
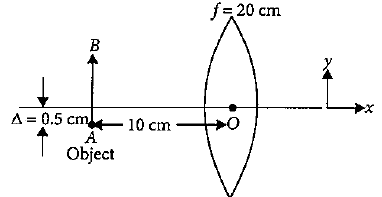
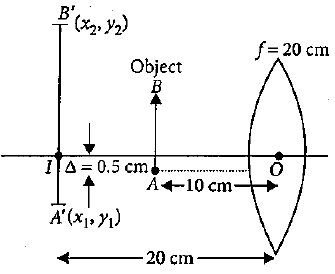
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given. A linear object of size $1.5\,cm$ placed at $10\,cm$ from a lens of focal length $20\,cm$. The optic centre of the lens and the object are displaced a distance $\delta = 0.5\,cm$ as shown in the figure. The magnification of the image formed is $m$ (Take optic centre as origin). The coordinates of image of A and B are $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ respectively. Then:
(A) $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( { - 20\,cm, - 1\,cm} \right)$
(B) $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( { - 20\,cm,\,2cm} \right)$
(C) $m = 3$
(D) $m = 2$

Answer
585k+ views
Hint:From the given values, using the lens formula, the distance of the image from the object is calculated. Then the object is displaced, so the magnification is obtained by dividing the distance of image from the lens and distance of object from the lens. By using the values of displaced co-ordinates and new magnification obtained, calculate the values of ${y_1}$ and ${y_2}$.
Formulae Used:
The refraction of the lens is given by
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where u is the distance of the object placed from the lens and v is the distance of the image placed from the lens and f is the focal length of the lens.
(2) Magnification of the lens is given by
$m = \dfrac{v}{u}$
Where m is the magnification.
Complete step-by-step solution:
By using the lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{
f \\
\\
}$
Substituting the values of u and f in the formula
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{{ - 10}} = \dfrac{1}{{20}}$
Distance of object from the lens is always taken as negative
By keeping $v$ in LHS and other term in RHS,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{10}} + \dfrac{1}{{20}}$
By simplifying the above equation,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{20}} - \dfrac{1}{{10}}$
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{20}}$
By further simplification,
$v = - 20$
Hence ${x_1}\,{\text{and}}\,{x_2}$ are obtained as $ - 20$
Magnification $m = \dfrac{v}{u}$
$m = \dfrac{{ - 20}}{{ - 10}}$
$m = 2$
Thus, the magnification is obtained as $2$.
After displacement of the object, it is $0.5\,cm$ below the optical centre. Hence
${y_1} = 0.5 \times 2$
${y_1} = - 1\,cm$.
Similarly, ${y_2} = 1 \times 2$
${y_2} = 2\,cm$.
Thus (A), (B) and (D) are correct.
Note:- Care must be taken in which distance of image from the lens is taken as positive and the distance of object from the lens is taken as negative. Optical centre is taken as the origin to calculate the coordinates of point A and B.
Formulae Used:
The refraction of the lens is given by
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where u is the distance of the object placed from the lens and v is the distance of the image placed from the lens and f is the focal length of the lens.
(2) Magnification of the lens is given by
$m = \dfrac{v}{u}$
Where m is the magnification.
Complete step-by-step solution:

By using the lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{
f \\
\\
}$
Substituting the values of u and f in the formula
$\dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{{ - 10}} = \dfrac{1}{{20}}$
Distance of object from the lens is always taken as negative
By keeping $v$ in LHS and other term in RHS,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{10}} + \dfrac{1}{{20}}$
By simplifying the above equation,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{20}} - \dfrac{1}{{10}}$
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{20}}$
By further simplification,
$v = - 20$
Hence ${x_1}\,{\text{and}}\,{x_2}$ are obtained as $ - 20$
Magnification $m = \dfrac{v}{u}$
$m = \dfrac{{ - 20}}{{ - 10}}$
$m = 2$
Thus, the magnification is obtained as $2$.
After displacement of the object, it is $0.5\,cm$ below the optical centre. Hence
${y_1} = 0.5 \times 2$
${y_1} = - 1\,cm$.
Similarly, ${y_2} = 1 \times 2$
${y_2} = 2\,cm$.
Thus (A), (B) and (D) are correct.
Note:- Care must be taken in which distance of image from the lens is taken as positive and the distance of object from the lens is taken as negative. Optical centre is taken as the origin to calculate the coordinates of point A and B.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




