
Choose and write the correct option in each of the following questions:
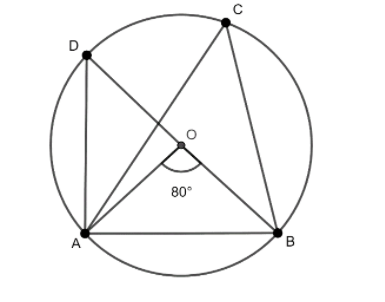
In the figure, if O is the centre of a circle, then the measure of $\angle ADB$ is:
a. $80^\circ $
b. $100^\circ $
c. $40^\circ $
d. $60^\circ $

Answer
522.3k+ views
Hint: We can use the exterior angle of the triangle \[\vartriangle DOA\] to find the interior angle $\angle ADO$ as we know the exterior angle $\angle AOB$. We will use the fact that both $AO$ and $DO$ are radii of the circle as $O$ is the center to find the relationship between the interior angles.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given figure we have to find the value of the angle $\angle ADB$. Observe that the angle is contained in two triangles $\vartriangle ADB$ and $\vartriangle ADO$. We will consider the triangle $\vartriangle ADO$ as the angle $\angle AOB$ whose value is given to be $80^\circ $ is an exterior angle of this triangle. WE use the exterior angle property with respect to the exterior angle $\angle AOB$.
Let us consider $\angle ADB$ to be $x$. Recall that the exterior angle property of a triangle states that the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of two opposite interior angles. Using this property, we can see that in $\vartriangle ADO$, the exterior angle $\angle AOB$ is equal to the sum of $\angle ADO$ and $\angle DAO$.
$ \Rightarrow \angle AOB = \angle ADO + \angle DAO$
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADO + \angle DAO = 80^\circ $ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (1)
Now since both $AO$ and $DO$ are radii of the circle as $O$ is the center of the circle, we can see that $AO = DO$.
We know the property that angles opposite to equal sides are equal. So, by using this and since $AO = DO$, we have the angles opposite to these sides $\angle ADO$ and $\angle DAO$ to be equal, that is $\angle ADO = \angle DAO$. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (2)
Now by using (2), we can write the equation (1) as,
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADO + \angle ADO = 80^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow 2\angle ADO = 80^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADO = \dfrac{{80^\circ }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADO = 40^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADB = 40^\circ $ [From the figure we have $\angle ADO = \angle ADB$]
So, the measure of the angle $\angle ADB$ is $40^\circ $.
Hence, the correct option is C. $40^\circ $.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: There are multiple ways of solving this question. One way is to use the angle sum property of a triangle for the triangles $\vartriangle AOB$ and $\vartriangle ADB$ along with using the property of an isosceles triangle. One has to know all the properties related to triangles and circles to solve questions from geometry.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given figure we have to find the value of the angle $\angle ADB$. Observe that the angle is contained in two triangles $\vartriangle ADB$ and $\vartriangle ADO$. We will consider the triangle $\vartriangle ADO$ as the angle $\angle AOB$ whose value is given to be $80^\circ $ is an exterior angle of this triangle. WE use the exterior angle property with respect to the exterior angle $\angle AOB$.
Let us consider $\angle ADB$ to be $x$. Recall that the exterior angle property of a triangle states that the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of two opposite interior angles. Using this property, we can see that in $\vartriangle ADO$, the exterior angle $\angle AOB$ is equal to the sum of $\angle ADO$ and $\angle DAO$.
$ \Rightarrow \angle AOB = \angle ADO + \angle DAO$
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADO + \angle DAO = 80^\circ $ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (1)
Now since both $AO$ and $DO$ are radii of the circle as $O$ is the center of the circle, we can see that $AO = DO$.
We know the property that angles opposite to equal sides are equal. So, by using this and since $AO = DO$, we have the angles opposite to these sides $\angle ADO$ and $\angle DAO$ to be equal, that is $\angle ADO = \angle DAO$. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (2)
Now by using (2), we can write the equation (1) as,
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADO + \angle ADO = 80^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow 2\angle ADO = 80^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADO = \dfrac{{80^\circ }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADO = 40^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADB = 40^\circ $ [From the figure we have $\angle ADO = \angle ADB$]
So, the measure of the angle $\angle ADB$ is $40^\circ $.
Hence, the correct option is C. $40^\circ $.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: There are multiple ways of solving this question. One way is to use the angle sum property of a triangle for the triangles $\vartriangle AOB$ and $\vartriangle ADB$ along with using the property of an isosceles triangle. One has to know all the properties related to triangles and circles to solve questions from geometry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





