
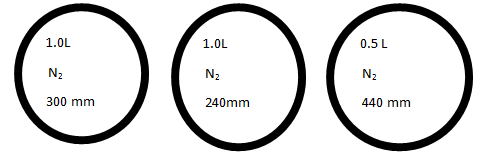
Consider the bulbs shown below.
If the pressure of the system when all the stop cocks are opened is \[{\text{x}}\](in atm) then find\[{\text{100x}}\]?
\[\left( {{\text{760mm = 1atm}}} \right)\]

Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: In atmosphere approximately \[78\% \] of nitrogen, \[21\% \] of oxygen and remaining \[1\% \] of other gases in the world. The symbol of nitrogen is \[{\text{N}}\]. The natural form of nitrogen gas is diatomic. The symbol of the diatomic nature of nitrogen is \[{{\text{N}}_2}\]. The chemical properties of the gas depend on the mixture of gases.
Formula used:
Boyle’s law,
\[{{P\propto }}\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{V}}}\] at constant temperature \[{\text{T}}\].
\[{\text{PV = constant}}\]
Here, the temperature of the gas is \[{\text{T}}\].
The pressure of the gas \[{\text{P}}\].
The volume of the gas \[{\text{V}}\].
Complete answer:
Boyle’s law states that pressure of the gas \[{\text{P}}\] is inversely proportional to volume of the gas \[{\text{V}}\] at constant temperature \[{\text{T}}\].
\[{{P\propto }}\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{V}}}\] at constant temperature \[{\text{T}}\].
\[{\text{PV = constant}}\]
The product of the pressure of the gas and volume of the gas \[{\text{V}}\] is always constant at constant temperature \[{\text{T}}\].
\[{{\text{P}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ = 300mm}}\]
\[{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}240{\text{mm}}\]
\[{{\text{P}}_3}{\text{ = }}44{\text{0mm}}\]
\[{{\text{V}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ = 1}}{\text{.0L}}\]
\[{{\text{V}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 1}}{\text{.0L}}\]
\[{{\text{V}}_3}{\text{ = 0}}{\text{.5L}}\]
The total volume of the container is equal to the sum of the all volume.
\[{{\text{V}}_4}{\text{ = }}{{\text{V}}_1}{\text{ + }}{{\text{V}}_2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{V}}_3}\]
Now we can substitute the known values we get,
\[{{\text{V}}_4}{\text{ = 1}}{\text{.0 + }}1.0{\text{ + }}0.{\text{5}}\]
On simplification we get,
\[{{\text{V}}_4}{\text{ = 2}}.{\text{5L}}\]
The total volume of the container is \[{{\text{V}}_4}\]and the total pressure of the container is\[{{\text{P}}_4}\].
\[{\text{PV = constant}}\]
\[{{\text{P}}_4}{{\text{V}}_4}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}_1}{{\text{V}}_1}{\text{ + }}{{\text{P}}_2}{{\text{V}}_2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{P}}_3}{{\text{V}}_3}\]
Now we can substitute the known values we get,
\[{{\text{P}}_4}{{\text{V}}_4}{\text{ = 300}} \times {\text{1}}{\text{.0 + 2}}40 \times 1.0{\text{ + }}44{\text{0}} \times 0.{\text{5}}\]
\[{\text{x}} \times 2.{\text{5 = 300 + 2}}40{\text{ + 220}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{x = }}\dfrac{{{\text{76}}0}}{{2.{\text{5}}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{x = }}304{\text{mm}}\]
\[{\text{1atm = 760mm}}\]
\[{\text{xatm = }}304{\text{mm}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{x = }}\dfrac{{304}}{{{\text{760}}}} = 0.4{\text{atm}}\]
According to the above calculation,
\[{\text{x = }}0.4{\text{atm}}\]
Then find \[{\text{100x}}\] is
\[{\text{x = }}0.4{\text{atm}}\]
\[{\text{100x = 100}} \times 0.4{\text{atm}}\]
\[{\text{100x = }}40{\text{atm}}\]
Note:
As we know that in chemistry, the periodic table plays a vital role. In the periodic table there are totally \[118\] elements. In the periodic table there are totally \[18\] columns and \[7\] rows. The columns are called groups. Hence, \[18\] groups in the periodic table. The rows are called periods. Hence, totally \[7\] period in the table. The atomic number of the element is nothing but the number of electrons or number of protons. The mass number of the atom is nothing but the sum of the number of protons and number of neutrons. The atomic number of nitrogen is \[7\]. The mass number of nitrogen is \[14\].
