
Consider the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{f({{k}^{2}}+2k+5)}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{f(k+11)}=1$ , where $f(x)$is a positive decreasing function, then value of $k$ for which major axis coincides with the $x$ axis is :
(a) $k\in (-7,-5)$
(b) $k\in (-5,-3)$
(c) $k\in (-3,2)$
(d) None of these
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: In an ellipse the lengths of the major and minor axis are different. The length of the major axis = $2a$ and the length of the minor axis = $2b$, if $a > b$and the length of the major axis = $2b$ and the length of the minor axis = $2a$, if $b > a$.
The general equation of an ellipse is $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$. Compare the equation given above with this general equation, and then apply some knowledge of increasing and decreasing functions after satisfying the condition given in the question.
Complete step-by-step solution -
For an ellipse having the general formula :
$\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$, the vertex of the ellipse is $(0,0)$.
If $a > b$: the major axis of the ellipse lies on the $x$ axis.
Here is a diagram of what such an ellipse would look like :
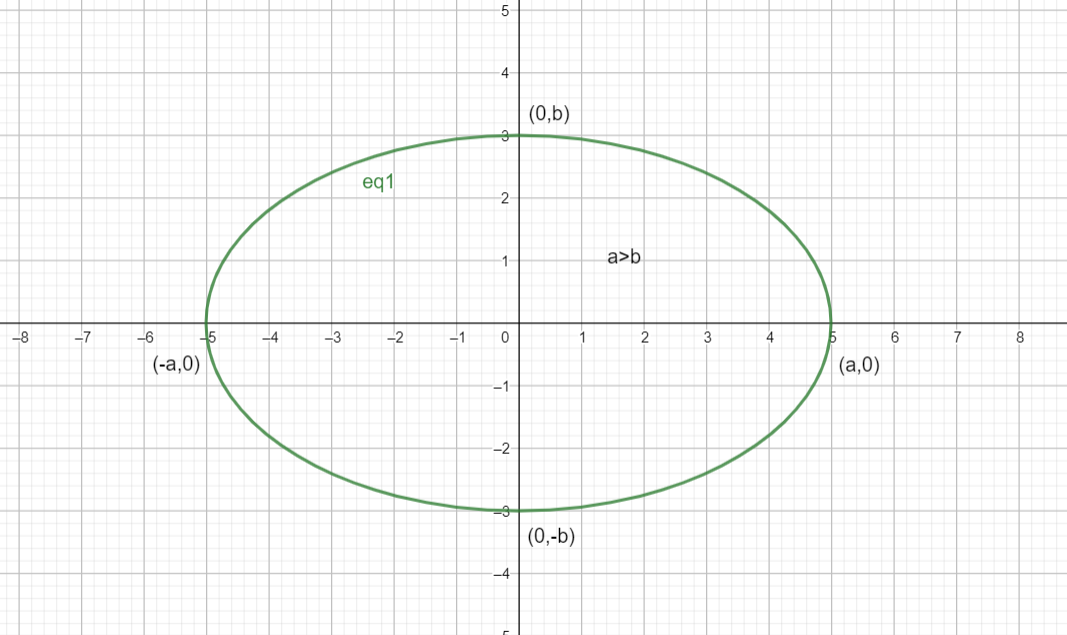
If $b > a$: the major axis of the ellipse lies on the $y$ axis.
Here is a diagram of what such an ellipse would look like :
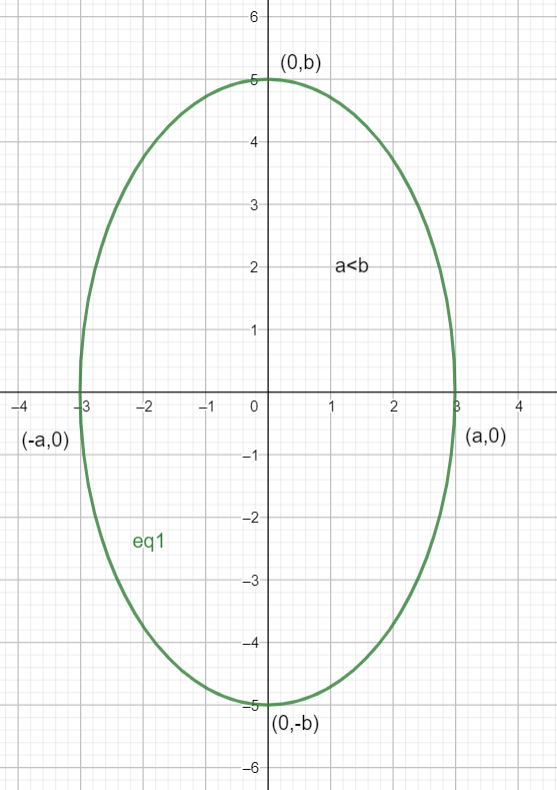
Comparing the equation given in the question, to the general formula of an ellipse, we get that :
${{a}^{2}}=f({{k}^{2}}+2k+5)$ and ${{b}^{2}}=f(k+11)$
It is told that the major axis of this ellipse should coincide with the $x$ axis.
This means that the $x$ axis has the major axis of the ellipse, and for that to be possible, we need that $b < a$.
