
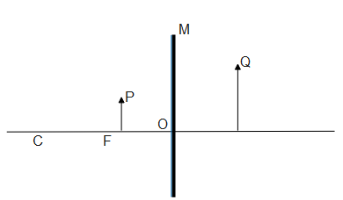
Consider the following diagram in which \[M\] is a mirror and $P$ is an object and $Q$ is its magnified image formed by the mirror.

Answer
502.2k+ views
Hint:We need to find the type of mirror based on the type of image formed by the mirror. The given image is a virtual, erect and magnified image. We need to draw a ray diagram and discuss the nature of the mirror.
Complete step by step answer:
We will draw the ray diagram first and try to identify the nature of the mirror.
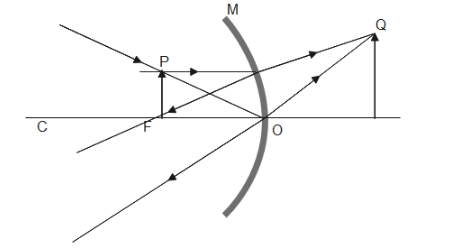
The object is kept between the focus and the pole of the mirror and as we can see when we draw a ray parallel to the principal axis and a ray passing through the pole of the mirror and when we extend the reflected rays to meet at a point where is image is formed, we can see that the nature of the mirror is converging as the incident rays are converging to a point in the other side of the mirror to form a virtual object.
Therefore the nature of the mirror is a concave mirror.
Additional information: When a ray strikes concave or convex mirrors obliquely at its pole, it is reflected obliquely. When a ray, parallel to the principal axis strikes concave or convex mirrors, the reflected ray passes through the focus on the principal axis. When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex mirrors, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. A ray passing through the centre of curvature of the spherical mirror will retrace its path after reflection.
Note:Concave mirrors form both real and virtual images. When the object is very close to the mirror, a virtual magnified image is formed and as we increase the distance between the mirror and the object, the size of the image decreases and real images are formed.
Complete step by step answer:
We will draw the ray diagram first and try to identify the nature of the mirror.

The object is kept between the focus and the pole of the mirror and as we can see when we draw a ray parallel to the principal axis and a ray passing through the pole of the mirror and when we extend the reflected rays to meet at a point where is image is formed, we can see that the nature of the mirror is converging as the incident rays are converging to a point in the other side of the mirror to form a virtual object.
Therefore the nature of the mirror is a concave mirror.
Additional information: When a ray strikes concave or convex mirrors obliquely at its pole, it is reflected obliquely. When a ray, parallel to the principal axis strikes concave or convex mirrors, the reflected ray passes through the focus on the principal axis. When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex mirrors, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. A ray passing through the centre of curvature of the spherical mirror will retrace its path after reflection.
Note:Concave mirrors form both real and virtual images. When the object is very close to the mirror, a virtual magnified image is formed and as we increase the distance between the mirror and the object, the size of the image decreases and real images are formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




