
What is codominance? Explain with an example.
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The term codominance is related to the dominance of two traits that cooperate and where each trait shows its characteristics. It is best seen in certain phenomena where expression of multiple traits is shown simultaneously.
Complete answer:
- In genetics, a dominant allele is the one that is always expressed and also covers the expression of the recessive allele when present in the genetic material of the organism. A dominant allele can be expressed as dominant over recessive or as codominant.
- Codominance is the condition where neither allele can mask the expression of the other, that is, neither allele is completely dominant, hence they are both expressed together.
- It is a heterozygous condition in which both alleles at a gene locus are fully expressed in the phenotype.
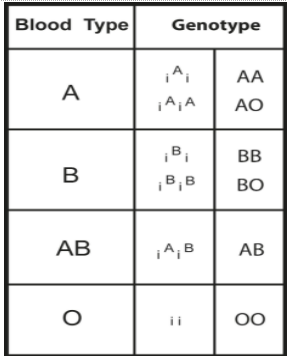
- The most common example of codominance is observed in the ABO blood group system. There are different versions of a gene that expresses proteins appearing on the surface of RBCs. They are A, B, and O. All of these alleles are identified by our body as its own. The progeny of a parent having A blood type and a parent having B blood type will show the AB blood type where both the proteins are expressed on the surface of the RBCs.
Additional Information: - Other examples of codominance include the ‘roan’ breed of cattle. When a breed with a red coat is crossed with a breed with a white coat, the resulting progeny has a coat of both red and white hair.
- Codominance is also observed in the MN blood group system in humans. Individuals homozygous for the M allele express M antigen while those homozygous for N allele express the N antigen, both on the surface of red blood cells. Heterozygotes with both alleles express both of these antigens.
Note: - Codominance can be easily spotted in animals and flowers of plants that show more than one pigment or color. It can produce visible as well as less visible progeny.
- It must be noted that if the homologous chromosome consists of two alleles that can be expressed, then both will be produced and form a different phenotype or have characteristics similar to that of a homozygote.
Complete answer:
- In genetics, a dominant allele is the one that is always expressed and also covers the expression of the recessive allele when present in the genetic material of the organism. A dominant allele can be expressed as dominant over recessive or as codominant.
- Codominance is the condition where neither allele can mask the expression of the other, that is, neither allele is completely dominant, hence they are both expressed together.
- It is a heterozygous condition in which both alleles at a gene locus are fully expressed in the phenotype.
- The most common example of codominance is observed in the ABO blood group system. There are different versions of a gene that expresses proteins appearing on the surface of RBCs. They are A, B, and O. All of these alleles are identified by our body as its own. The progeny of a parent having A blood type and a parent having B blood type will show the AB blood type where both the proteins are expressed on the surface of the RBCs.
Additional Information: - Other examples of codominance include the ‘roan’ breed of cattle. When a breed with a red coat is crossed with a breed with a white coat, the resulting progeny has a coat of both red and white hair.
- Codominance is also observed in the MN blood group system in humans. Individuals homozygous for the M allele express M antigen while those homozygous for N allele express the N antigen, both on the surface of red blood cells. Heterozygotes with both alleles express both of these antigens.

Note: - Codominance can be easily spotted in animals and flowers of plants that show more than one pigment or color. It can produce visible as well as less visible progeny.
- It must be noted that if the homologous chromosome consists of two alleles that can be expressed, then both will be produced and form a different phenotype or have characteristics similar to that of a homozygote.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




