
Complete the following equation.
A. $2NaOH + C{l_2} \to \\
coldanddil \\ $
B. $C{l_2} + 3{F_2}\xrightarrow{{573K}} \\
{\text{ (excess)}} \\$
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: \[NaOH\]is known as sodium hydroxide. It is also called caustic soda. It is an ionic compound which is made of \[N{a^ + }\] ion and \[O{H^ - }\] ion. \[C{l_2}\] is chlorine gas where two chlorine atoms are bonded to each other. \[{F_2}\] is fluorine gas where two fluorine atoms are bonded to each other.
Complete step by step answer: \[NaOH\] in cold and dilute solution is present in dissociated form i.e. \[N{a^ + }\] and \[O{H^ - }\] and some ion exchange reaction will take place. Specifically this is an example of disproportionation reaction.
A disproportionation reaction is a type of redox reaction in which a molecule undergoes oxidation as well as reduction to generate products. The oxidation and reduction products can be found by determining the change in oxidation state of the products compared with the reactant.
In reaction a), the reaction of \[NaOH\] and \[C{l_2}\] will give:
$2NaOH + C{l_2} \to NaCl + NaOCl + {H_2}O$
The products formed from the reaction of \[NaOH\] and \[C{l_2}\] are sodium chloride salt \[NaCl\] and sodium chlorate or sodium hypochlorite \[NaOCl\] and water. In order to check whether any reduction or oxidation took place let us analyse the reaction in terms of change of oxidation state.
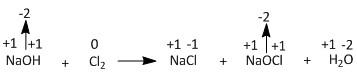
From the above picture it is clear that out of all the elements i.e. \[Na\], \[O\], \[H\] and \[Cl\], only \[Cl\] is changing the oxidation state from \[0\] to \[ - 1\] and \[ + 1\]. The gain of electrons is termed as reduction and the loss of electrons is termed as oxidation. Therefore \[Cl\left( 0 \right)\] to \[Cl\left( { - 1} \right)\] is the reduction of chlorine and \[Cl\left( 0 \right)\] to \[Cl\left( { + 1} \right)\] is the oxidation of chlorine. Hence this is a disproportionation reaction.
In reaction b), the reaction of \[C{l_2}\] and excess \[{F_2}\] will give:
$C{l_2} + 5{F_2}\xrightarrow{{573K}}2Cl{F_5}$
The product formed from the reaction of chlorine and fluorine gas is chlorine pentafluoride. The reaction usually takes place at \[300^\circ C\]. The reaction takes place in a stepwise manner. Actually \[Cl{F_3}\] is formed when \[C{l_2}\] and \[{F_2}\] combine. Then \[Cl{F_3}\] combine with \[{F_2}\] to give \[Cl{F_5}\].
$C{l_2} + 3{F_2} \to 2Cl{F_3}$
$2Cl{F_3} + 2{F_2} \to 2Cl{F_5}$
In \[Cl{F_5}\], the oxidation state of \[Cl\] atom is \[ + 5\] which is very much possible as \[Cl\] has vacant \[3d\] orbital. So the electrons from \[F\] atom can easily be filled in the vacant \[3d\] orbitals. Thus the valency of \[Cl\] atoms is extended and the bonds are formed with five fluorine atoms.
Note: The change in oxidation state has to be monitored to evaluate the type of reaction. \[Cl\] atom with its vacant \[3d\] orbitals has the ability to extend its valency and form bonds with multiple atoms.
Complete step by step answer: \[NaOH\] in cold and dilute solution is present in dissociated form i.e. \[N{a^ + }\] and \[O{H^ - }\] and some ion exchange reaction will take place. Specifically this is an example of disproportionation reaction.
A disproportionation reaction is a type of redox reaction in which a molecule undergoes oxidation as well as reduction to generate products. The oxidation and reduction products can be found by determining the change in oxidation state of the products compared with the reactant.
In reaction a), the reaction of \[NaOH\] and \[C{l_2}\] will give:
$2NaOH + C{l_2} \to NaCl + NaOCl + {H_2}O$
The products formed from the reaction of \[NaOH\] and \[C{l_2}\] are sodium chloride salt \[NaCl\] and sodium chlorate or sodium hypochlorite \[NaOCl\] and water. In order to check whether any reduction or oxidation took place let us analyse the reaction in terms of change of oxidation state.

From the above picture it is clear that out of all the elements i.e. \[Na\], \[O\], \[H\] and \[Cl\], only \[Cl\] is changing the oxidation state from \[0\] to \[ - 1\] and \[ + 1\]. The gain of electrons is termed as reduction and the loss of electrons is termed as oxidation. Therefore \[Cl\left( 0 \right)\] to \[Cl\left( { - 1} \right)\] is the reduction of chlorine and \[Cl\left( 0 \right)\] to \[Cl\left( { + 1} \right)\] is the oxidation of chlorine. Hence this is a disproportionation reaction.
In reaction b), the reaction of \[C{l_2}\] and excess \[{F_2}\] will give:
$C{l_2} + 5{F_2}\xrightarrow{{573K}}2Cl{F_5}$
The product formed from the reaction of chlorine and fluorine gas is chlorine pentafluoride. The reaction usually takes place at \[300^\circ C\]. The reaction takes place in a stepwise manner. Actually \[Cl{F_3}\] is formed when \[C{l_2}\] and \[{F_2}\] combine. Then \[Cl{F_3}\] combine with \[{F_2}\] to give \[Cl{F_5}\].
$C{l_2} + 3{F_2} \to 2Cl{F_3}$
$2Cl{F_3} + 2{F_2} \to 2Cl{F_5}$
In \[Cl{F_5}\], the oxidation state of \[Cl\] atom is \[ + 5\] which is very much possible as \[Cl\] has vacant \[3d\] orbital. So the electrons from \[F\] atom can easily be filled in the vacant \[3d\] orbitals. Thus the valency of \[Cl\] atoms is extended and the bonds are formed with five fluorine atoms.
Note: The change in oxidation state has to be monitored to evaluate the type of reaction. \[Cl\] atom with its vacant \[3d\] orbitals has the ability to extend its valency and form bonds with multiple atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




