
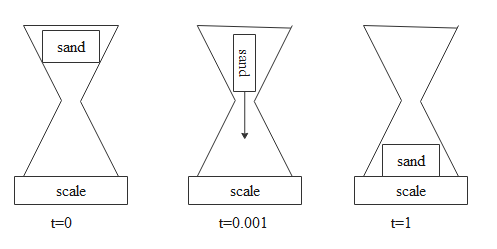
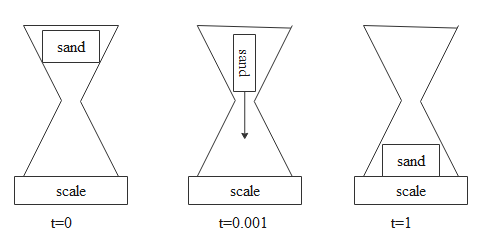
Consider an hourglass on a scale pictured below at the times t=0,0.001 and at 1hr. what happens to the scale’s measure of weight of the hour glass plus sand combination as the sand falls?
A. The weight is constant
B. The weight decreases and then increases
C. The weight increases
D. The weight increases and then decreases.

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: This question can be answered by using newton’s second law. According to Newton's second law for a particular system, rate of change of momentum will be equal to the external force acting on the system. Here external force will be due to the motion of this sand in the hour glass.
Formula used:
${F_{ext}} = \dfrac{{d{p_{system}}}}{{dt}}$
Complete step by step answer:
In the first case the sand is at rest initially. We have the formula
${F_{ext}} = \dfrac{{d{p_{system}}}}{{dt}}$ where ‘p’ is the momentum of the sand here
In the initial case it doesn’t have any momentum as sand is at rest momentum is zero so there will be no external force due to that sand. Hence initially it doesn’t experience any force so initial weight will be zero.
Then in the second case sand starts moving which means it gains some momentum and momentum keeps on increasing as it moves and then external force also keeps on increasing so the weight increases.
Then in the third case the sand falls on the floor as it's an hourglass that is within one hour and falls on the floor. So then sand will be at rest. If sand is at rest then there will be no momentum for the sand then weight will again become zero.
So the answer would be first weight will increase and then it will decrease.
Hence answer would be option D.
Note:
Since it is an hourglass it is clear that exactly after one hour the entire sand must be falling down within one hour of the time span. So the rate of change of momentum is what that determines the weight and if momentum is constant then there will be no force too.
Formula used:
${F_{ext}} = \dfrac{{d{p_{system}}}}{{dt}}$
Complete step by step answer:

In the first case the sand is at rest initially. We have the formula
${F_{ext}} = \dfrac{{d{p_{system}}}}{{dt}}$ where ‘p’ is the momentum of the sand here
In the initial case it doesn’t have any momentum as sand is at rest momentum is zero so there will be no external force due to that sand. Hence initially it doesn’t experience any force so initial weight will be zero.
Then in the second case sand starts moving which means it gains some momentum and momentum keeps on increasing as it moves and then external force also keeps on increasing so the weight increases.
Then in the third case the sand falls on the floor as it's an hourglass that is within one hour and falls on the floor. So then sand will be at rest. If sand is at rest then there will be no momentum for the sand then weight will again become zero.
So the answer would be first weight will increase and then it will decrease.
Hence answer would be option D.
Note:
Since it is an hourglass it is clear that exactly after one hour the entire sand must be falling down within one hour of the time span. So the rate of change of momentum is what that determines the weight and if momentum is constant then there will be no force too.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




