
Consider the following statements for $\mathop C\limits^ \bullet {H_3} = X$ and $\mathop C\limits^ \bullet {F_3} = Y$.
(I) When X dimerises bond angle decreases.
(II) When X dimerises bond angle increases.
(III) In $X - Y$ molecule, $C - C$ bond length is less than that in the $Y - Y$ molecule.
(IV) Bond angle X is greater than that in Y.
Which of the given statements are correct?
A. II, III
B. I, II, III
C. I, IV
D. II, III, IV
Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint: In organic chemistry, radicals are the chemical species which is electrically neutral and consist of an unshared electron in it. It is represented by a dot on the atom consisting of an unshared electron like $\mathop C\limits^ \bullet {H_3}$ and it is formed by homolytic cleavage of the organic compounds.
Complete answer:
In the given question, we are given two radicals i.e., methyl radical and trifluoromethyl radical and we need to compare various bond parameters for both radicals. So, lets check each given fact separately as follows:
Structure of methyl radical is as follows:
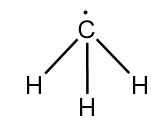
As the hydrogen atom is less electronegative than carbon, so it does not attract the radical to participate in hybridization. Hence, only three hydrogen atoms participate in hybridization.
Therefore, steric number $ = 3$
So, the hybridization of carbon in methyl radical $ = s{p^2}$
$\therefore $ bond angle in X $ = {120^o}$
Now, when methyl radical dimerises i.e., reacts with other mole of methyl radical, then formation of ethane takes place as follows:
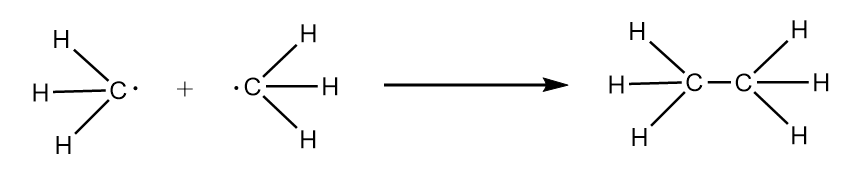
Hybridization state of carbon in methane $ = s{p^3}$
$\therefore $ bond angle in ethane $ = {109^o}28'$
Hence, when X dimerises a decrease in bond angle is observed.
Now, let us consider $X - Y$ molecule and $Y - Y$ molecule:
The structure of $X - Y$ molecule will be as follows:
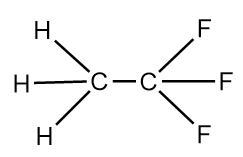
The structure of $Y - Y$ molecule is as follows:
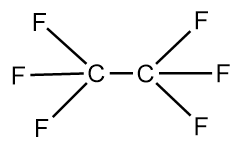
We know that, greater the number electronegative atoms bonded to carbon, the more will be the tendency of atoms to pull the pair of electrons toward itself from the bond and thus, lead to the reduction in the bond length. As, in the $Y - Y$ molecule there are six fluorine atoms which are highly electronegative, are bonded whereas in the $X - Y$ molecule only three fluorine atoms are bonded to the carbon atom. Hence, in the $X - Y$ molecule, $C - C$ bond length is greater than that in the $Y - Y$ molecule.
As discussed earlier, bond angle in X $ = {120^o}$. Now, let's check the bond angle in Y radical.
Structure of trifluoromethyl radical is as follows:
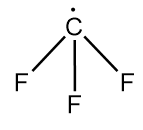
As in the given radical, fluorine is bonded with a carbon atom which is a highly electronegative element. So, it attracts the unshared electron present on the carbon atom towards itself and thus, the unshared electron will also participate in the hybridization.
So, steric number $ = 4$
Hybridization state of carbon in Y $ = s{p^3}$
$\therefore $ bond angle in Y $ = {109^o}28'$
Hence, bond angle X is greater than that in Y.
Therefore, we can conclude among given statements, only statement I and IV is correct.
So, option (C) is the right answer.
Note:
It is important to note that $\mathop C\limits^ \bullet {H_3}$ radical is much stable than $\mathop C\limits^ \bullet {F_3}$ radical because a radical is an electron deficient species and the fluorine atoms in $\mathop C\limits^ \bullet {F_3}$ acts as an electron withdrawing group due to which the deficiency on carbon atom increases and it becomes less stable.
Complete answer:
In the given question, we are given two radicals i.e., methyl radical and trifluoromethyl radical and we need to compare various bond parameters for both radicals. So, lets check each given fact separately as follows:
Structure of methyl radical is as follows:

As the hydrogen atom is less electronegative than carbon, so it does not attract the radical to participate in hybridization. Hence, only three hydrogen atoms participate in hybridization.
Therefore, steric number $ = 3$
So, the hybridization of carbon in methyl radical $ = s{p^2}$
$\therefore $ bond angle in X $ = {120^o}$
Now, when methyl radical dimerises i.e., reacts with other mole of methyl radical, then formation of ethane takes place as follows:
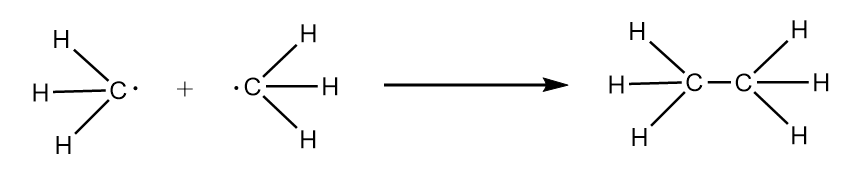
Hybridization state of carbon in methane $ = s{p^3}$
$\therefore $ bond angle in ethane $ = {109^o}28'$
Hence, when X dimerises a decrease in bond angle is observed.
Now, let us consider $X - Y$ molecule and $Y - Y$ molecule:
The structure of $X - Y$ molecule will be as follows:

The structure of $Y - Y$ molecule is as follows:

We know that, greater the number electronegative atoms bonded to carbon, the more will be the tendency of atoms to pull the pair of electrons toward itself from the bond and thus, lead to the reduction in the bond length. As, in the $Y - Y$ molecule there are six fluorine atoms which are highly electronegative, are bonded whereas in the $X - Y$ molecule only three fluorine atoms are bonded to the carbon atom. Hence, in the $X - Y$ molecule, $C - C$ bond length is greater than that in the $Y - Y$ molecule.
As discussed earlier, bond angle in X $ = {120^o}$. Now, let's check the bond angle in Y radical.
Structure of trifluoromethyl radical is as follows:

As in the given radical, fluorine is bonded with a carbon atom which is a highly electronegative element. So, it attracts the unshared electron present on the carbon atom towards itself and thus, the unshared electron will also participate in the hybridization.
So, steric number $ = 4$
Hybridization state of carbon in Y $ = s{p^3}$
$\therefore $ bond angle in Y $ = {109^o}28'$
Hence, bond angle X is greater than that in Y.
Therefore, we can conclude among given statements, only statement I and IV is correct.
So, option (C) is the right answer.
Note:
It is important to note that $\mathop C\limits^ \bullet {H_3}$ radical is much stable than $\mathop C\limits^ \bullet {F_3}$ radical because a radical is an electron deficient species and the fluorine atoms in $\mathop C\limits^ \bullet {F_3}$ acts as an electron withdrawing group due to which the deficiency on carbon atom increases and it becomes less stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




