
What is the collective name for layers of soil.
(a)A-horizon
(b)B-horizon
(c)C -horizon
(d)Soil profile
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Soil has many layers that are arranged during the formation of soil. These layers of soil can easily be identified by their color and size of particles of the soil. The main layers of the soil are A-horizon, B-horizon, C-horizon, R-horizon, and O-horizon.
Complete answer:
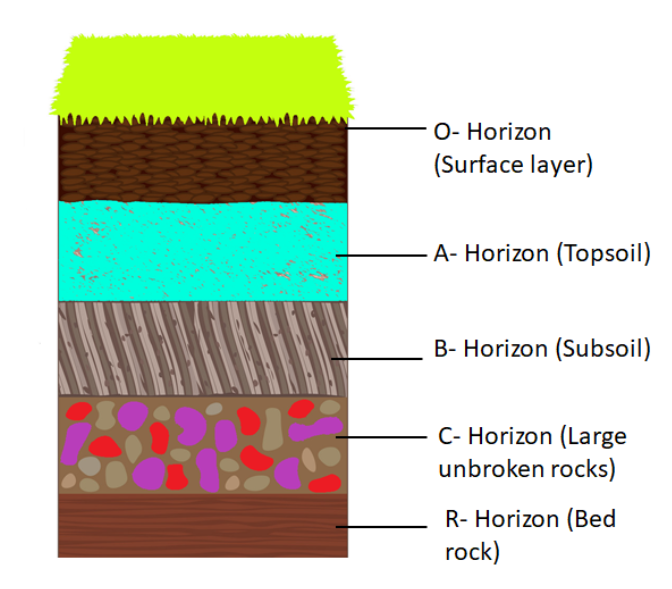
The soil profile is the collective name for layers of soil. The layers are known as called horizons and their physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. The layers of soil are the soil profile. Additional information:
A-horizon or Topsoil- or humus layer is rich in organic material. This layer consists of decomposed material and organic matter, the reason why the topsoil has a dark brown color. The topsoil is soft, porous to hold enough air and water because of the hummus. This is the layer where the seeds germinate, roots grow and other living organisms like earthworms, centipedes, bacteria, and fungi are found in this layer of soil.
B- horizon or Subsoil- this lies below the topsoil and is comparatively harder and compact than topsoil. There is less humus in this layer so it is lighter in color and is less organic but is rich in minerals brought down from the topsoil. It contains metal salts mainly iron oxide in a large proportion. Farmers often mix topsoil and subsoil when plowing their fields.
C-horizon or parent rock- lies just below the subsoil. It is made up of stones, rocks and contains no organic matter. The C-horizon layer acts as a transition zone between the earth’s bedrock and B-horizon.
So, the correct answer is ‘Soil profile’.
Note: The soil has taken nearly thousands of years to just form 1cm. Big rocks break down into smaller rocks mainly by two types of weathering- physical weathering and chemical weathering. Several other forces (agents) like wind, water, the sun’s heat, and plants and animals work to break down the parent rock into tiny particles of soil. These pieces get further broken down to form sand, silt, and then finally into finer particles and the process continues.
Complete answer:
The soil profile is the collective name for layers of soil. The layers are known as called horizons and their physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. The layers of soil are the soil profile. Additional information:
A-horizon or Topsoil- or humus layer is rich in organic material. This layer consists of decomposed material and organic matter, the reason why the topsoil has a dark brown color. The topsoil is soft, porous to hold enough air and water because of the hummus. This is the layer where the seeds germinate, roots grow and other living organisms like earthworms, centipedes, bacteria, and fungi are found in this layer of soil.
B- horizon or Subsoil- this lies below the topsoil and is comparatively harder and compact than topsoil. There is less humus in this layer so it is lighter in color and is less organic but is rich in minerals brought down from the topsoil. It contains metal salts mainly iron oxide in a large proportion. Farmers often mix topsoil and subsoil when plowing their fields.
C-horizon or parent rock- lies just below the subsoil. It is made up of stones, rocks and contains no organic matter. The C-horizon layer acts as a transition zone between the earth’s bedrock and B-horizon.
So, the correct answer is ‘Soil profile’.
Note: The soil has taken nearly thousands of years to just form 1cm. Big rocks break down into smaller rocks mainly by two types of weathering- physical weathering and chemical weathering. Several other forces (agents) like wind, water, the sun’s heat, and plants and animals work to break down the parent rock into tiny particles of soil. These pieces get further broken down to form sand, silt, and then finally into finer particles and the process continues.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




