
Choroid is
A.Loose connective tissue with pigment cells and vascular supply.
B. Muscular tissue is rich in blood supply.
C. Epithelium
D. Nervous system
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: The human eye has three layers namely the sclera, choroid, and retina. The choroid is found inside the sclera which is a protective layer. The choroid is the middle layer which is dark and pigmented and has ample blood vessels.
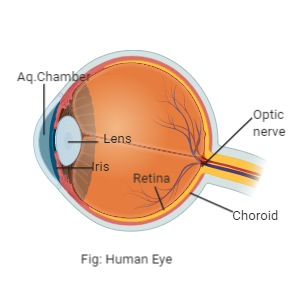
Complete step by step answer: The choroid is a layer of the human eye. The choroid is the layer next to the sclera which is the outermost layer and can be distinguished by the appearance of blood vessels. It is highly pigmented, thin, and vascular. It is found between the sclera (outermost layer) and retina (inner layer). The ciliary body is also a part of the choroid which extends to form a pigmented and opaque structure called the iris which is a visible colored portion of the eye. The eyeball consists of a crystalline lens that is transparent and is held in place by ligaments that are connected with ciliary muscles. In front of the lens, in the human eye is an aperture that is surrounded by iris and is called the pupil, the diameter of the pupil is regulated by the muscle fibers. Choroid consists of loose connective tissue and several blood vessels. It seems to be bluish in color because pigment cells are present. The eyeball is thin over the posterior part and thick over the anterior part wherever it forms a membrane. It is responsible for providing oxygen and nutrients to the eye.
So, the correct answer is A-Loose connective tissue with pigment cells and vascular supply.
Note: Choroidal dystrophy is a condition where the choroid is infected. Choroidal dystrophy is caused because of gene abnormality and is passed down through families which means is inherited from parents. It mostly affects males in childhood.
Complete step by step answer: The choroid is a layer of the human eye. The choroid is the layer next to the sclera which is the outermost layer and can be distinguished by the appearance of blood vessels. It is highly pigmented, thin, and vascular. It is found between the sclera (outermost layer) and retina (inner layer). The ciliary body is also a part of the choroid which extends to form a pigmented and opaque structure called the iris which is a visible colored portion of the eye. The eyeball consists of a crystalline lens that is transparent and is held in place by ligaments that are connected with ciliary muscles. In front of the lens, in the human eye is an aperture that is surrounded by iris and is called the pupil, the diameter of the pupil is regulated by the muscle fibers. Choroid consists of loose connective tissue and several blood vessels. It seems to be bluish in color because pigment cells are present. The eyeball is thin over the posterior part and thick over the anterior part wherever it forms a membrane. It is responsible for providing oxygen and nutrients to the eye.

So, the correct answer is A-Loose connective tissue with pigment cells and vascular supply.
Note: Choroidal dystrophy is a condition where the choroid is infected. Choroidal dystrophy is caused because of gene abnormality and is passed down through families which means is inherited from parents. It mostly affects males in childhood.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




