
How many chiral centers are in cortisone?
Answer
535.5k+ views
Hint: To find out the chiral centers in cortisol, we first need to know what cortisol is. Cortisol is a glucocorticoid class of steroid hormone. Its IUPAC name is $11\beta ,17\alpha ,21-Trihydroxyprengn-4-3n3-3,20-dione$. Its structure is as follows

Complete answer:
A tetrahedral atom in a molecule that has four different bonded groups or ligands, with lone pairs, is known as a chiral atom or a chiral center. A chiral center has a non-superimposable mirror image.
For example, in lactic acid,

The carbon molecule which is circled red is the chiral center. This is because it is tetrahedral in nature and has four different ligands $C{{H}_{3}},\text{ H, OH, and COOH}\text{.}$
When a carbon atom is a chiral center, it can also be known as an asymmetric carbon atom.
Chiral centers can be spotted by looking at the structure of a molecule.
Any atoms which have two or more identical groups attached to them cannot be a chiral center. For example, carbon atoms of straight-chain alkyl group will not be considered as chiral centers, this is because they have two or more hydrogens attached to them $(-C{{H}_{2}}\text{ or -C}{{\text{H}}_{3}})$.
A carbon atom that is attached to other atoms via multiple bonds like a double bond or triple bond cannot be a chiral center as it can not form four distinct ligands.
So, while looking at a structure of a molecule, look for an atom that is bonded through a single bond to four distinct ligands.
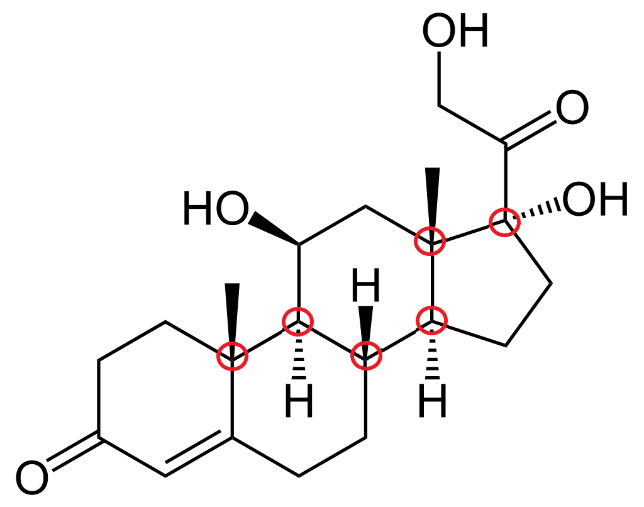
By looking at the structure of cortisol, we can find out it has 6 chiral centers. The chiral centers of carbon are marked in red.
Note:
It should be noted that the term chiral center is often synonymously used along with stereogenic center or stereocenter. But since stereocenters are any atoms that are bonded to three or more distinct ligands, all chiral centers are considered stereocenters but not all stereocenters are considered to be chiral centers.

Complete answer:
A tetrahedral atom in a molecule that has four different bonded groups or ligands, with lone pairs, is known as a chiral atom or a chiral center. A chiral center has a non-superimposable mirror image.
For example, in lactic acid,

The carbon molecule which is circled red is the chiral center. This is because it is tetrahedral in nature and has four different ligands $C{{H}_{3}},\text{ H, OH, and COOH}\text{.}$
When a carbon atom is a chiral center, it can also be known as an asymmetric carbon atom.
Chiral centers can be spotted by looking at the structure of a molecule.
Any atoms which have two or more identical groups attached to them cannot be a chiral center. For example, carbon atoms of straight-chain alkyl group will not be considered as chiral centers, this is because they have two or more hydrogens attached to them $(-C{{H}_{2}}\text{ or -C}{{\text{H}}_{3}})$.
A carbon atom that is attached to other atoms via multiple bonds like a double bond or triple bond cannot be a chiral center as it can not form four distinct ligands.
So, while looking at a structure of a molecule, look for an atom that is bonded through a single bond to four distinct ligands.
By looking at the structure of cortisol, we can find out it has 6 chiral centers. The chiral centers of carbon are marked in red.

Note:
It should be noted that the term chiral center is often synonymously used along with stereogenic center or stereocenter. But since stereocenters are any atoms that are bonded to three or more distinct ligands, all chiral centers are considered stereocenters but not all stereocenters are considered to be chiral centers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




