
Compound $ X $ can also be formed in:
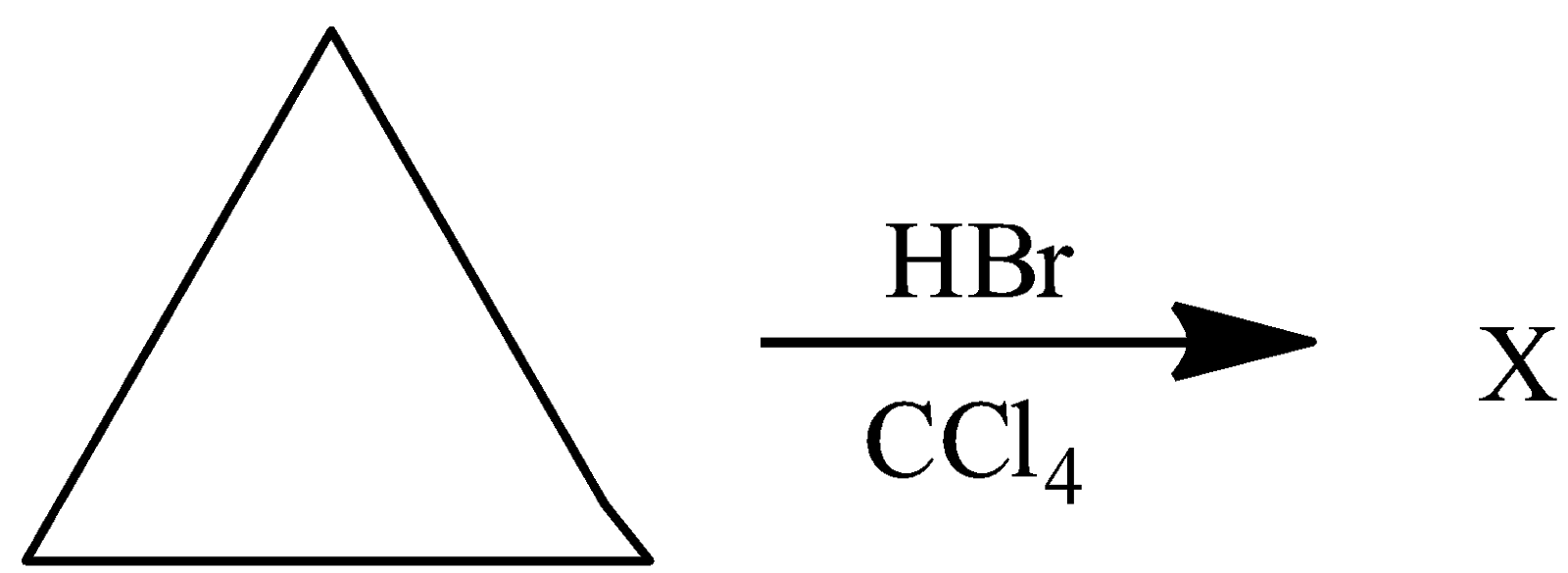
(A) $ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + HBr \to $
(B) $ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + HBr + {R_2}{O_2} \to $
(C) $ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + B{r_2} + CC{l_4} \to $
(D) $ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + NBS \to $

Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: This is a free radical mechanism and here addition of $ HBr $ takes place by anti-markovnikov rule. Anti-Markovnikov rule describes the regiochemistry where the substituent is bonded to a less substituted carbon, rather than the more substituted carbon. This process is quite unusual, as carbon cations which are commonly formed during alkene, or alkyne reactions tend to favor the more substituted carbon.
Complete answer:
Free-radical addition is an addition reaction in which free radicals are involved. The addition may occur between a radical and a non-radical, or between two radicals.
The basic steps with examples of the free radical addition are:
Initiation by a radical initiator: A radical is created from a non-radical precursor.
