
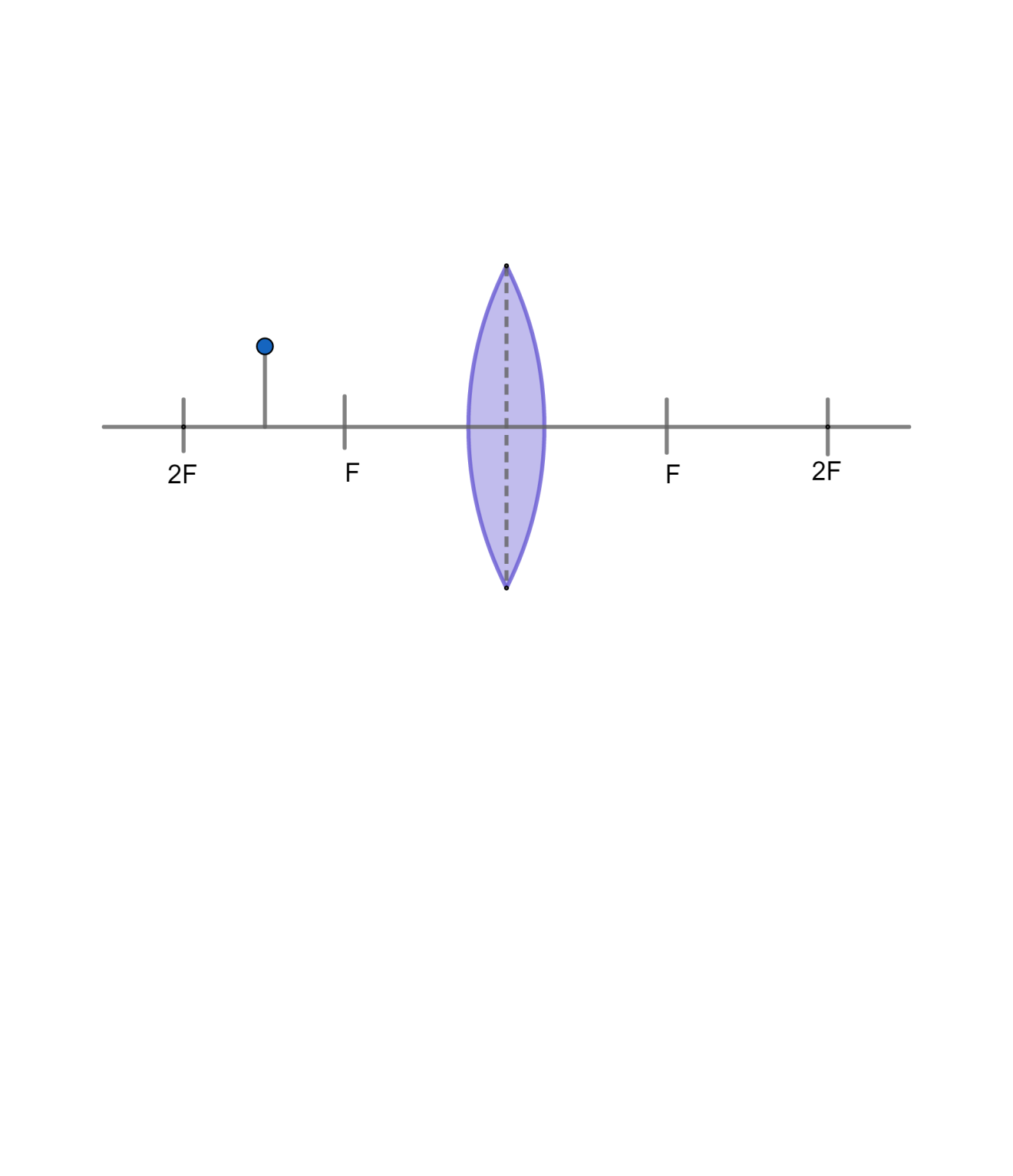
Complete the following ray diagram

Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Use the thin lens formula to find the image distance. Use the rules of refraction through the lens to construct the ray diagram.
