
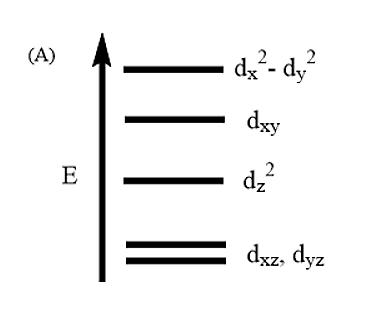
Complete removal of both the axial ligands (along the Z-axis) from an octahedral complex leads to which of the following splitting patterns? (Relative orbital energies not on scale).




Answer
542.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we should be aware of axial orbitals and non-axial orbital as well as their energy. In order to know the energy of the orbital we should be thorough with the crystal field splitting of d-orbitals in octahedral complexes.
Complete answer:
There are five d-orbitals:
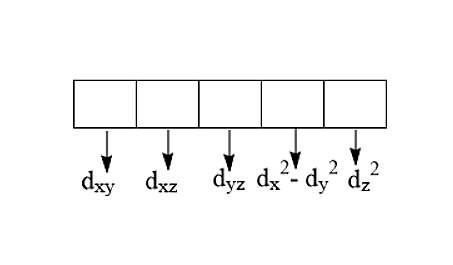
The subscripts denote xy, xz, yz, \[{x^2} - {y^2}\] and \[{z^2}\] are the orientation lobes in the XYZ plane.
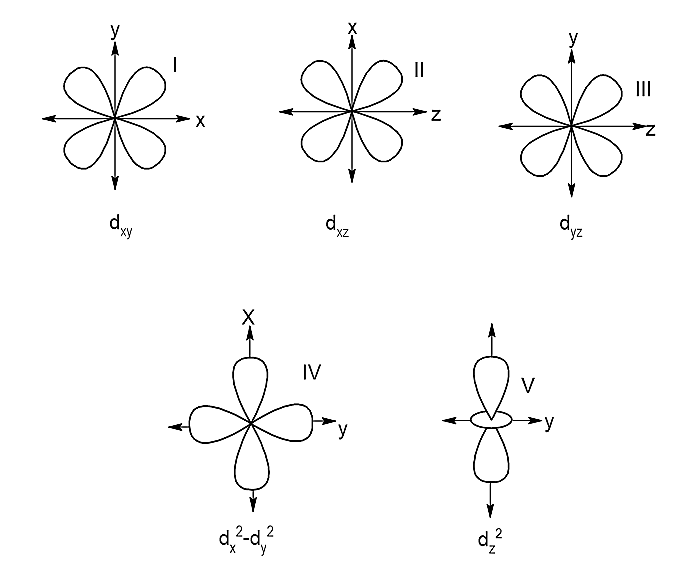
On basis of the orientation of the lobes they are grouped into two sets:
- \[{e_g}\] set of orbitals: e refers to doubly regenerate sets. The set that consists of the orbitals which have their lobes along the axes, hence they are called axial orbitals. The axial orbitals are \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\]and \[{d_{{z^2}}}\].
- \[{t_{2g}}\] set of orbitals: t refers to a triply degenerate set. The set that consists of the orbitals whose lobes lie in between the axes, hence they are called non-axial orbitals. The non-axial orbitals are \[{d_{xy}},{d_{xz}},{d_{yz}}\].
Now, let’s see about the octahedral complex.
An octahedral complex consists of a central metal cation \[[{M^{n + }}]\] that is placed in the centre of the octahedron and it is surrounded by six ligands which are placed at the corners.
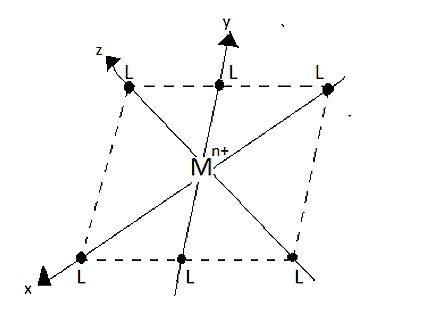
The ligands on each of the three axes are allowed to approach towards the central metal cation \[[{M^{n + }}]\], from the ends of the axes. Since, the lobes of the axial orbitals in the \[{e_g}\] set lie directly in the path of the approaching ligands. Hence, the electrons in these orbitals experience greater force of repulsion than those in three \[{t_{2g}}\] orbitals (i.e., non-axial orbitals). Thus, the energy of axial orbitals is increased and the energy of non-axial orbital decreases.
If we remove the ligands lying on Z-axes, the octahedral field will be changed to a square planar field.
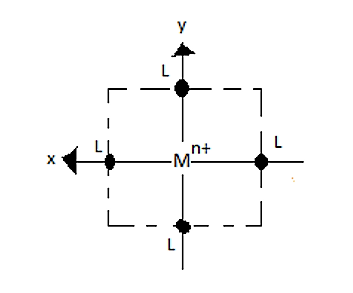
So, the energy of the orbitals also changes.
The change in energy can be understood through the crystal field splitting diagram:
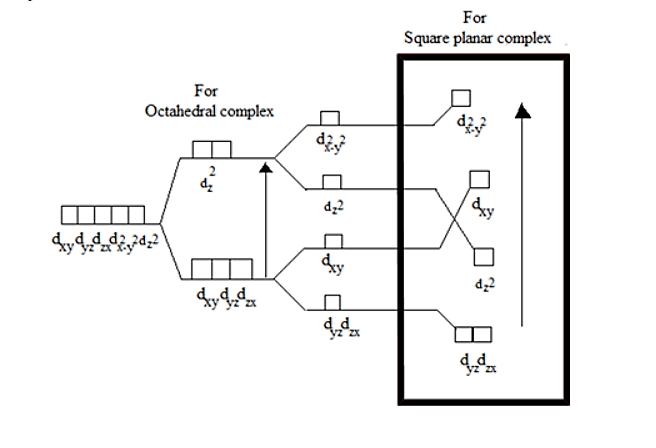
\[{\Delta _o}\] is the energy gap.
Thus, from the above diagram it is evident that Option A is the correct answer.
Note:
Explanation of the crystal field splitting in square planar: The ligands in X-axis and y-axis are approaching towards the ligand so there will be more repulsion between them. Hence, \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\]and \[{d_{xy}}\] possess higher energy. \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] has higher energy than \[{d_{xy}}\] because \[{e_g}\] has higher energy than \[{t_{2g}}\]. The electrons in the Z-axis are moved away from the central metal atom, so, \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] energy decreases. Due to the same reason the energy of \[{d_{xz}}\]and \[{d_{yz}}\] also decrease. Understand the crystal field splitting well in order to answer this question within no time.
Complete answer:
There are five d-orbitals:

