
When compound (A) reacts with $N{a_2}Cr{O_4}$ solution, the colour of the compound formed is _______
A. Black
B. Red
C. Yellow
D. White
$\left( A \right) + NaCl \to \left( B \right)$ (white ppt.)
$\left( B \right) + KI \to (C)$ (green ppt.)
$\left( C \right) + \mathop {KI}\limits_{excess} \to (D) + (E)$ (colourless solution)
$\left( E \right) + N{H_3} + KOH \to \left( F \right)$
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: The colour of a compound is the physical property of that compound which is caused due to the excitation of electrons, i.e. the compound or chemical absorbs some amount of energy. The colour of the compound which we see is not the actual colour it absorbs. So it is the complementary colour of the actual colour absorbed by the compound. The absorption of energy was first observed in atomic or molecular spectroscopy.
Complete step by step answer:
In the first step $H{g_2}{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2}$ (compound A) reacts with sodium chloride to form $H{g_2}C{l_2}$ (compound B) which is a white ppt. compound. The balanced chemical reaction is written below:
$H{g_2}{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2} + 2NaCl \to H{g_2}C{l_2} \downarrow + 2NaN{O_3}$
In the second step $H{g_2}C{l_2}$ (compound B) reacts with KI to form $H{g_2}{I_2}$ (compound C) which is green ppt. compound. The balanced chemical reaction is written below:
$H{g_2}C{l_2} + 2KI \to H{g_2}{I_2} \downarrow + 2KCl$
In the third step $H{g_2}{I_2}$ (compound C) reacts with excess of KI to form ${K_2}\left[ {Hg{I_4}} \right]$ which is a soluble complex and is commonly known as Nessler reagent. The solution is colorless. The balanced chemical reaction is written below:
$H{g_2}{I_2} + \mathop {2KI}\limits_{excess} \to Hg + {K_2}\left[ {Hg{I_4}} \right]$
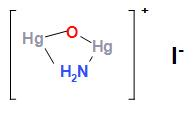
In the fourth step ${K_2}\left[ {Hg{I_4}} \right]$(compound E) also known as Nessler reagent reacts with ammonia and potassium hydroxide to form a brown colour complex. The balanced chemical reaction is written below:
${K_2}\left[ {Hg{I_4}} \right] + N{H_3} + KOH \to $
The compound A $H{g_2}{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2}$ reacts with $N{a_2}Cr{O_4}$ which forms $H{g_2}Cr{O_4}$ a red ppt. compound. The balanced chemical reaction is written below:
$H{g_2}{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2} + N{a_2}Cr{O_4} \to H{g_2}Cr{O_4}$
After discussing we can say that the colour of the compound is red.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Transition metals often form coloured compounds. The reason is that they have one or more unpaired electrons in their d- orbitals and when visible light falls on them the unpaired electrons absorb some amount of energy and get excited from higher energy level to lower energy due to which they show the complementary colour of the actual colour they absorbed.
Compounds which have completely filled or no electron in the d- orbital do not form coloured compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
In the first step $H{g_2}{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2}$ (compound A) reacts with sodium chloride to form $H{g_2}C{l_2}$ (compound B) which is a white ppt. compound. The balanced chemical reaction is written below:
$H{g_2}{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2} + 2NaCl \to H{g_2}C{l_2} \downarrow + 2NaN{O_3}$
In the second step $H{g_2}C{l_2}$ (compound B) reacts with KI to form $H{g_2}{I_2}$ (compound C) which is green ppt. compound. The balanced chemical reaction is written below:
$H{g_2}C{l_2} + 2KI \to H{g_2}{I_2} \downarrow + 2KCl$
In the third step $H{g_2}{I_2}$ (compound C) reacts with excess of KI to form ${K_2}\left[ {Hg{I_4}} \right]$ which is a soluble complex and is commonly known as Nessler reagent. The solution is colorless. The balanced chemical reaction is written below:
$H{g_2}{I_2} + \mathop {2KI}\limits_{excess} \to Hg + {K_2}\left[ {Hg{I_4}} \right]$
In the fourth step ${K_2}\left[ {Hg{I_4}} \right]$(compound E) also known as Nessler reagent reacts with ammonia and potassium hydroxide to form a brown colour complex. The balanced chemical reaction is written below:
${K_2}\left[ {Hg{I_4}} \right] + N{H_3} + KOH \to $

The compound A $H{g_2}{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2}$ reacts with $N{a_2}Cr{O_4}$ which forms $H{g_2}Cr{O_4}$ a red ppt. compound. The balanced chemical reaction is written below:
$H{g_2}{\left( {N{O_3}} \right)_2} + N{a_2}Cr{O_4} \to H{g_2}Cr{O_4}$
After discussing we can say that the colour of the compound is red.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Transition metals often form coloured compounds. The reason is that they have one or more unpaired electrons in their d- orbitals and when visible light falls on them the unpaired electrons absorb some amount of energy and get excited from higher energy level to lower energy due to which they show the complementary colour of the actual colour they absorbed.
Compounds which have completely filled or no electron in the d- orbital do not form coloured compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