Formula used: $\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Here
$v$ is image distance
$u$ is object distance
$f$ is focal length of lens
Complete step by step solution:
As shown in the figure
$\begin{align}
& f=+F \\
& u=-\dfrac{3}{2}F \\
\end{align}$
Substituting in the given formula
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{u}+\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=-\dfrac{2}{3}\dfrac{1}{F}+\dfrac{1}{F} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{3}\dfrac{1}{F} \\
& v=3F \\
\end{align}$
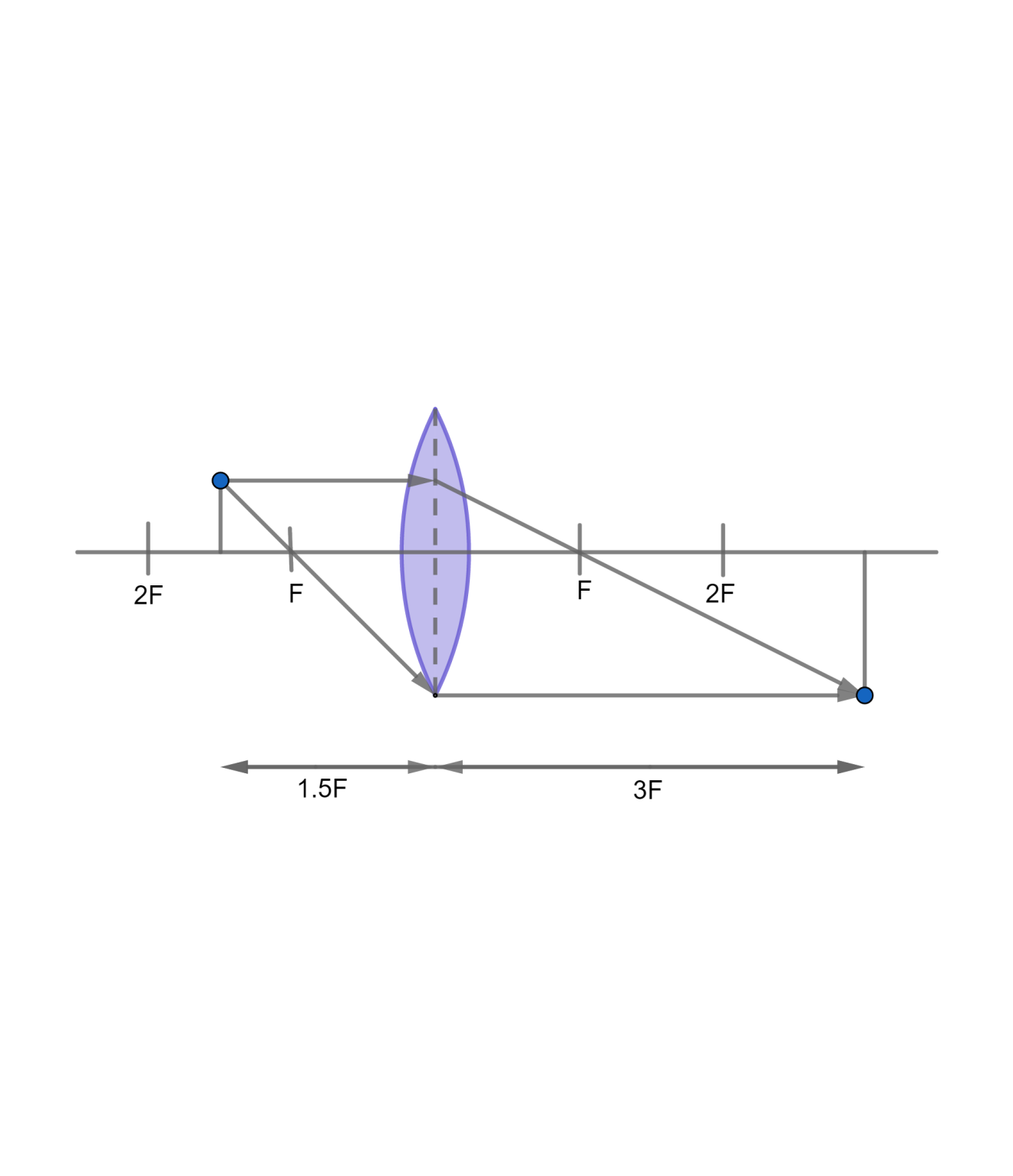
Therefore, the image will be formed on the opposite side of the lens as that of the object.
Magnification is
$m=\dfrac{v}{u}=-2$
Therefore, the image will be inverted and twice the size of the object.
The ray diagram can be constructed using the following rules
1. A ray passing parallel to the principal axis will pass through the focus after refraction.
2. A ray passing through the focus will pass parallel to the principal axis after refraction.
A real, inverted and magnified image will be formed as shown below
Note: A convex lens produces a real image when the object is farther than the focus and a virtual image when the object is nearer than the focus. A concave lens always produces a virtual image.
Formula used: $\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Here
$v$ is image distance
$u$ is object distance
$f$ is focal length of lens
Complete step by step solution:
As shown in the figure
$\begin{align}
& f=+F \\
& u=-\dfrac{3}{2}F \\
\end{align}$
Substituting in the given formula
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{u}+\dfrac{1}{f} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=-\dfrac{2}{3}\dfrac{1}{F}+\dfrac{1}{F} \\
& \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{3}\dfrac{1}{F} \\
& v=3F \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the image will be formed on the opposite side of the lens as that of the object.
Magnification is
$m=\dfrac{v}{u}=-2$
Therefore, the image will be inverted and twice the size of the object.
The ray diagram can be constructed using the following rules
1. A ray passing parallel to the principal axis will pass through the focus after refraction.
2. A ray passing through the focus will pass parallel to the principal axis after refraction.
A real, inverted and magnified image will be formed as shown below

Note: A convex lens produces a real image when the object is farther than the focus and a virtual image when the object is nearer than the focus. A concave lens always produces a virtual image.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




