
Compare the structures of Diamond and Graphite.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: The difference in structures of Diamond and graphite also changes physical as well as chemical properties. Both diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon. Allotropes are compounds which are chemically the same but vary in their physical properties.
Complete step by step answer:
Before differentiating the properties and structures of diamond and graphite, let us look at carbon. It belongs to the$\text{II}$ period and $\text{XIV}$ group of the periodic table. Therefore, it is a metalloid which means its electronegativity and electropositivity are well balanced. Being the first member of its group, carbon is the smallest size and does not have d-orbitals. All of these properties make it an element which has the highest self-linking property. It also forms strong bonds with metals, nonmetals and metalloids. Diamond and graphite are large molecules of carbon which do not have a specific formula. Their size completely depends on the extent of their physical structures.
Let us look at the differences between diamond and graphite via a table:
Note: There are many significant physical differences in diamond and graphite, but the chemical properties are similar because both are composed of the same element (carbon) than their macrostructure and other conditions that gave birth to their physical differences.
Complete step by step answer:
Before differentiating the properties and structures of diamond and graphite, let us look at carbon. It belongs to the$\text{II}$ period and $\text{XIV}$ group of the periodic table. Therefore, it is a metalloid which means its electronegativity and electropositivity are well balanced. Being the first member of its group, carbon is the smallest size and does not have d-orbitals. All of these properties make it an element which has the highest self-linking property. It also forms strong bonds with metals, nonmetals and metalloids. Diamond and graphite are large molecules of carbon which do not have a specific formula. Their size completely depends on the extent of their physical structures.
Let us look at the differences between diamond and graphite via a table:
| DIAMOND | GRAPHITE |
1. The hybridisation of carbon here is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$. Therefore it has a tetrahedral structure.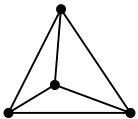
| 1. The hybridisation of carbon is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{2}}$. The structure is trigonal planar.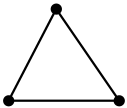
|
Note: There are many significant physical differences in diamond and graphite, but the chemical properties are similar because both are composed of the same element (carbon) than their macrostructure and other conditions that gave birth to their physical differences.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




