
Complete the equation:
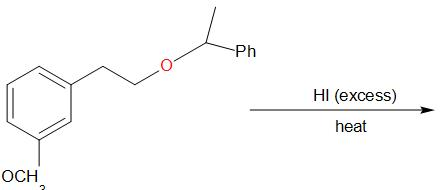
A.
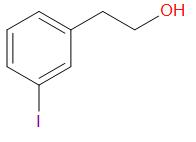
B.
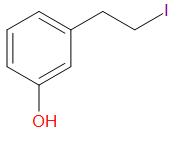
C.
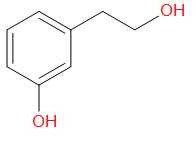
D.
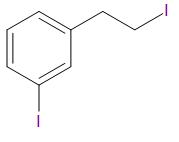





Answer
573k+ views
Hint: The given reaction is that for the cleavage of ethers by halogen acids. The given ether is an unsymmetrical ether. In such a case, when two different alkyl groups are present on the oxygen, then the formation of the alkyl iodide and alcohol depends on the nature of the alkyl groups attached.
Complete step by step solution:
For ease of solving and explanation, we number the two ether groups as follows.
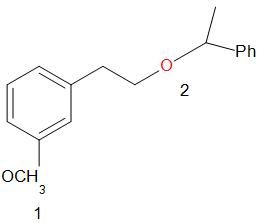
First, the oxygen atom in the ether is protonated by the acid. If both the alkyl groups attached to the oxygen are primary or secondary, the reaction proceeds by ${S_N}2$ path. The iodide ion attacks the smaller of the two alkyl groups forming an alkyl iodide.
As the iodide ion attacks by the ${S_N}2$ mechanism, we must consider steric factors while determining the product of the reaction. So the smaller of the two groups forms a bond with the iodide ion and the larger group forms an alcohol.
In the given compound, at the oxygen 1, the two groups are a phenyl group and a methyl group. The iodide ion will leave with the smaller of the two groups that is methyl group and an alcohol is obtained in the main product.
At the oxygen 2, of the two groups attached, one is primary while the other is a secondary group. So, the iodide ion preferably forms a bond with the primary alkyl group and a secondary alcohol leaves the molecule giving the product as,
Thus, the correct answer is B.
Note:
Ethers under vigorous conditions like concentrated acids and high temperatures undergo cleavage. The acids used are usually hydrogen bromide or hydrogen iodide. Since the reaction proceeds by the ${S_N}2$ mechanism, the nucleophile, in this case halide ion, must be a strong nucleophile. Thus, we use only hydrogen iodide in the cleavage of aromatic ethers.
Complete step by step solution:
For ease of solving and explanation, we number the two ether groups as follows.

First, the oxygen atom in the ether is protonated by the acid. If both the alkyl groups attached to the oxygen are primary or secondary, the reaction proceeds by ${S_N}2$ path. The iodide ion attacks the smaller of the two alkyl groups forming an alkyl iodide.
As the iodide ion attacks by the ${S_N}2$ mechanism, we must consider steric factors while determining the product of the reaction. So the smaller of the two groups forms a bond with the iodide ion and the larger group forms an alcohol.
In the given compound, at the oxygen 1, the two groups are a phenyl group and a methyl group. The iodide ion will leave with the smaller of the two groups that is methyl group and an alcohol is obtained in the main product.
At the oxygen 2, of the two groups attached, one is primary while the other is a secondary group. So, the iodide ion preferably forms a bond with the primary alkyl group and a secondary alcohol leaves the molecule giving the product as,
Thus, the correct answer is B.
Note:
Ethers under vigorous conditions like concentrated acids and high temperatures undergo cleavage. The acids used are usually hydrogen bromide or hydrogen iodide. Since the reaction proceeds by the ${S_N}2$ mechanism, the nucleophile, in this case halide ion, must be a strong nucleophile. Thus, we use only hydrogen iodide in the cleavage of aromatic ethers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