The subscripts denote xy, xz, yz, \[{x^2} - {y^2}\] and \[{z^2}\] are the orientation lobes in the XYZ plane.

On basis of the orientation of the lobes they are grouped into two sets:
- \[{e_g}\] set of orbitals: e refers to doubly regenerate sets. The set that consists of the orbitals which have their lobes along the axes, hence they are called axial orbitals. The axial orbitals are \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\]and \[{d_{{z^2}}}\].
- \[{t_{2g}}\] set of orbitals: t refers to a triply degenerate set. The set that consists of the orbitals whose lobes lie in between the axes, hence they are called non-axial orbitals. The non-axial orbitals are \[{d_{xy}},{d_{xz}},{d_{yz}}\].
Now, let’s see about the octahedral complex.
An octahedral complex consists of a central metal cation \[[{M^{n + }}]\] that is placed in the centre of the octahedron and it is surrounded by six ligands which are placed at the corners.

The ligands on each of the three axes are allowed to approach towards the central metal cation \[[{M^{n + }}]\], from the ends of the axes. Since, the lobes of the axial orbitals in the \[{e_g}\] set lie directly in the path of the approaching ligands. Hence, the electrons in these orbitals experience greater force of repulsion than those in three \[{t_{2g}}\] orbitals (i.e., non-axial orbitals). Thus, the energy of axial orbitals is increased and the energy of non-axial orbital decreases.
If we remove the ligands lying on Z-axes, the octahedral field will be changed to a square planar field.

So, the energy of the orbitals also changes.
The change in energy can be understood through the crystal field splitting diagram:

\[{\Delta _o}\] is the energy gap.
Thus, from the above diagram it is evident that Option A is the correct answer.
Note:
Explanation of the crystal field splitting in square planar: The ligands in X-axis and y-axis are approaching towards the ligand so there will be more repulsion between them. Hence, \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\]and \[{d_{xy}}\] possess higher energy. \[{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}\] has higher energy than \[{d_{xy}}\] because \[{e_g}\] has higher energy than \[{t_{2g}}\]. The electrons in the Z-axis are moved away from the central metal atom, so, \[{d_{{z^2}}}\] energy decreases. Due to the same reason the energy of \[{d_{xz}}\]and \[{d_{yz}}\] also decrease. Understand the crystal field splitting well in order to answer this question within no time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




