
Compound with geometry square pyramidal and $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization is:
A.$XeO{{F}_{2}}$
B.$XeO{{F}_{4}}$
C.$Xe{{O}_{4}}$
D.$Xe{{O}_{2}}{{F}_{2}}$
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: The shape of $A{{B}_{5}}$ molecule with zero lone pair is square bipyramidal and with 5 bond pairs and one lone pair is square pyramidal and with 4 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs is square planar. We need to know about VSEPR theory for more details.
Complete step by step answer:
-VSEPR theory is defined as the electron pairs surrounding the central atom must be arranged in space as far apart as possible to minimize the electrostatic repulsion experienced between them.
-A central atom can be defined as any atom that is bonded to two or more than two other atoms. The first and the most important rule of the VSEPR theory is that the bond angles about a central atom are those that minimize the total repulsion experienced between the Electron pairs in the atom’s valence shell.
Rules:
-A lone pair of electrons occupy more space than a bonding pair of electrons because lone pair of electron is under the influence of only one nucleus of the central atom, they are expected to occupy more space with a greater electron density than the bond pair electrons which are under the influence of two nuclei.The decreasing order of repulsion is mentioned below
-Lone pair-Lone pair repulsion>Lone pair-Bond pair repulsion>Bond pair- bond pair repulsion
Repulsion forces decrease sharply with increasing interior angle.They are stronger at 90 degree weak at 120 degree and very weak at 180 degree.
-The tendency of electron pairs bonding decreases with increasing value of electronegativity of an atom forming a molecule.
-Multiple bonds behave equivalent to a single electron pair for the purpose of VSEPR bond theory.
-The two electron pair of a double bond occupies more space than one electron pair of a single bond.
-The lone pair electrons repels bond pair electrons giving rise to some distortions in the molecular shape.
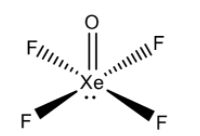
-Hybridization of an atom is identified by calculating the sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs.
-If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 2, then we have sp hybridization
-If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 3, then we have $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization
-If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 4, then we have $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization
-If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 5, then we have $s{{p}^{3}}d$ hybridization
-If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 6, then we have $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization.
-So the given molecule has 5 sigma bonds 1 lone pair that the sum is 6. So its hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$, and therefore the shape is square pyramidal.
Hence option B is correct.
Note: As a result of the distortions created, different types of shapes are arised. Bond angle in the compound depends upon the repulsion between lone pair- lone pair, bond pair -bond pair and bond pair -lone pair.
Complete step by step answer:
-VSEPR theory is defined as the electron pairs surrounding the central atom must be arranged in space as far apart as possible to minimize the electrostatic repulsion experienced between them.
-A central atom can be defined as any atom that is bonded to two or more than two other atoms. The first and the most important rule of the VSEPR theory is that the bond angles about a central atom are those that minimize the total repulsion experienced between the Electron pairs in the atom’s valence shell.
Rules:
-A lone pair of electrons occupy more space than a bonding pair of electrons because lone pair of electron is under the influence of only one nucleus of the central atom, they are expected to occupy more space with a greater electron density than the bond pair electrons which are under the influence of two nuclei.The decreasing order of repulsion is mentioned below
-Lone pair-Lone pair repulsion>Lone pair-Bond pair repulsion>Bond pair- bond pair repulsion
Repulsion forces decrease sharply with increasing interior angle.They are stronger at 90 degree weak at 120 degree and very weak at 180 degree.
-The tendency of electron pairs bonding decreases with increasing value of electronegativity of an atom forming a molecule.
-Multiple bonds behave equivalent to a single electron pair for the purpose of VSEPR bond theory.
-The two electron pair of a double bond occupies more space than one electron pair of a single bond.
-The lone pair electrons repels bond pair electrons giving rise to some distortions in the molecular shape.

-Hybridization of an atom is identified by calculating the sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs.
-If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 2, then we have sp hybridization
-If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 3, then we have $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization
-If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 4, then we have $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization
-If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 5, then we have $s{{p}^{3}}d$ hybridization
-If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 6, then we have $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization.
-So the given molecule has 5 sigma bonds 1 lone pair that the sum is 6. So its hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$, and therefore the shape is square pyramidal.
Hence option B is correct.
Note: As a result of the distortions created, different types of shapes are arised. Bond angle in the compound depends upon the repulsion between lone pair- lone pair, bond pair -bond pair and bond pair -lone pair.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




