
\[{[{\text{Co}}{{\text{F}}_6}]^{3 - }}\]
is a coordination complex ion. How many unpaired electrons are there in the complex?
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: F is a weak field ligand which causes small crystal field splitting. Weak ligands lead to formation of high spin complexes.
Complete answer:
We will first calculate the oxidation state of \[{\text{Co}}\]
in \[{[{\text{Co}}{{\text{F}}_6}]^{3 - }}\]
We take the oxidation state of \[{\text{Co}}\]
as ‘x’ and the charge on one is \[ - 1\]. Total charge on the complex is \[{\text{ - 3}}\].
So, \[{\text{x + ( - 6) = - 3}}\]
\[{\text{ x = - 3 + 6}}\]
\[{\text{x = + 3}}\]
The outer electronic configuration of \[{\text{Co}}\]is \[[{\text{Ar] 3}}{{\text{d}}^7}{\text{4}}{{\text{s}}^2}\].
So, in \[{\text{C}}{{\text{o}}^{ + 3}}\]it becomes \[[{\text{Ar] 3}}{{\text{d}}^6}\].
Since F is a weak field ligand, it will lead to splitting of d orbitals. First it leads to \[{{\text{t}}_{2g}}\]to be half filled and then \[{e_g}\]to be half filled too and then pairing will occur.
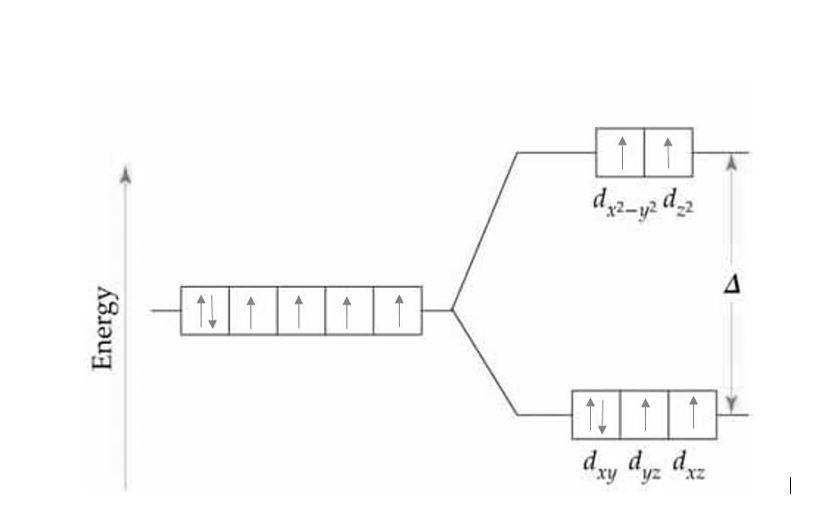
Hence, there will be 4 unpaired electrons.
Additional information: Crystal field splitting describes breaking of orbitals in complex formed by transition metal ions due to ligands. It considers the bond between metal and ligand to be purely ionic. Theory says that this bond arises due to electrostatic interactions between metal and the ligand. In case of anionic complexes, ligands are considered as point charges. It is a qualitative measure of the strength of metal-ligand bond.
\[{[{\text{Co}}{{\text{F}}_6}]^{3 - }}\]is a high spin complex since fluorine is a weak field ligand that causes small splitting. On the other hand, ligands that cause large crystal field splitting, result in formation of low spin complexes and are called strong ligands.
Note: To remember this easily, we will keep in mind that weak field ligands form high spin complexes and strong field ligands form low spin complexes.
Complete answer:
We will first calculate the oxidation state of \[{\text{Co}}\]
in \[{[{\text{Co}}{{\text{F}}_6}]^{3 - }}\]
We take the oxidation state of \[{\text{Co}}\]
as ‘x’ and the charge on one is \[ - 1\]. Total charge on the complex is \[{\text{ - 3}}\].
So, \[{\text{x + ( - 6) = - 3}}\]
\[{\text{ x = - 3 + 6}}\]
\[{\text{x = + 3}}\]
The outer electronic configuration of \[{\text{Co}}\]is \[[{\text{Ar] 3}}{{\text{d}}^7}{\text{4}}{{\text{s}}^2}\].
So, in \[{\text{C}}{{\text{o}}^{ + 3}}\]it becomes \[[{\text{Ar] 3}}{{\text{d}}^6}\].
Since F is a weak field ligand, it will lead to splitting of d orbitals. First it leads to \[{{\text{t}}_{2g}}\]to be half filled and then \[{e_g}\]to be half filled too and then pairing will occur.

Hence, there will be 4 unpaired electrons.
Additional information: Crystal field splitting describes breaking of orbitals in complex formed by transition metal ions due to ligands. It considers the bond between metal and ligand to be purely ionic. Theory says that this bond arises due to electrostatic interactions between metal and the ligand. In case of anionic complexes, ligands are considered as point charges. It is a qualitative measure of the strength of metal-ligand bond.
\[{[{\text{Co}}{{\text{F}}_6}]^{3 - }}\]is a high spin complex since fluorine is a weak field ligand that causes small splitting. On the other hand, ligands that cause large crystal field splitting, result in formation of low spin complexes and are called strong ligands.
Note: To remember this easily, we will keep in mind that weak field ligands form high spin complexes and strong field ligands form low spin complexes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




