
Chromatin material which remains condensed during interphase is called
(a) Heterochromatin
(b) Euchromatin
(c) Chromonemata
(d) Megachromatin
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Chromatin is the condensed form of DNA. DNA is condensed by wrapping itself around histone proteins. Normally the DNA is loosely wrapped but just before cell division, it coils itself to form chromatin which further coils to form structures known as chromosomes.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
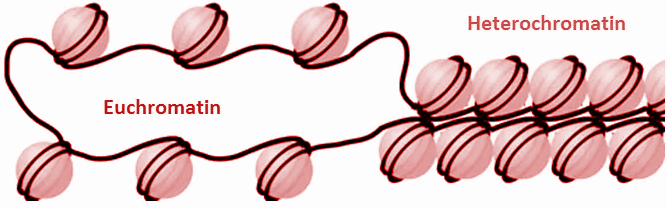
Interphase is referred to as that phase of the cell cycle in which cell division does not take place. In interphase, the cell grows in size i.e. G1 phase, synthesis, or doubles it DNA content i.e. S phase, and prepares itself for cell division i.e. G2 phase. During interphase, the cell is metabolically active and thus the DNA is in loose form to allow transcription and translation. This part of DNA that is not condensed during interphase is known as Euchromatin.
But there is also part of DNA that does not open or remains condensed during interphase and is known as Heterochromatin. It remains condensed because it does not have any genes. Hence, it does not need to take part in transcription and translation.
So, the correct option is ‘Heterochromatin’.
Additional information: Heterochromatin and euchromatin are classified on the basis of how they appear under a microscope.
Euchromatin: It stains lightly and has a transcriptionally active part of DNA.
Heterochromatin: It gets highly stained because of the dense DNA present in it. Also because it has high ribonucleic acid content. It has a high number of tandem repeats in it as well.
Note:
- Chromatin is made up of a repeating unit known as nucleosomes.
- Nucleosomes are made up by coiling a negatively charged DNA around an octamer of positively charged histone proteins.
- Each nucleosome is made up of 200 base pairs of DNA.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Interphase is referred to as that phase of the cell cycle in which cell division does not take place. In interphase, the cell grows in size i.e. G1 phase, synthesis, or doubles it DNA content i.e. S phase, and prepares itself for cell division i.e. G2 phase. During interphase, the cell is metabolically active and thus the DNA is in loose form to allow transcription and translation. This part of DNA that is not condensed during interphase is known as Euchromatin.
But there is also part of DNA that does not open or remains condensed during interphase and is known as Heterochromatin. It remains condensed because it does not have any genes. Hence, it does not need to take part in transcription and translation.
So, the correct option is ‘Heterochromatin’.
Additional information: Heterochromatin and euchromatin are classified on the basis of how they appear under a microscope.
Euchromatin: It stains lightly and has a transcriptionally active part of DNA.
Heterochromatin: It gets highly stained because of the dense DNA present in it. Also because it has high ribonucleic acid content. It has a high number of tandem repeats in it as well.

Note:
- Chromatin is made up of a repeating unit known as nucleosomes.
- Nucleosomes are made up by coiling a negatively charged DNA around an octamer of positively charged histone proteins.
- Each nucleosome is made up of 200 base pairs of DNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




