
Consider the figure given below, find the measure of $\angle PRS$. \[\]
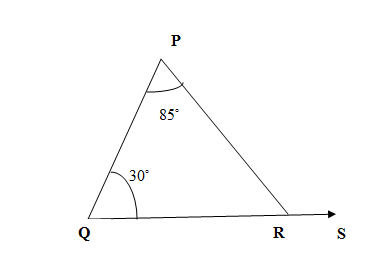

Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: We see in the given figure of triangle PQR that the external angle $\angle PRS$ has internal angles $\angle PQR,\angle QPR$ whose measures are given in the figure. We use external angle theorem “the measure of an external angle is equal to sum of measures of remote internal angles” to find measure of $\angle PRS$. \[\]
Complete step by step answer:
We know that internal angles otherwise known as interior angles are angles formed by the polygon by two sides in the interior of the polygon. The exterior angle or external angles are an angle produced by a side and line extended from adjacent sides. The six external angles of triangle ABC are shown below. \[\]
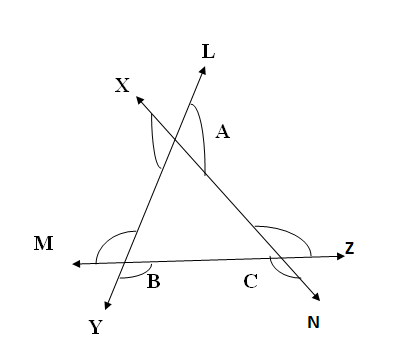
The external angles in above diagram are
\[\angle BAL,\angle CAX,\angle ABM,\angle CBY,\angle ACZ,\angle BCN\]
The internal angles are
\[\angle ABC,\angle ACB,\angle BAC\]
The internal angles that do not share vertex with the external angle are called the opposite internal angle or remote internal angle of that external angle. \[\]
Let us observe the exterior angles at the point $\angle ACZ$ are formed with AC and extension of side BC. It shares the vertex C with internal angle $\angle ACB$ and does not share any vertex with internal angles $\angle ABC,\angle BAC$. So $\angle ABC,\angle BAC$ are called remote internal angles. \[\]
The external angle theorem states that the measure of an external angle is equal to the sum of measures of remote internal angles. So at point C we have,
\[\angle ACZ=\angle ABC+\angle BAC\]
Let us observe the given figure in the question.
We are given a triangle PQR whose side QR has been extended to get the ray $\overrightarrow{QS}$. We are also given the measure of two internal angles.
\[\angle PQR={{30}^{\circ }},\angle QPR={{85}^{\circ }}\]
Let us observe the external angle formed at point R that is $\angle PRS$. It shares the vertex R with internal angle $\angle PRQ$ and does not share vertex with internal angles$\angle PQR,\angle QPR$ which makes $\angle PQR,\angle QPR$ remote internal angles of $\angle PRS$. We use the external angle theorem and have,
\[\angle PRS=\angle PQR+\angle QPR\]
We put the measures of given angles $\angle PQR={{30}^{\circ }},\angle QPR={{85}^{\circ }}$ in above equation and have the required result as
\[\angle PRS={{30}^{\circ }}+{{85}^{\circ }}={{115}^{\circ }}\]
Note: We must not confuse between external angle theorem and exterior angle sum theorem which states that the sum of exterior angles of polygon is ${{360}^{\circ }}$.The measure of two external angles subtended at one vertex are equal because they are vertically opposite angles. The sum of internal angles of $n$ sides is $\left( n-2 \right){{180}^{\circ }}$. We have an alternate method to solve this question. We can first find the third angle, i.e angle PRQ of the triangle using the fact that the sum of all angles is ${180}^{\circ}$. Then, the angles PRQ and PRS form a linear pair, so their sum must be ${180}^{\circ}$. Using this fact, we can find the angle PRS.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that internal angles otherwise known as interior angles are angles formed by the polygon by two sides in the interior of the polygon. The exterior angle or external angles are an angle produced by a side and line extended from adjacent sides. The six external angles of triangle ABC are shown below. \[\]

The external angles in above diagram are
\[\angle BAL,\angle CAX,\angle ABM,\angle CBY,\angle ACZ,\angle BCN\]
The internal angles are
\[\angle ABC,\angle ACB,\angle BAC\]
The internal angles that do not share vertex with the external angle are called the opposite internal angle or remote internal angle of that external angle. \[\]
Let us observe the exterior angles at the point $\angle ACZ$ are formed with AC and extension of side BC. It shares the vertex C with internal angle $\angle ACB$ and does not share any vertex with internal angles $\angle ABC,\angle BAC$. So $\angle ABC,\angle BAC$ are called remote internal angles. \[\]
The external angle theorem states that the measure of an external angle is equal to the sum of measures of remote internal angles. So at point C we have,
\[\angle ACZ=\angle ABC+\angle BAC\]
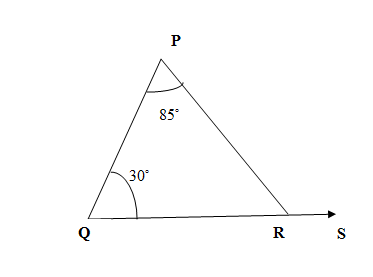
Let us observe the given figure in the question.

We are given a triangle PQR whose side QR has been extended to get the ray $\overrightarrow{QS}$. We are also given the measure of two internal angles.
\[\angle PQR={{30}^{\circ }},\angle QPR={{85}^{\circ }}\]
Let us observe the external angle formed at point R that is $\angle PRS$. It shares the vertex R with internal angle $\angle PRQ$ and does not share vertex with internal angles$\angle PQR,\angle QPR$ which makes $\angle PQR,\angle QPR$ remote internal angles of $\angle PRS$. We use the external angle theorem and have,
\[\angle PRS=\angle PQR+\angle QPR\]
We put the measures of given angles $\angle PQR={{30}^{\circ }},\angle QPR={{85}^{\circ }}$ in above equation and have the required result as
\[\angle PRS={{30}^{\circ }}+{{85}^{\circ }}={{115}^{\circ }}\]
Note: We must not confuse between external angle theorem and exterior angle sum theorem which states that the sum of exterior angles of polygon is ${{360}^{\circ }}$.The measure of two external angles subtended at one vertex are equal because they are vertically opposite angles. The sum of internal angles of $n$ sides is $\left( n-2 \right){{180}^{\circ }}$. We have an alternate method to solve this question. We can first find the third angle, i.e angle PRQ of the triangle using the fact that the sum of all angles is ${180}^{\circ}$. Then, the angles PRQ and PRS form a linear pair, so their sum must be ${180}^{\circ}$. Using this fact, we can find the angle PRS.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