Therefore, for this ellipse we need that :
$\begin{align}
& a > b \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{f({{k}^{2}}+2k+5)} > \sqrt{f(k+11)} \\
\end{align}$
Squaring both sides, we get :
$f({{k}^{2}}+2k+5) > f(k+11)$
Now, we’re given that $f(x)$ is a positive decreasing function. The fact that it is a decreasing function means that it gives a lower value of $f(x)$ at a higher value of $x$. Written mathematically, it means that :
If $\begin{align}
& f({{x}_{1}}) > f({{x}_{2}}) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}} < {{x}_{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Applying this result to the inequality we got from the ellipse, we can say that
$\begin{align}
f({{k}^{2}}+2k+5) > f(k+11) \\
\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}+2k+5 < k+11 \\
\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}+k-6 < 0 \\
\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}+3k-2k-6 < 0 \\
\Rightarrow k(k+3)-2(k+3) < 0 \\
\Rightarrow (k-2)(k+3) < 0 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the sign of a product of two numbers will be negative when the signs of the individual numbers to be multiplied are opposite. Therefore, the last step will be satisfied when
(k-2) is positive and (k+3) is negative $\Rightarrow k-2 > 0\text{ and }k+3 < 0\Rightarrow k > 2\text{ and }k < -3$ which is never possible....................................(i)
Or
(k-2) is negative and (k+3) is positive $\Rightarrow k-2 < 0\text{ and }k+3 > 0\Rightarrow k < 2\text{ and }k > -3$ which means that k should lie in the interval $k\in (-3,2)$
Thus, for the given condition, the interval which $k$ belongs to should be (-3,2) which matches option (c). Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Note: Some knowledge of increasing and decreasing functions is used in this question. So, you should revise the theory of that topic a bit, before attempting this question. In general, for an increasing function,
If $\begin{align}
& f({{x}_{1}}) > f({{x}_{2}}) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}} > {{x}_{2}} \\
\end{align}$
And for a decreasing function, if $\begin{align}
& f({{x}_{1}}) > f({{x}_{2}}) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}} < {{x}_{2}} \\
\end{align}$.
The general equation of an ellipse is $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$. Compare the equation given above with this general equation, and then apply some knowledge of increasing and decreasing functions after satisfying the condition given in the question.
Complete step-by-step solution -
For an ellipse having the general formula :
$\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$, the vertex of the ellipse is $(0,0)$.
If $a > b$: the major axis of the ellipse lies on the $x$ axis.
Here is a diagram of what such an ellipse would look like :

If $b > a$: the major axis of the ellipse lies on the $y$ axis.
Here is a diagram of what such an ellipse would look like :

Comparing the equation given in the question, to the general formula of an ellipse, we get that :
${{a}^{2}}=f({{k}^{2}}+2k+5)$ and ${{b}^{2}}=f(k+11)$
It is told that the major axis of this ellipse should coincide with the $x$ axis.
This means that the $x$ axis has the major axis of the ellipse, and for that to be possible, we need that $b < a$.
Therefore, for this ellipse we need that :
$\begin{align}
& a > b \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{f({{k}^{2}}+2k+5)} > \sqrt{f(k+11)} \\
\end{align}$
Squaring both sides, we get :
$f({{k}^{2}}+2k+5) > f(k+11)$
Now, we’re given that $f(x)$ is a positive decreasing function. The fact that it is a decreasing function means that it gives a lower value of $f(x)$ at a higher value of $x$. Written mathematically, it means that :
If $\begin{align}
& f({{x}_{1}}) > f({{x}_{2}}) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}} < {{x}_{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Applying this result to the inequality we got from the ellipse, we can say that
$\begin{align}
f({{k}^{2}}+2k+5) > f(k+11) \\
\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}+2k+5 < k+11 \\
\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}+k-6 < 0 \\
\Rightarrow {{k}^{2}}+3k-2k-6 < 0 \\
\Rightarrow k(k+3)-2(k+3) < 0 \\
\Rightarrow (k-2)(k+3) < 0 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the sign of a product of two numbers will be negative when the signs of the individual numbers to be multiplied are opposite. Therefore, the last step will be satisfied when
(k-2) is positive and (k+3) is negative $\Rightarrow k-2 > 0\text{ and }k+3 < 0\Rightarrow k > 2\text{ and }k < -3$ which is never possible....................................(i)
Or
(k-2) is negative and (k+3) is positive $\Rightarrow k-2 < 0\text{ and }k+3 > 0\Rightarrow k < 2\text{ and }k > -3$ which means that k should lie in the interval $k\in (-3,2)$
Thus, for the given condition, the interval which $k$ belongs to should be (-3,2) which matches option (c). Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Note: Some knowledge of increasing and decreasing functions is used in this question. So, you should revise the theory of that topic a bit, before attempting this question. In general, for an increasing function,
If $\begin{align}
& f({{x}_{1}}) > f({{x}_{2}}) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}} > {{x}_{2}} \\
\end{align}$
And for a decreasing function, if $\begin{align}
& f({{x}_{1}}) > f({{x}_{2}}) \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}} < {{x}_{2}} \\
\end{align}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




