct answer, the false statement is only (II) as both complexes are paramagnetic.
Note: The number of ligands which combine with the central metal ion is referred as the coordination number of the complex. From every ligand the metal ion accepts electrons and forms coordinate covalent bonds. The ligands are Lewis bases and are electron donors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