Formula used:
Boyle’s law,
\[{{P\propto }}\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{V}}}\] at constant temperature \[{\text{T}}\].
\[{\text{PV = constant}}\]
Here, the temperature of the gas is \[{\text{T}}\].
The pressure of the gas \[{\text{P}}\].
The volume of the gas \[{\text{V}}\].
Complete answer:
Boyle’s law states that pressure of the gas \[{\text{P}}\] is inversely proportional to volume of the gas \[{\text{V}}\] at constant temperature \[{\text{T}}\].
\[{{P\propto }}\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{{\text{V}}}\] at constant temperature \[{\text{T}}\].
\[{\text{PV = constant}}\]
The product of the pressure of the gas and volume of the gas \[{\text{V}}\] is always constant at constant temperature \[{\text{T}}\].
\[{{\text{P}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ = 300mm}}\]
\[{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}240{\text{mm}}\]
\[{{\text{P}}_3}{\text{ = }}44{\text{0mm}}\]
\[{{\text{V}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ = 1}}{\text{.0L}}\]
\[{{\text{V}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = 1}}{\text{.0L}}\]
\[{{\text{V}}_3}{\text{ = 0}}{\text{.5L}}\]
The total volume of the container is equal to the sum of the all volume.
\[{{\text{V}}_4}{\text{ = }}{{\text{V}}_1}{\text{ + }}{{\text{V}}_2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{V}}_3}\]
Now we can substitute the known values we get,
\[{{\text{V}}_4}{\text{ = 1}}{\text{.0 + }}1.0{\text{ + }}0.{\text{5}}\]
On simplification we get,
\[{{\text{V}}_4}{\text{ = 2}}.{\text{5L}}\]
The total volume of the container is \[{{\text{V}}_4}\]and the total pressure of the container is\[{{\text{P}}_4}\].
\[{\text{PV = constant}}\]
\[{{\text{P}}_4}{{\text{V}}_4}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}_1}{{\text{V}}_1}{\text{ + }}{{\text{P}}_2}{{\text{V}}_2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{P}}_3}{{\text{V}}_3}\]
Now we can substitute the known values we get,
\[{{\text{P}}_4}{{\text{V}}_4}{\text{ = 300}} \times {\text{1}}{\text{.0 + 2}}40 \times 1.0{\text{ + }}44{\text{0}} \times 0.{\text{5}}\]
\[{\text{x}} \times 2.{\text{5 = 300 + 2}}40{\text{ + 220}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{x = }}\dfrac{{{\text{76}}0}}{{2.{\text{5}}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{x = }}304{\text{mm}}\]
\[{\text{1atm = 760mm}}\]
\[{\text{xatm = }}304{\text{mm}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{x = }}\dfrac{{304}}{{{\text{760}}}} = 0.4{\text{atm}}\]
According to the above calculation,
\[{\text{x = }}0.4{\text{atm}}\]
Then find \[{\text{100x}}\] is
\[{\text{x = }}0.4{\text{atm}}\]
\[{\text{100x = 100}} \times 0.4{\text{atm}}\]
\[{\text{100x = }}40{\text{atm}}\]
Note:
As we know that in chemistry, the periodic table plays a vital role. In the periodic table there are totally \[118\] elements. In the periodic table there are totally \[18\] columns and \[7\] rows. The columns are called groups. Hence, \[18\] groups in the periodic table. The rows are called periods. Hence, totally \[7\] period in the table. The atomic number of the element is nothing but the number of electrons or number of protons. The mass number of the atom is nothing but the sum of the number of protons and number of neutrons. The atomic number of nitrogen is \[7\]. The mass number of nitrogen is \[14\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




