
Choose the correct combination of labelling in a potato osmoscope.
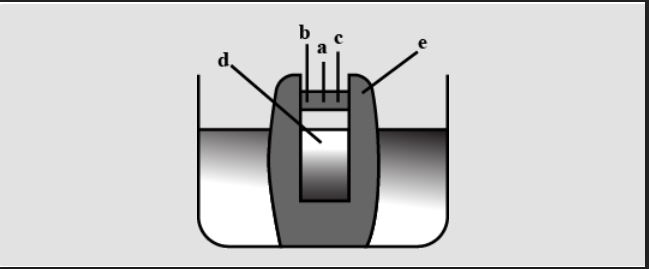
(a) a-Final level, b-Dot pin, c-Initial level, d-Sugar solution, e-Potato tuber
(b) a-Initial level, b-Dot pin, c-Final level, d-Water, e-Potato tuber
(c) a-Final level, b-Dot pin, c-Initial level, d-Water, e-Potato tuber
(d) a-Final level, b-Dot pin, c-Initial level, d-Water, e-Container

Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: Osmosis is a special type of diffusion of water across a differentially semi-permeable membrane. The demonstration of this process in a living system is shown using a potato osmoscope. It denotes the rise in water level from initial to final with a pin.
Complete answer:
Cell wall and cell membrane surround the plant cell. The cell wall is freely permeable to water and substances in solution; hence it is not a barrier to the moment. The cell membrane of plant cells and the membrane of vacuole together play an important role in determining the moment of molecules in and out of the cell.
Osmosis can be defined as the passage of solvent molecules from a region of their higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis is given by two factors, Concentration of dissolved solutes in a solution and pressure gradient. Both these factors determine the chemical potential of water, which is the driving force for water movement in plants. Water moves from a region of the high chemical potential of water to a region of the low chemical potential of water until equilibrium is reached. Water potential should be the same in both the chambers at equilibrium. Osmosis can be demonstrated by a potato osmometer.
If the tuber is placed in water, the cavity in the potato tuber containing the concentrated solution of sugar collects the water due to osmosis.
So, the answer is, ‘a-Final level, b-Dot pin, c-Initial level, d-Sugar solution, e-Potato tuber’.
Note:
Equilibrium is a dynamic state in which the rates of the forward and backward reactions are equal.
It should not be confused with the steady-state. When the equilibrium state is achieved, there is no visible increase or decrease in level, not because the water stopped entering. It is because the net amounts of exit and entry of water at that point in time are equal.
Complete answer:
Cell wall and cell membrane surround the plant cell. The cell wall is freely permeable to water and substances in solution; hence it is not a barrier to the moment. The cell membrane of plant cells and the membrane of vacuole together play an important role in determining the moment of molecules in and out of the cell.
Osmosis can be defined as the passage of solvent molecules from a region of their higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis is given by two factors, Concentration of dissolved solutes in a solution and pressure gradient. Both these factors determine the chemical potential of water, which is the driving force for water movement in plants. Water moves from a region of the high chemical potential of water to a region of the low chemical potential of water until equilibrium is reached. Water potential should be the same in both the chambers at equilibrium. Osmosis can be demonstrated by a potato osmometer.
If the tuber is placed in water, the cavity in the potato tuber containing the concentrated solution of sugar collects the water due to osmosis.
So, the answer is, ‘a-Final level, b-Dot pin, c-Initial level, d-Sugar solution, e-Potato tuber’.
Note:
Equilibrium is a dynamic state in which the rates of the forward and backward reactions are equal.
It should not be confused with the steady-state. When the equilibrium state is achieved, there is no visible increase or decrease in level, not because the water stopped entering. It is because the net amounts of exit and entry of water at that point in time are equal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




