
What is the common element in hemoglobin and myoglobin?
(a) Fe
(b) Cu
(c) Mn
(d) Mg
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: It is a globular heme protein present in red blood cells of vertebrates which binds oxygen. The common element present in it belongs to the 8 groups and 4 periods of the periodic table and is a cofactor of ribonucleotide reductase enzyme.
Complete step by step answer:
Fe is the common element in hemoglobin and myoglobin. Hemoglobin is an oxygen carrier protein in our body that serves to transport oxygen in the blood whereas myoglobin serves to store oxygen in muscles.
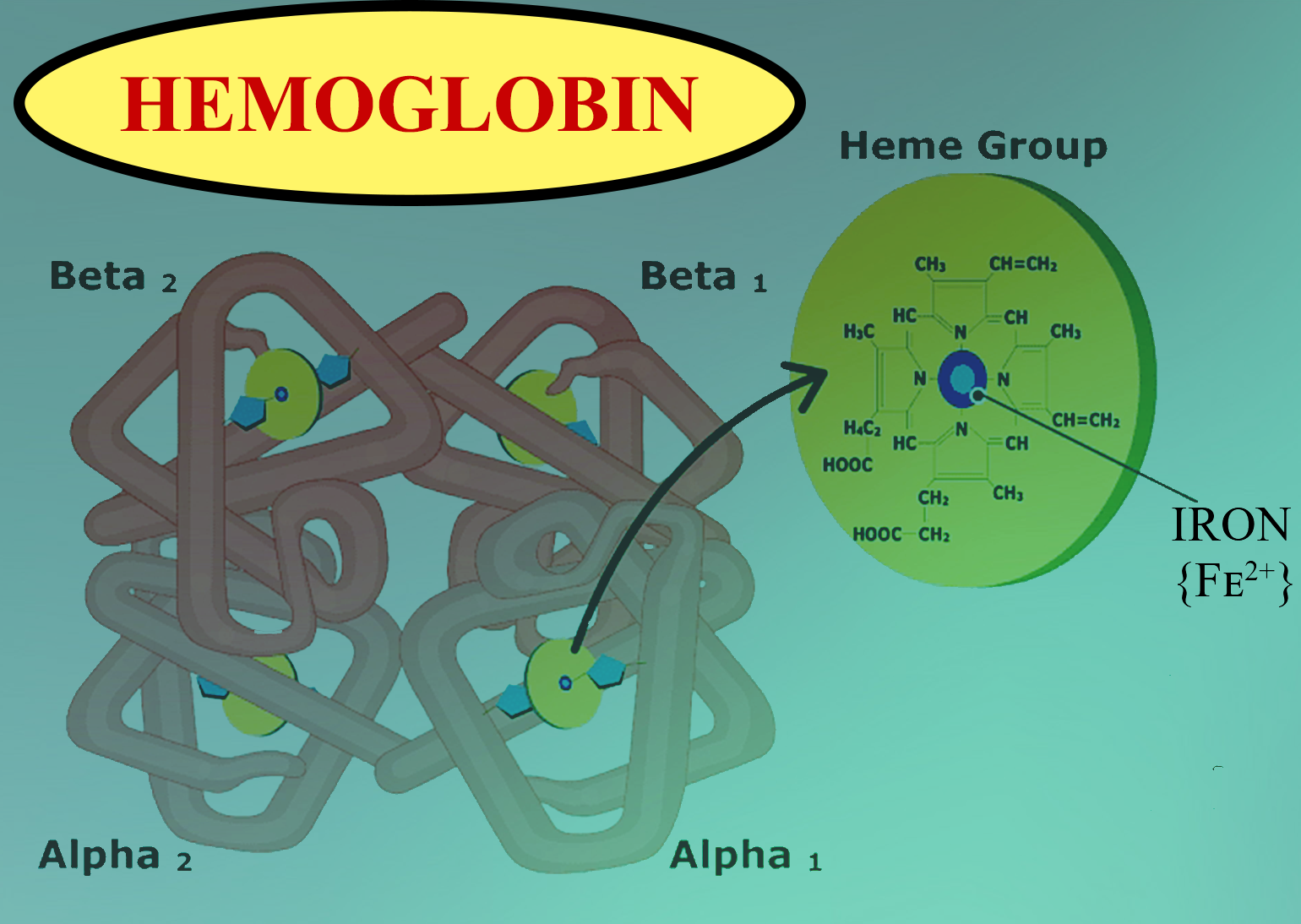
- Hemoglobin binds to oxygen molecules forming oxyhemoglobin and supplies oxygen to the tissues from the lungs and in turn, receives carbon dioxide present in the tissue forming carbaminohemoglobin and thereby returns carbon dioxide to the lungs.
- Hemoproteins are of types: Hemoglobin and myoglobin; they are differentiated on the basis of their ability to bind molecular oxygen.
- Oxygen carried by both Haemoglobin and myoglobin is bound directly to the ferrous iron (Fe2+) atom of the heme prosthetic group.
- Hemoglobin is responsible for binding oxygen in the lungs and transporting the bound oxygen throughout the body, where it is used in aerobic metabolic pathways.
- Oxidation of the iron to the ferric state (Fe3+) renders the molecule incapable of normal oxygen binding.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Fe’.
Note: Hemoglobin is heterotetrameric with two alpha and beta chains oxygen transfer protein found in red blood cells. Each subunit of Haemoglobin tetramer has a heme prosthetic group identical to that of myoglobin. Myoglobin is a monomeric protein found mainly in muscle tissue where it serves as an intracellular storage site for oxygen. Each myoglobin molecule contains a single heme group inserted into the hydrophobic cleft in the protein.
Complete step by step answer:
Fe is the common element in hemoglobin and myoglobin. Hemoglobin is an oxygen carrier protein in our body that serves to transport oxygen in the blood whereas myoglobin serves to store oxygen in muscles.

- Hemoglobin binds to oxygen molecules forming oxyhemoglobin and supplies oxygen to the tissues from the lungs and in turn, receives carbon dioxide present in the tissue forming carbaminohemoglobin and thereby returns carbon dioxide to the lungs.
- Hemoproteins are of types: Hemoglobin and myoglobin; they are differentiated on the basis of their ability to bind molecular oxygen.
- Oxygen carried by both Haemoglobin and myoglobin is bound directly to the ferrous iron (Fe2+) atom of the heme prosthetic group.
- Hemoglobin is responsible for binding oxygen in the lungs and transporting the bound oxygen throughout the body, where it is used in aerobic metabolic pathways.
- Oxidation of the iron to the ferric state (Fe3+) renders the molecule incapable of normal oxygen binding.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Fe’.
Note: Hemoglobin is heterotetrameric with two alpha and beta chains oxygen transfer protein found in red blood cells. Each subunit of Haemoglobin tetramer has a heme prosthetic group identical to that of myoglobin. Myoglobin is a monomeric protein found mainly in muscle tissue where it serves as an intracellular storage site for oxygen. Each myoglobin molecule contains a single heme group inserted into the hydrophobic cleft in the protein.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




