
Complete the reaction:
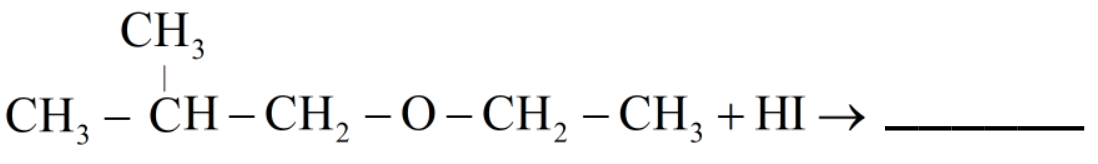
Which of the following compounds will be formed :
A.
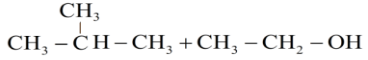
B.
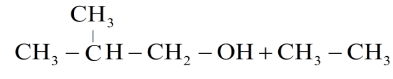
C.
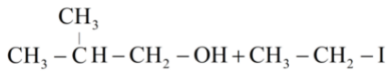
D.
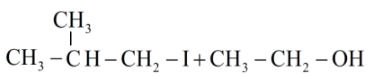
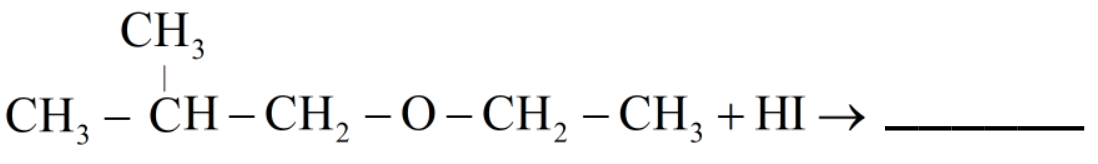
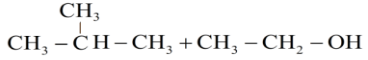
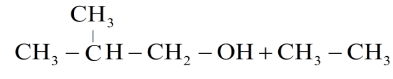
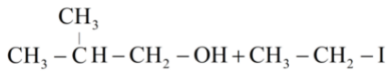
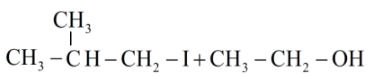
Answer
510k+ views
Hint: When ethers are heated in presence of HI it dissociates into alcohol and alkyl iodide. Ether is a compound where two alkyl or aryl or one alkyl and one aryl group is bonded with oxygen. It can be formed by the dehydration of alcohols by emitting water molecules using dehydrating agents like concentrates.
Complete answer:
In the presence of acid, ether can be dissociated.
The general reaction is as follows:
\[ROR'\xrightarrow{{HI}}ROH + R'I\xrightarrow{{H{I_{(excess)}}}}RI + R'I\]
Mechanism :
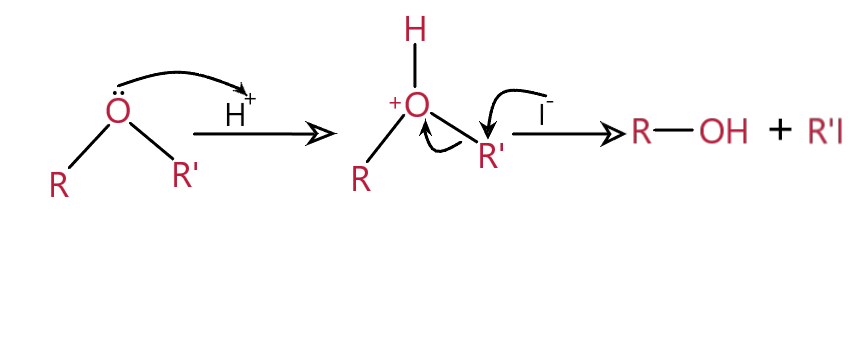
This mechanism follows \[S{N^2}\] mechanism.
The formation of alcohol and alkyl iodide depends upon the group attached to the oxygen.
The order of alkyl groups favouring the \[S{N^2}\] mechanism at the iodide nucleophile to form the corresponding alkyl iodide (i.e., alkyl group in the place of R’) is as follows:
Tertiary alkyl group < Secondary alkyl group < Primary alkyl group.
So, the primary alkyl group is the first one to form alkyl iodide.
The first step is the protonation of oxygen and then the intermediate is formed. Then \[{I^ - }\] attack takes place (depending on the type of alkyl group) where the R’ bond breaks and forms corresponding alcohol and alkyl iodide.
So, let us see the reaction of given organic compound 2-ethoxy-3-methylpropane.

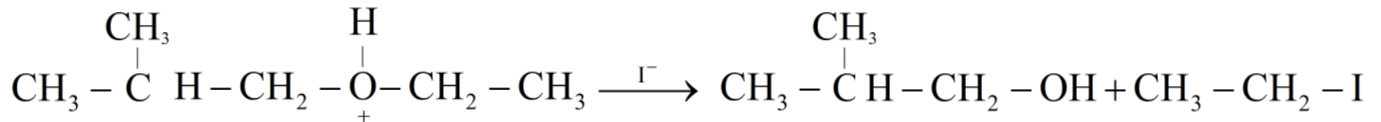
Hence the products obtained are 2-methylpropanol and ethyl iodide.
So, the right answer is option (c).
Note:
Ether undergoes combustion reaction, reacts with oxygen, and forms carbon dioxide and water. It is highly flammable and reacts with halogens like chlorine or bromine to form halogen-substituted ether that undergoes substitution reaction in the absence of sunlight.
Complete answer:
In the presence of acid, ether can be dissociated.
The general reaction is as follows:
\[ROR'\xrightarrow{{HI}}ROH + R'I\xrightarrow{{H{I_{(excess)}}}}RI + R'I\]
Mechanism :

This mechanism follows \[S{N^2}\] mechanism.
The formation of alcohol and alkyl iodide depends upon the group attached to the oxygen.
The order of alkyl groups favouring the \[S{N^2}\] mechanism at the iodide nucleophile to form the corresponding alkyl iodide (i.e., alkyl group in the place of R’) is as follows:
Tertiary alkyl group < Secondary alkyl group < Primary alkyl group.
So, the primary alkyl group is the first one to form alkyl iodide.
The first step is the protonation of oxygen and then the intermediate is formed. Then \[{I^ - }\] attack takes place (depending on the type of alkyl group) where the R’ bond breaks and forms corresponding alcohol and alkyl iodide.
So, let us see the reaction of given organic compound 2-ethoxy-3-methylpropane.

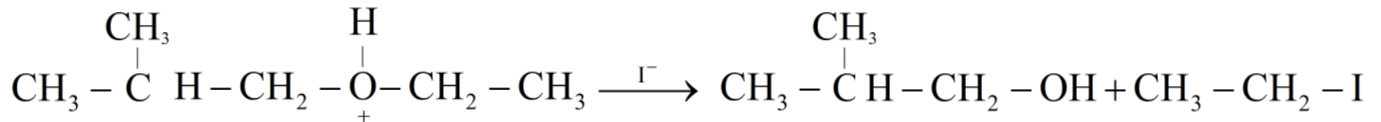
Hence the products obtained are 2-methylpropanol and ethyl iodide.
So, the right answer is option (c).
Note:
Ether undergoes combustion reaction, reacts with oxygen, and forms carbon dioxide and water. It is highly flammable and reacts with halogens like chlorine or bromine to form halogen-substituted ether that undergoes substitution reaction in the absence of sunlight.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