Chain propagation: A radical reacts with a non-radical to produce a new radical species
Chain termination: Two radicals react with each other to create a non-radical species
Free Radical Addition Of $ HBr $ to Alkenes Leads To Anti-Markovnikov Products. Alkenes normally react with $ HBr $ to give products of Markovnikov addition; the bromine ends up on the most substituted carbon of the alkene, and the hydrogen ends up on the least substituted carbon
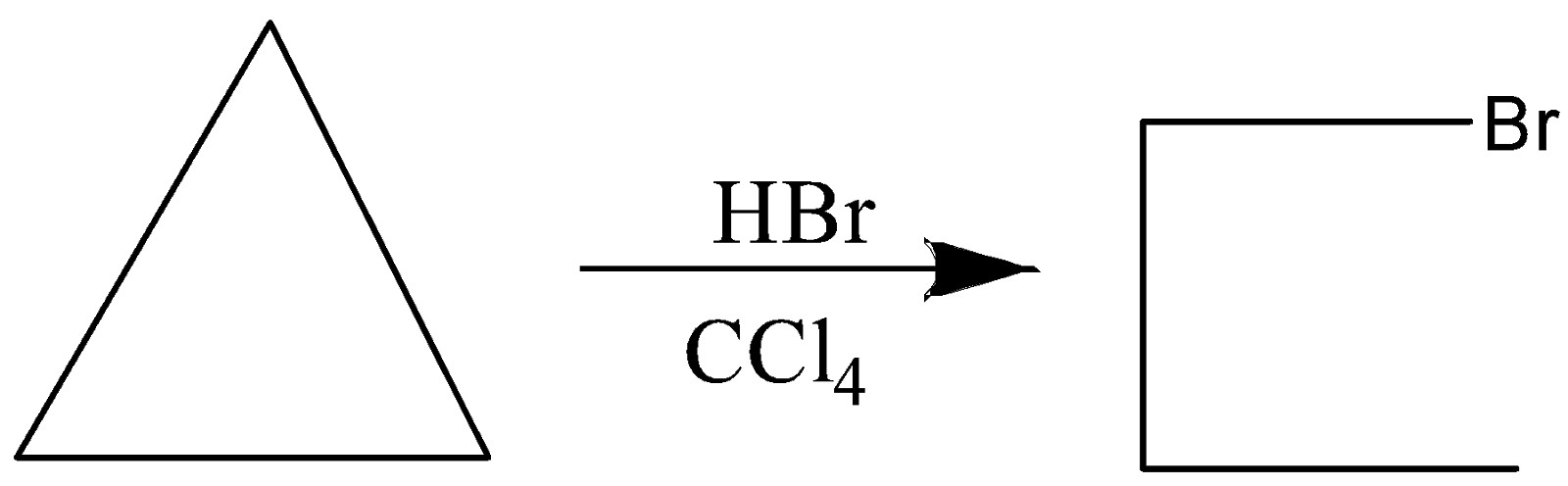
$ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + HBr + {R_2}{O_2} $
So, the correct answer is B) $ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + HBr + {R_2}{O_2} \to $
Note:
Free-radical reactions depend on a reagent having a weak bond, allowing it to homolyse to form radicals (often with heat or light). Reagents without such a weak bond would likely proceed via a different mechanism. An example of an additional reaction involving aryl radicals is the Meerwein arylation.
Complete answer:
Free-radical addition is an addition reaction in which free radicals are involved. The addition may occur between a radical and a non-radical, or between two radicals.
The basic steps with examples of the free radical addition are:
Initiation by a radical initiator: A radical is created from a non-radical precursor.
Chain propagation: A radical reacts with a non-radical to produce a new radical species
Chain termination: Two radicals react with each other to create a non-radical species
Free Radical Addition Of $ HBr $ to Alkenes Leads To Anti-Markovnikov Products. Alkenes normally react with $ HBr $ to give products of Markovnikov addition; the bromine ends up on the most substituted carbon of the alkene, and the hydrogen ends up on the least substituted carbon

$ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + HBr + {R_2}{O_2} $
So, the correct answer is B) $ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + HBr + {R_2}{O_2} \to $
Note:
Free-radical reactions depend on a reagent having a weak bond, allowing it to homolyse to form radicals (often with heat or light). Reagents without such a weak bond would likely proceed via a different mechanism. An example of an additional reaction involving aryl radicals is the Meerwein arylation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




