
Who coined the term ‘cell’ and how?
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The term ‘cell’ was coined by a European scientist who observed the dead cork cells under his microscope and later compared it with the compartments or cavities of a honeycomb.
Complete answer:
Robert Hooke was a European scientist in the Royal Society of London. He built a microscope in 1665 to examine the thin sections of cork he had cut with a penknife. He observed a number of tiny boxlike structures that resembled honeycomb. He named these structures as ‘cells’. The word ‘cell’ originated from a Latin word ‘cellula’ which means little room. Though Robert Hooke didn’t realize that they were dead, he did notice in the cells of other plant tissues that were filled with’ juices’. But his discovery was limited due to the magnification power of his microscope. His findings are recorded and published in the book ‘Micrographia.’
Additional Information: -The discovery of the cell was carried forward by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. He was a Dutch textile merchant and produced lenses that could magnify an object up to 300 times.
-This made him the first one to study the living cells ranging from sperm cells to blood cells to single-celled organisms such as algae. But his observation was again restricted by the limited resolving power of his lenses.
-Resolving power of a lens is its ability to distinguish between two extremely closely present objects in a specimen. This hindered the possibility to properly deduce the internal compartments of a cell.
-This problem was solved in the 1800s when the compound microscope was invented. Later, by using this technology, Robert Brown declared the presence of a rounder structure in every cell. This was named as ‘nucleus’.
Note: In a compound microscope, there are two lenses - an eyepiece and an objective lens. Here, one lens i.e. an eyepiece magnifies an image created by the second lens i.e objective. This served the dual purpose by enhancing magnification as well as a better resolution. This made the possibility of seeing structures that were as tiny as 1μm clearly.
Complete answer:
Robert Hooke was a European scientist in the Royal Society of London. He built a microscope in 1665 to examine the thin sections of cork he had cut with a penknife. He observed a number of tiny boxlike structures that resembled honeycomb. He named these structures as ‘cells’. The word ‘cell’ originated from a Latin word ‘cellula’ which means little room. Though Robert Hooke didn’t realize that they were dead, he did notice in the cells of other plant tissues that were filled with’ juices’. But his discovery was limited due to the magnification power of his microscope. His findings are recorded and published in the book ‘Micrographia.’
Additional Information: -The discovery of the cell was carried forward by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. He was a Dutch textile merchant and produced lenses that could magnify an object up to 300 times.
-This made him the first one to study the living cells ranging from sperm cells to blood cells to single-celled organisms such as algae. But his observation was again restricted by the limited resolving power of his lenses.
-Resolving power of a lens is its ability to distinguish between two extremely closely present objects in a specimen. This hindered the possibility to properly deduce the internal compartments of a cell.
-This problem was solved in the 1800s when the compound microscope was invented. Later, by using this technology, Robert Brown declared the presence of a rounder structure in every cell. This was named as ‘nucleus’.
Note: In a compound microscope, there are two lenses - an eyepiece and an objective lens. Here, one lens i.e. an eyepiece magnifies an image created by the second lens i.e objective. This served the dual purpose by enhancing magnification as well as a better resolution. This made the possibility of seeing structures that were as tiny as 1μm clearly.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

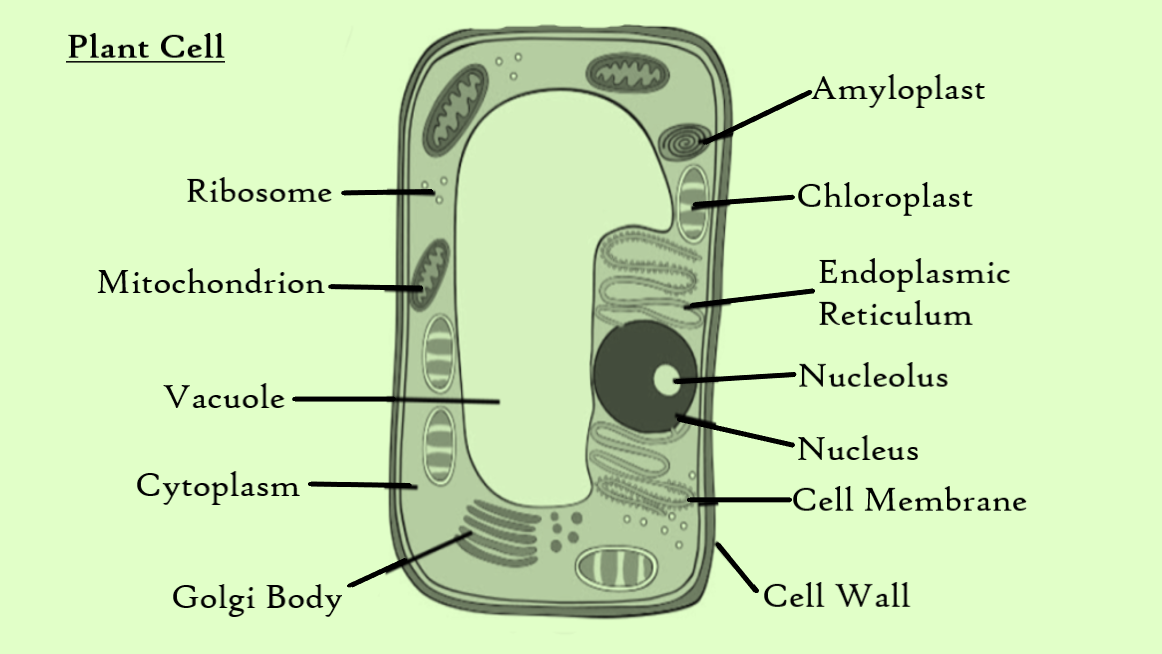
Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




